Abstract
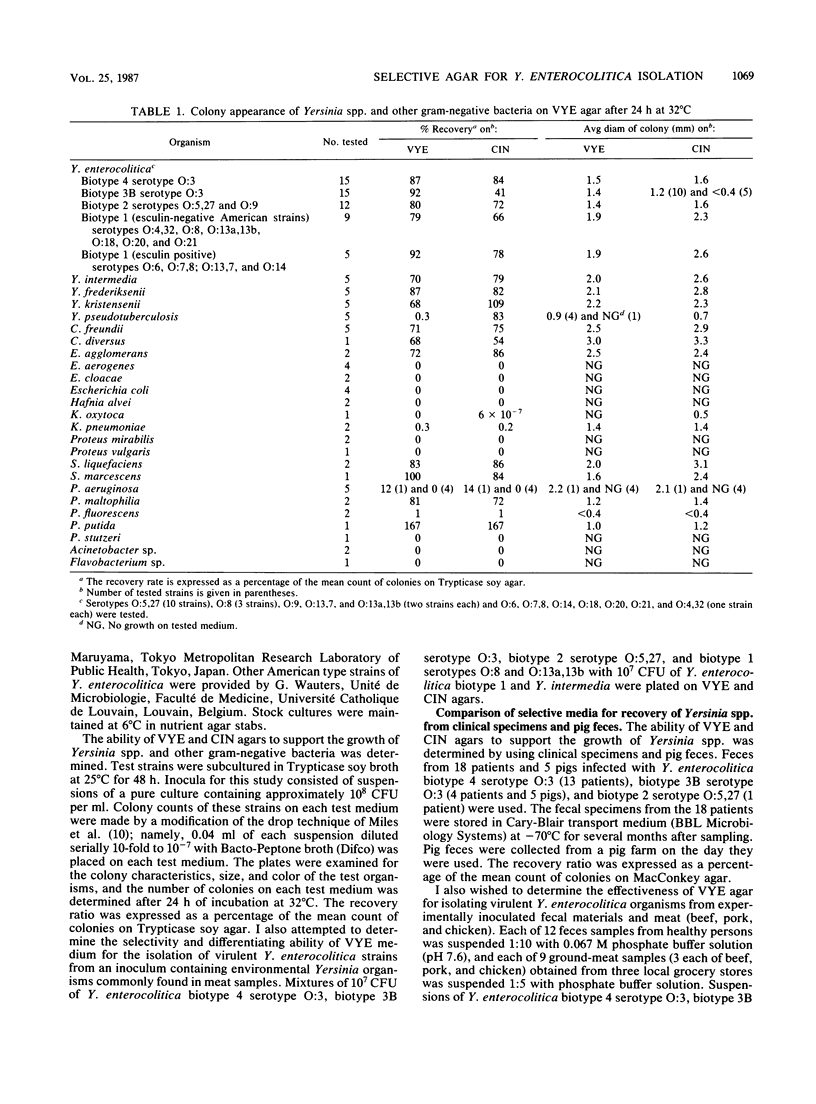
A selective agar medium for isolation of virulent Yersinia enterocolitica (VYE agar) was developed for the rapid and accurate isolation of virulent Y. enterocolitica from environmental samples highly contaminated with environmental Yersinia organisms, as well as for isolation from clinical specimens. VYE agar provided a quantitative recovery of 51 different strains of virulent Y. enterocolitica at 32 degrees C after incubation for 24 h. The cefsulodin, irgasan, josamycin, and oleandomycin content of the medium resulted in a high selectivity, and the mannitol and esculin content provided some differentiation. The greatest advantage of VYE agar is that virulent Y. enterocolitica, which forms red colonies, is easily differentiated from most environmental Yersinia organisms and other gram-negative bacteria, which form dark colonies with a dark peripheral zone as a result of esculin hydrolysis. Use of VYE agar led to a high recovery of Y. enterocolitica biotype 3B serotype O:3 strains from experimentally inoculated meat samples, compared with use of CIN agar. Biotype 2 serotypes O:5,27 and O:9 and biotype 1 esculin-negative serotypes O:4,32, O:8, O:13a,13b, O:18, O:20, and O:21 (American types) were readily differentiated from other environmental organisms able to grow on VYE agar. Epidemiological studies on Y. enterocolitica should be greatly facilitated by the use of this selective agar medium.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davey G. M., Bruce J., Drysdale E. M. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica and related species from the faeces of cows. J Appl Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;55(3):439–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1983.tb01683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., Gomyoda M. Growth of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 3B serotype O3 inhibited on cefsulodin-Irgasan-novobiocin agar. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):116–120. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.116-120.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., Tsubokura M., Otsuki K., Kawaoka Y., Nishio R., Moriki S., Nishino Y., Mototsune H., Karino K. Epidemiological study of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis infections in Shimane Prefecture, Japan. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1985 May;180(5-6):515–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., Tsubokura M. Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 3B serotype 03 phage type II infection in pigs. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1985 Dec;47(6):1011–1015. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.47.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head C. B., Whitty D. A., Ratnam S. Comparative study of selective media for recovery of Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):615–621. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.615-621.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandolo K., Wauters G. Pyrazinamidase activity in Yersinia enterocolitica and related organisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):980–982. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.980-982.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollaret H. H., Bercovier H., Alonso J. M. Summary of the data received at the WHO Reference Center for Yersinia enterocolitica. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:174–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A. Synthesis of a selective agar medium for Yersinia enterocolitica. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Nov;25(11):1298–1304. doi: 10.1139/m79-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler P. R. Nachweis von Yersinia enterocolitica aus Trinkwasserversorgungsanlagen in Südbayern. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1984 Dec;180(1):76–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toma S., Wauters G., McClure H. M., Morris G. K., Weissfeld A. S. O:13a,13b, a new pathogenic serotype of Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):843–845. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.843-845.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Lembke C., Schäfer R. Vergleichende Anwendung von zwei im Handel erhältlichen Selektivnährböden zur Isolierung von :ersinia enterocolitica aus Tonsillen von Schlachtschweinen. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1983 Aug;30(7):532–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]