Abstract
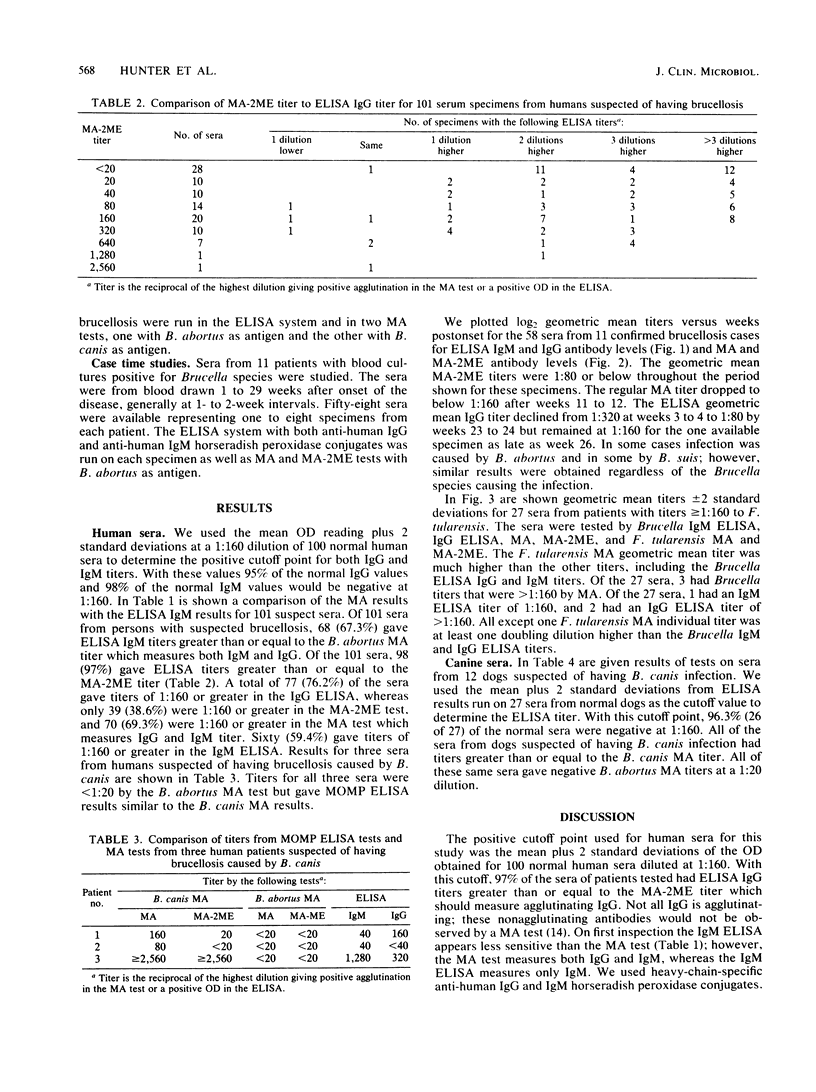
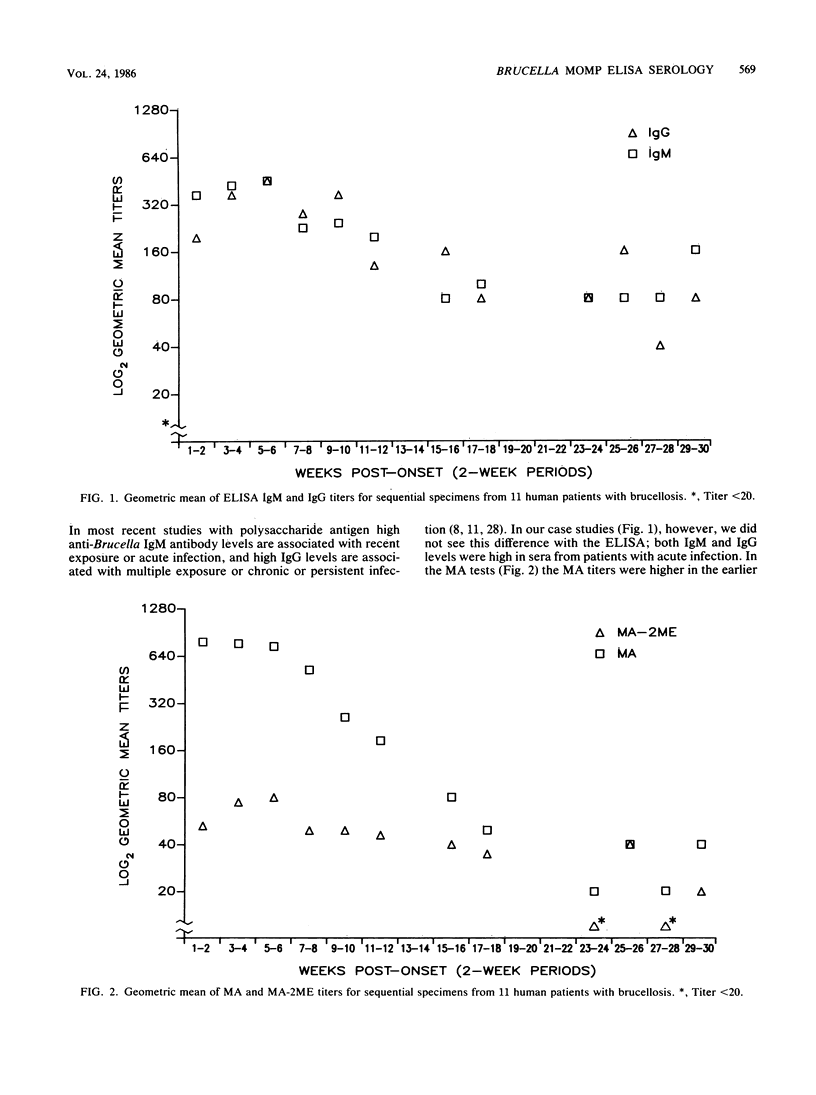
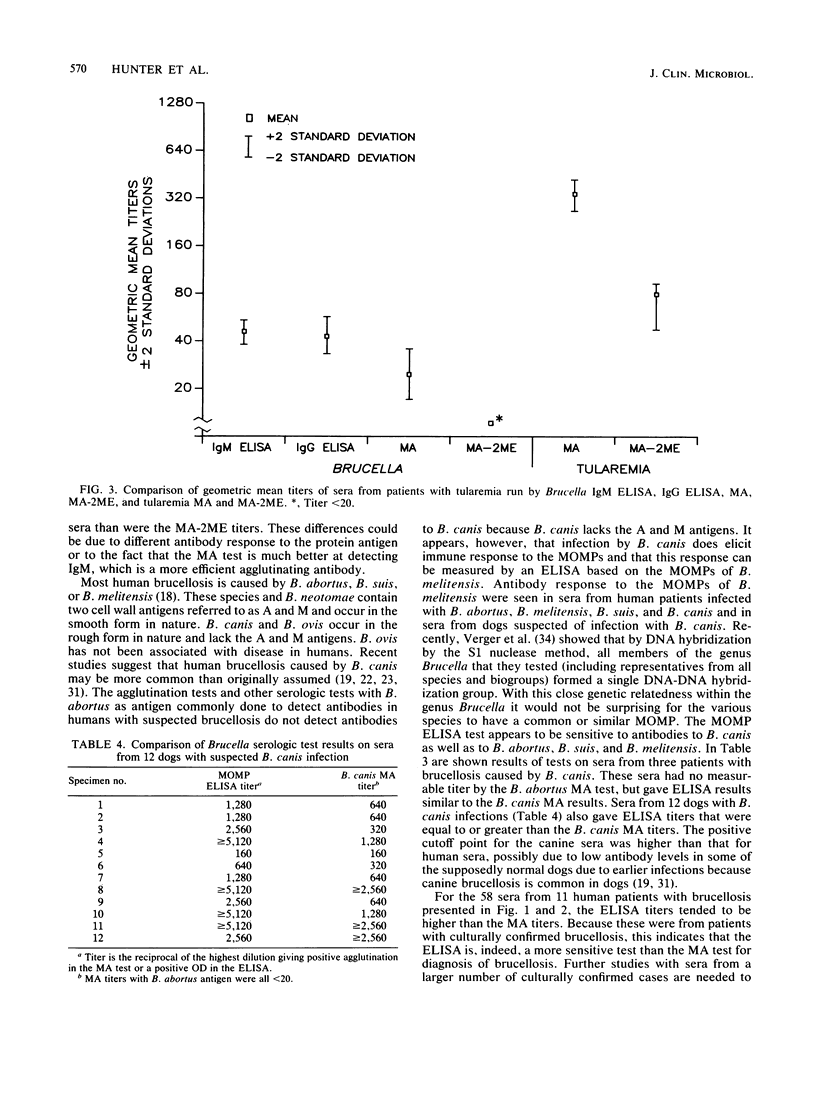
We developed an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) system to measure human immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM response to the major outer membrane proteins of Brucella melitensis. The ELISA was more sensitive in detecting antibody than a standard microagglutination (MA) test with B. abortus antigen. Of 101 sera from persons with suspected brucellosis, 79 (78.2%) gave ELISA IgM titers greater than or equal to the B. abortus MA titer without 2-mercaptoethanol (2ME), which measures both IgM and IgG. Of the 101 sera, 97% gave ELISA IgG titers greater than or equal to the MA with 2ME titer. A total of 58 sera, drawn from 11 human patients from 1 to 29 weeks after onset of brucellosis, gave higher geometric mean titers for the ELISA IgG test than for the MA with 2ME test. These 58 sera also gave ELISA IgM geometric mean titers that were greater than or within one doubling dilution of the geometric mean titers of MA without 2ME. In addition to detecting antibody response to B. abortus, B. melitensis, and B. suis, the ELISA was sensitive to antibody response to human and canine infections with B. canis. The B. canis antibody response is not detected by the MA test with B. abortus antigen. The ELISA, with a standard preparation of major outer membrane proteins of B. melitensis as antigen, appears to be useful in measuring antibody response in humans to infections by all species of Brucella known to infect humans.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badakhsh F. F., Foster J. W. Detoxification and immunogenic properties of endotoxin-containing precipitate of Brucella abortus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):494–498. doi: 10.1002/path.1700910224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. L., Klein G. C., McKinney F. T., Jones W. L. Safranin O-stained antigen microagglutination test for detection of brucella antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):398–400. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.398-400.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. L., McKinney F. T., Klein G. C., Jones W. L. Evaluation of a safranin-O-stained antigen microagglutination test for francisella tularensis antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):146–148. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.146-148.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson H. E., Hurvell B., Lindberg A. A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for titration of antibodies against Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Jun;84(3):168–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damp S. C., Crumrine M. H., Lewis G. E., Jr Microtiter plate agglutination test for Brucella canis antibodies. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):489–490. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.489-490.