Abstract
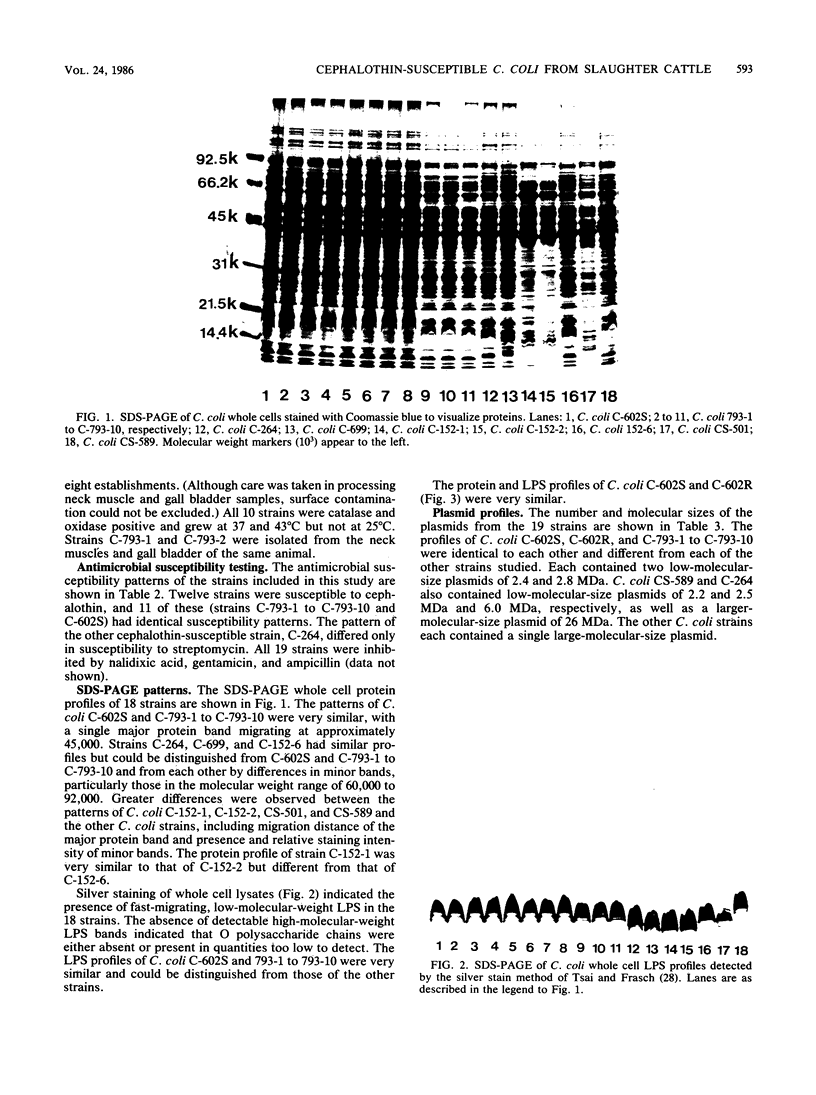
In a recent meat survey, 10 of 13 (77%) Campylobacter coli isolates were susceptible to cephalothin. These organisms were isolated from nine slaughter cattle from eight meat packing establishments. All 10 isolates grew at 43 degrees C but not at 25 degrees C, were catalase and oxidase positive, and were susceptible to nalidixic acid (30 micrograms) and cephalothin (30 micrograms). The cultures were subsequently identified as C. coli serogroup 20, biotype I (Lior scheme). Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis showed that protein and lipopolysaccharide profiles of whole cell preparations of the 10 cephalothin-susceptible strains and the reference strain for C. coli serogroup 20 were very similar. The plasmid profiles of these 11 strains were identical.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Hopkins J. A., Berka R. M., Vasil M. L., Wang W. L. Identification and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):276–284. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.276-284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Dekeyser P., Lafontaine T. Susceptibility of related vibrios and Vibrio fetus to twelve antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):86–89. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Roman D. J. Recovery of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from inoculated foods by selective enrichment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1343–1353. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1343-1353.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. M., Lior H., Stewart R. B., Ruckerbauer G. M., Trudel J. R., Skljarevski A. Isolation, characterization, and serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from slaughter cattle. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):667–672. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.667-672.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., De Grandis S., Fleming P. C. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus to eight cephalosporins with special reference to species differentiation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Dec;18(6):948–951. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.6.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauwers S., De Boeck M., Butzler J. P. Campylobacter enteritis in Brussels. Lancet. 1978 Mar 18;1(8064):604–605. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H. New, extended biotyping scheme for Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and "Campylobacter laridis". J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):636–640. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.636-640.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Woodward D. L., Edgar J. A., Laroche L. J., Gill P. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.761-768.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Outer membrane characteristics of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):898–906. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.898-906.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Structural and antigenic heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):210–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.210-216.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G., McBride H., Pearson A. D. The identification of outer membrane proteins and flagella of Campylobacter jejuni. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 May;130(5):1201–1208. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-5-1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Lipopolysaccharide characteristics of pathogenic campylobacters. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):353–359. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.353-359.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop R. M., 2nd, Smibert R. M., Johnson J. L., Krieg N. R. Differential characteristics of catalase-positive campylobacters correlated with DNA homology groups. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Jul;30(7):938–951. doi: 10.1139/m84-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosef O. Isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from the gallbladder of normal slaughter pigs, using an enrichment procedure. Acta Vet Scand. 1981;22(1):149–151. doi: 10.1186/BF03547219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Ng L. K., Lior H. Susceptibility of Campylobacter species to nalidixic acid, enoxacin, and other DNA gyrase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):708–710. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Williams S., Gordon K. P., Nolan C., Plorde J. J. Survey of plasmids and resistance factors in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):37–41. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoof R., Vanderlinden M. P., Dierickx R., Lauwers S., Yourassowsky E., Butzler J. P. Susceptibility of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni to twenty-nine antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):553–556. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenman W. M., Chai J., Louie T. J., Goudreau C., Lior H., Newell D. G., Pearson A. D., Taylor D. E. Antigenic analysis of Campylobacter flagellar protein and other proteins. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):108–112. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.108-112.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]