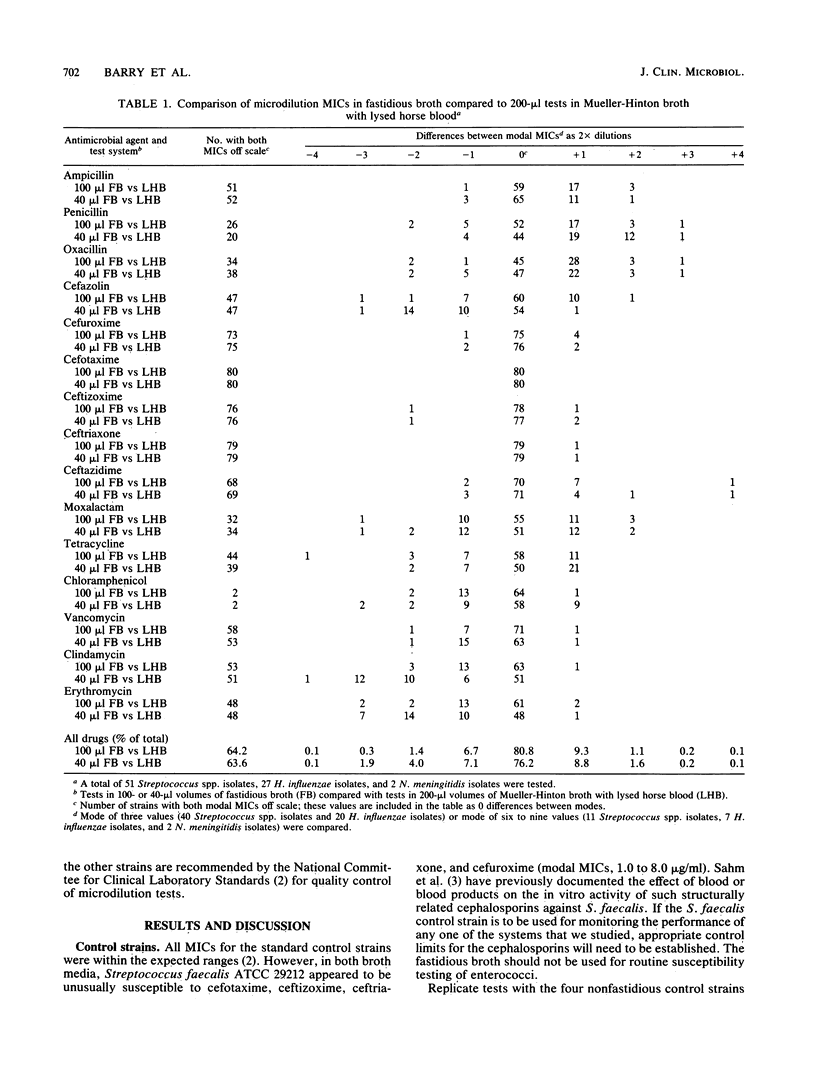
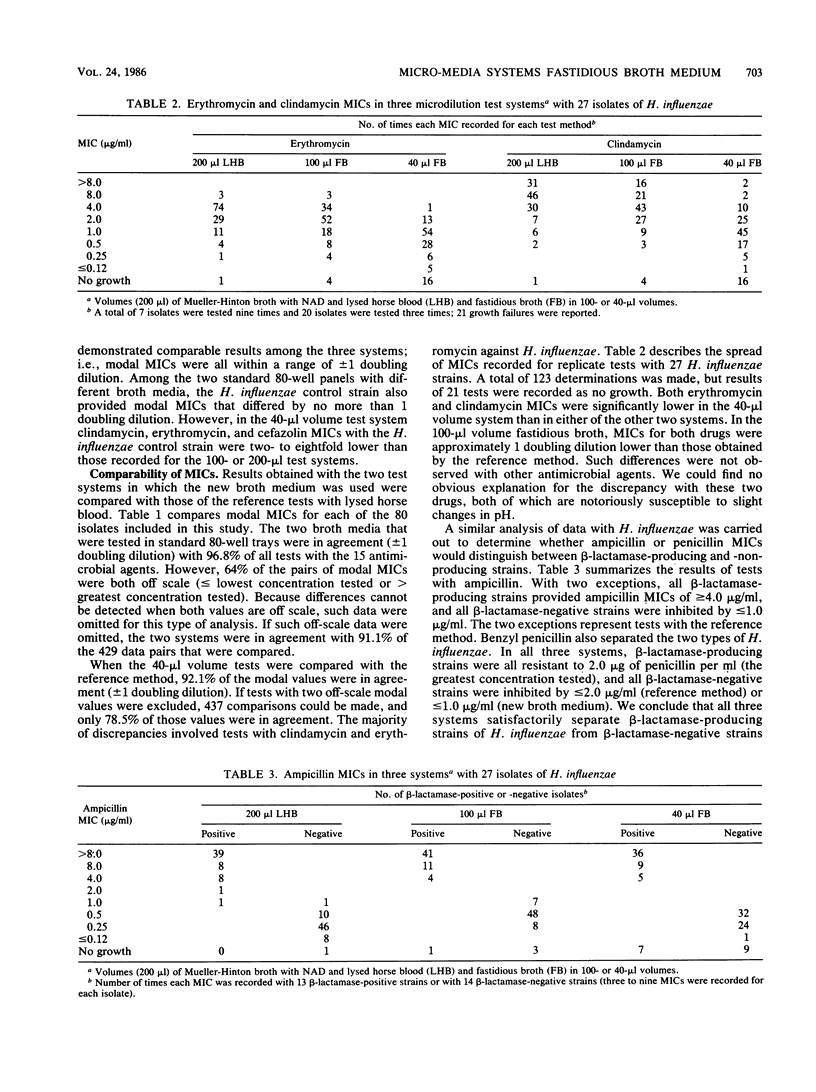
Abstract
For microdilution susceptibility tests with nutritionally fastidious microorganisms, a new clear broth medium developed at Micro-Media Systems, Inc., Potomac, Md., was evaluated in a three-laboratory collaborative study. Replicate tests were performed with 80 isolates (51 Streptococcus spp., 27 Haemophilus influenzae isolates, and 2 Neisseria meningitidis isolates) against 15 antimicrobial agents. In standard 100-microliters volumes, results of tests in the new broth medium were comparable to those in the reference medium (Mueller-Hinton broth with 2 to 3% lysed horse blood), but MICs were somewhat easier to read in the new broth medium. Results of similar tests in smaller panels, containing 40 microliters in each well, were less satisfactory; i.e., growth failures and poorly defined endpoints were more commonly encountered. With drugs other than erythromycin or clindamycin, the 40-microliters panels provided MICs which compared favorably with those obtained by standard reference methods.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Braun L. E. Reader error in determining minimal inhibitory concentrations with microdilution susceptibility test panels. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):228–230. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.228-230.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahm D. F., Baker C. N., Jones R. N., Thornsberry C. Influence of growth medium on the in vitro activities of second- and third-generation cephalosporins against Streptococcus faecalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):561–567. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.561-567.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