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Klerk E., Anderson R. Comparative evaluation of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the laboratory diagnosis of brucellosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):381–386. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.381-386.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. M., Tannahill A. J., Bradstreet C. M. Comparison of the indirect fluorescent antibody test with agglutination, complement-fixation, and Coombs test for Brucella antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1970 Mar;23(2):161–165. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert G. L., Hawes L. A. The antibody response to Brucella: immunoglobulin response measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and conventional tests. Aust N Z J Med. 1981 Feb;11(1):40–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1981.tb03734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt W. G., Payne D. J. Estimation of IgG and IgM brucella antibodies in infected and non-infected persons by a radioimmune technique. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jun;37(6):692–696. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.6.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinchliffe P. M., Robertson L. Detection of complement fixation by enzyme linked immunosorbant assay (COMPELISA). J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jan;36(1):100–103. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr W. R., McCaughey W. J., Coghlan J. D., Payne D. J., Quaife R. A., Robertson L., Farrell I. D. Techniques and interpretations in the serological diagnosis of brucellosis in man. J Med Microbiol. 1968 Nov;1(2):181–193. doi: 10.1099/00222615-1-2-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb V. L., Jones L. M., Schurig G. G., Berman D. T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for bovine immunoglobulin subclass-specific response to Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):240–247. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.240-247.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Haeggman S., Karlson K., Carlsson H. E., Mair N. S. Enzyme immunoassay of the antibody response to Brucella and Yersinia enterocolitica 09 infections in humans. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Apr;88(2):295–307. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee J. T. An enzyme-labelled immunosorbent assay for Brucella abortus antibodies. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):167–172. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe P. W., Silberg S. L., Morgan P. M., Adess M. Seroepidemiological investigation of Brucella canis antibodies in different human population groups. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Nov;2(5):382–386. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.5.382-386.