Abstract
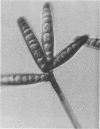
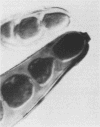
A 27-year-old man with a 6-year history of allergies developed nasal polyps that occluded his nose and prevented visual examination beyond the nasal vestibules. Histological examination of the polyps and bony tissue revealed septate, dematiaceous hyphae invading the bone trabeculae. A dematiaceous fungus was isolated in pure culture from the diseased tissue. Detailed mycological examination of the isolate showed that it produced numerous, distinctive poroconidia from erect, geniculate, sympodial conidiophores. The conidia were straight and cylindroellipsoidal, had 8 to 13 distosepta, and had protruding hila. The outer cell walls of the conidia, which were initially smooth, became unevenly roughened on aging. Comparison with other Exserohilum species revealed that the isolate represented an undescribed species; it is named Exserohilum mcginnisii sp. nov.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Forster R. K., Rebell G., Wilson L. A. Dematiaceous fungal keratitis. Clinical isolates and management. Br J Ophthalmol. 1975 Jul;59(7):372–376. doi: 10.1136/bjo.59.7.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuste F. J., Ajello L., Threlkeld R., Henry J. E., Jr Drechslera hawaiiensis: causative agent of a fatal fungal meningo-encephalitis. Sabouraudia. 1973 Mar;11(1):59–63. doi: 10.1080/00362177385190131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan W., Chandler F. W., Ajello L., Gauther R., Higgins R., Cayouette P. Equine phaeohyphomycosis caused by Drechslera spicifera. Can Vet J. 1975 Jul;16(7):205–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis M. R., Rinaldi M. G., Winn R. E. Emerging agents of phaeohyphomycosis: pathogenic species of Bipolaris and Exserohilum. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):250–259. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.250-259.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie R. A., Connole M. D. Mycotic nasal granuloma in cattle. Aust Vet J. 1977 Jun;53(6):268–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1977.tb00212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller G. H., Kaplan W., Ajello L., Padhye A. A. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Drechslera spicifera in a cat. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1975 Jan 15;166(2):150–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton C. S. Helminthosporium speciferum as the cause of dermal and nasal maduromycosis in a cow. Cornell Vet. 1977 Apr;67(2):236–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard D., Chick B. F., Connole M. D. Eumycotic mycetoma due to Drechslera rostrata infection in a cow. Aust Vet J. 1977 May;53(5):241–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1977.tb00197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolston K. V., Hopfer R. L., Larson D. L. Infections caused by Drechslera species: case report and review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):525–529. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.4.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauffler A. F. Maduromycotic mycetoma in an aged mare. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Apr 1;160(7):998–1000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimori R. N., Moore R. A., Itabashi H. H., Fujikawa D. G. Phaeohyphomycosis of brain: granulomatous encephalitis caused by Drechslera spicifera. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Mar;77(3):363–370. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.3.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C. N., Swart J. G., Ackermann D., Davidge-Pitts K. Nasal obstruction and bone erosion caused by Drechslera hawaiiensis. J Laryngol Otol. 1978 Feb;92(2):137–143. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100085145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapater R. C., Albesi E. J., Garcia G. H. Mycotic keratitis by Drechslera spicifera. Sabouraudia. 1975 Nov;13(3):295–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]