Abstract
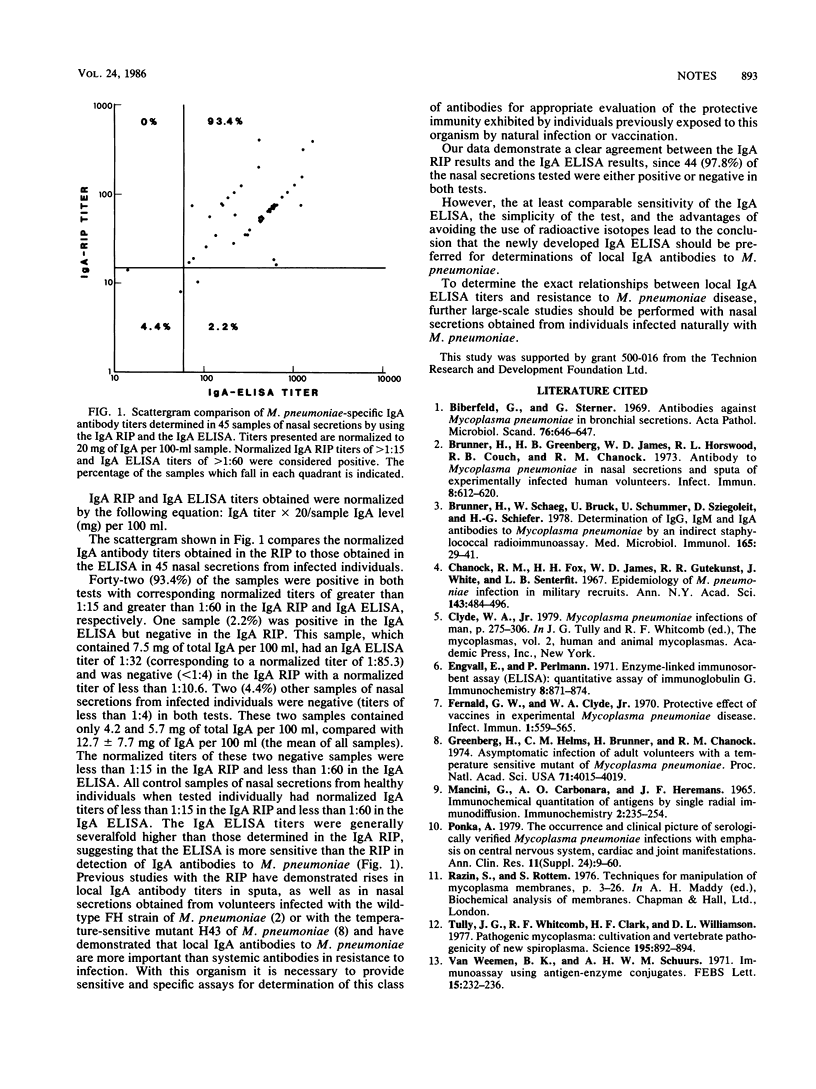
An immunoglobulin A (IgA) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was developed and compared with the radioimmunoprecipitation test in determinations of IgA antibodies to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Of 45 nasal secretions obtained from infected volunteers, 42 (93.4%) were positive and 2 (4.4%) were negative in both tests. The IgA enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is at least as sensitive as the IgA radioimmunoprecipitation test but is simpler and safer and should therefore be preferred.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biberfeld G., Sterner G. Antibodies against Mycoplasma pneumoniae in bronchial secretions. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;76(4):646–647. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1969.tb03296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H., Greenberg H. B., James W. D., Horswood R. L., Couch R. B., Chanock R. M. Antibody to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in nasal secretions and sputa of experimentally infected human volunteers. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):612–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.612-620.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H., Schaeg W., Brück U., Schummer U., Sziegoleit D., Schiefer H. Determination of IgG, IgM, and IgA antibodies to Mycoplasma pneumoniae by an indirect staphylococcal radioimmunoassy. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1978 May 26;165(1):29–41. doi: 10.1007/BF02121230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanock R. M., Fox H. H., James W. D., Gutekunst R. R., White R. J., Senterfit L. B. Epidemiology of M. pneumoniae infection in military recruits. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):484–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernald G. W., Clyde W. A. Protective Effect of Vaccines in Experimental Mycoplasma pneumoniae Disease. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):559–565. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.559-565.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H., Helms C. M., Brunner H., Chanock R. M. Asymptomatic infection of adult volunteers with a temperature sensitive mutant of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4015–4019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pönkä A. The occurrence and clinical picture of serologically verified Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections with emphasis on central nervous system, cardiac and joint manifestations. Ann Clin Res. 1979;11 (Suppl 24):1–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Whitcomb R. F., Clark H. F., Williamson D. L. Pathogenic mycoplasmas: cultivation and vertebrate pathogenicity of a new spiroplasma. Science. 1977 Mar 4;195(4281):892–894. doi: 10.1126/science.841314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Weemen B. K., Schuurs A. H.W.M. Immunoassay using antigen-enzyme conjugates. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80319-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