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K., Stiller J., Adams G., Williams R. Binding of Brucella abortus whole cell and lipopolysaccharide antigens to plastics. Res Vet Sci. 1983 Mar;34(2):131–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parratt D., Nielsen K. H., White R. G. Radioimmunoassay of IgM, IgG, and IgA Brucella antibodies. Lancet. 1977 May 21;1(8021):1075–1078. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92334-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polt S. S., Dismukes W. E., Flint A., Schaefer J. Human brucellosis caused by Brucella canis: clinical features and immune response. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Nov;97(5):717–719. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-5-717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polt S. S., Schaefer J. A microagglutination test for human Brucella canis antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jun;77(6):740–744. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.6.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REDDIN J. L., ANDERSON R. K., JENNESS R., SPINK W. W. SIGNIFICANCE OF 7S AND MACROGLOBULIN BRUCELLA AGGLUTININS IN HUMAN BRUCELLOSIS. N Engl J Med. 1965 Jun 17;272:1263–1268. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196506172722403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P. Characterization of the major envelope protein from Escherichia coli. Regular arrangement on the peptidoglycan and unusual dodecyl sulfate binding. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8019–8029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppanner R., Meyer M. E., Willeberg P., Behymer D. E. Comparison of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with other tests for brucellosis, using sera from experimentally infected heifers. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Aug;41(8):1329–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos J. M., Verstreate D. R., Perera V. Y., Winter A. J. Outer membrane proteins from rough strains of four Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):188–194. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.188-194.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel J. E., El-Masry N. A., Farid Z. Diagnosis of human brucellosis with ELISA. Lancet. 1982 Jul 3;2(8288):19–21. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91154-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. M., Carmichael L. E., Cundy K. R. Human infection with Brucella canis. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Mar;76(3):435–438. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-3-435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabatabai L. B., Deyoe B. L. Biochemical and biological properties of soluble protein preparations from Brucella abortus. Dev Biol Stand. 1984;56:199–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabatabai L. B., Deyoe B. L. Specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of bovine antibody to Brucella abortus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):209–213. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.209-213.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


