Abstract
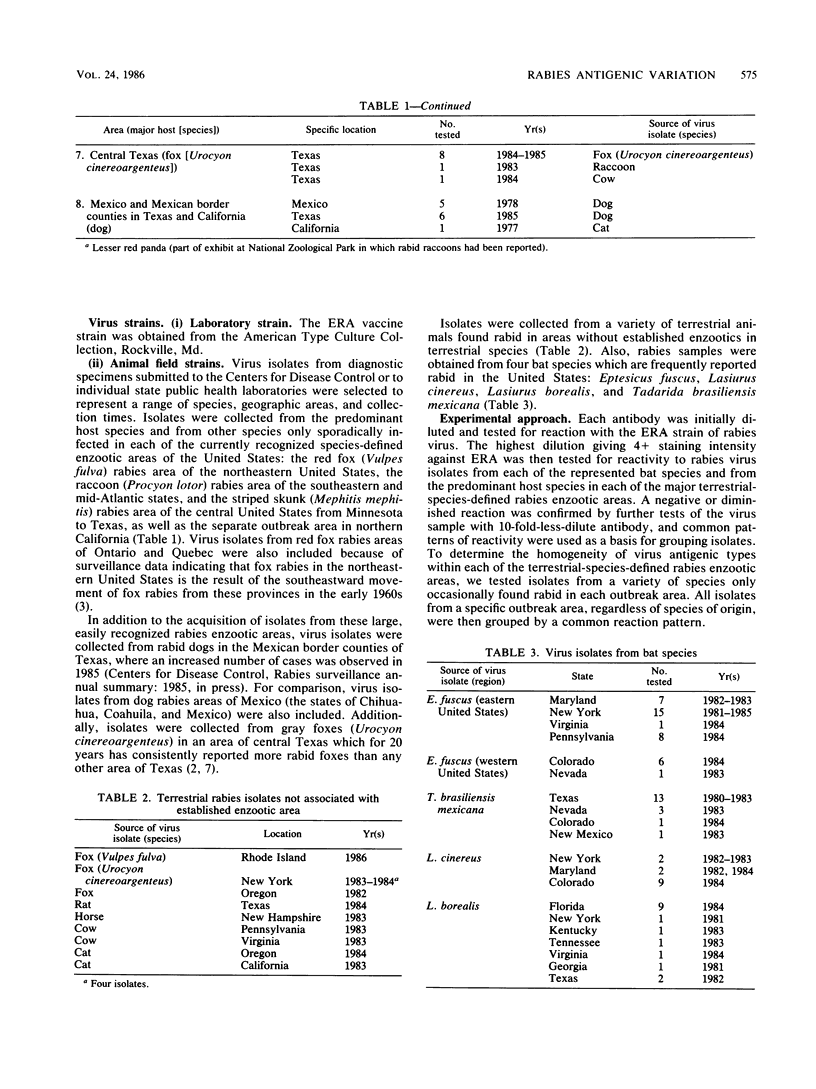
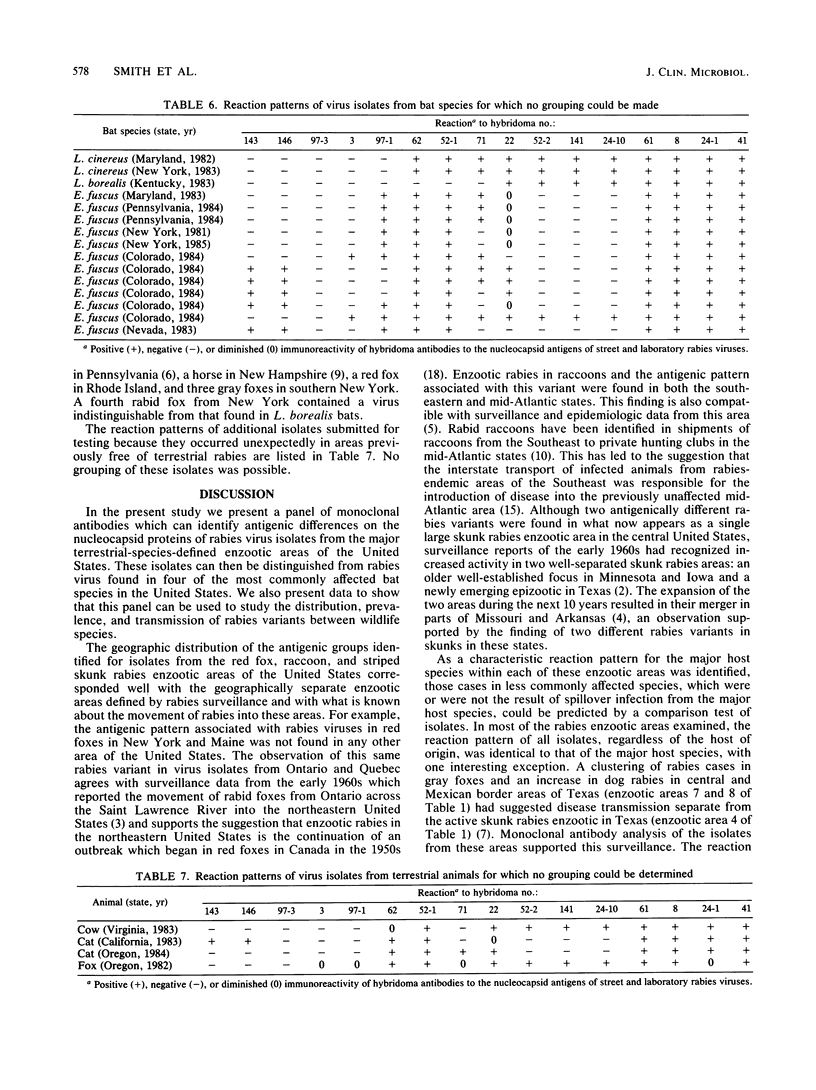
Rabies virus isolates from terrestrial animals in six areas of the United States were examined with a panel of monoclonal antibodies to nucleocapsid proteins. Characteristic differences in immunofluorescence reactions permitted the formation of four antigenically distinct reaction groups from the 231 isolates tested. The geographic distribution of these groups corresponded well with separate rabies enzootic areas recognized by surveillance of sylvatic rabies in the United States. Distinctive reaction patterns were also identified for viral proteins from four infected bat species, and identical patterns were found in eight isolated cases of rabies in terrestrial animals. These findings suggest that monoclonal antibodies can be used to study the prevalence, distribution, and transmission of rabies among wildlife species.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Constantine D. G. An updated list of rabies-infected bats in North America. J Wildl Dis. 1979 Apr;15(2):347–349. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-15.2.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller J. E., Jr A case of equine rabies. N Engl J Med. 1984 Feb 23;310(8):525–526. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198402233100812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nettles V. F., Shaddock J. H., Sikes R. K., Reyes C. R. Rabies in translocated raccoons. Am J Public Health. 1979 Jun;69(6):601–602. doi: 10.2105/ajph.69.6.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar B. S., Parks N. F., Clark H. F. Altered expression of rabies virus antigenic determinants associated with chronic infection and virulence. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):251–254. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCATTERDAY J. E., SCHNEIDER N. J., JENNINGS W. L., LEWIS A. L. Sporadic animal rabies in Florida. Public Health Rep. 1960 Oct;75:945–953. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider L. G., Dietzschold B., Dierks R. E., Matthaeus W., Enzmann P. J., Strohmaier K. Rabies group-specific ribonucleoprotein antigen and a test system for grouping and typing of rhabdoviruses. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):748–755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.748-755.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Sumner J. W., Roumillat L. F., Baer G. M., Winkler W. G. Antigenic characteristics of isolates associated with a new epizootic of raccoon rabies in the United States. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):769–774. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Sumner J. W., Roumillat L. F. Enzyme immunoassay for rabies antibody in hybridoma culture fluids and its application to differentiation of street and laboratory strains of rabies virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):267–272. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.267-272.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENTERS H. D., HOFFERT W. R., SCHATTERDAY J. E., HARDY A. V. Rabies in bats in Florida. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1954 Feb;44(2):182–185. doi: 10.2105/ajph.44.2.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


