Abstract
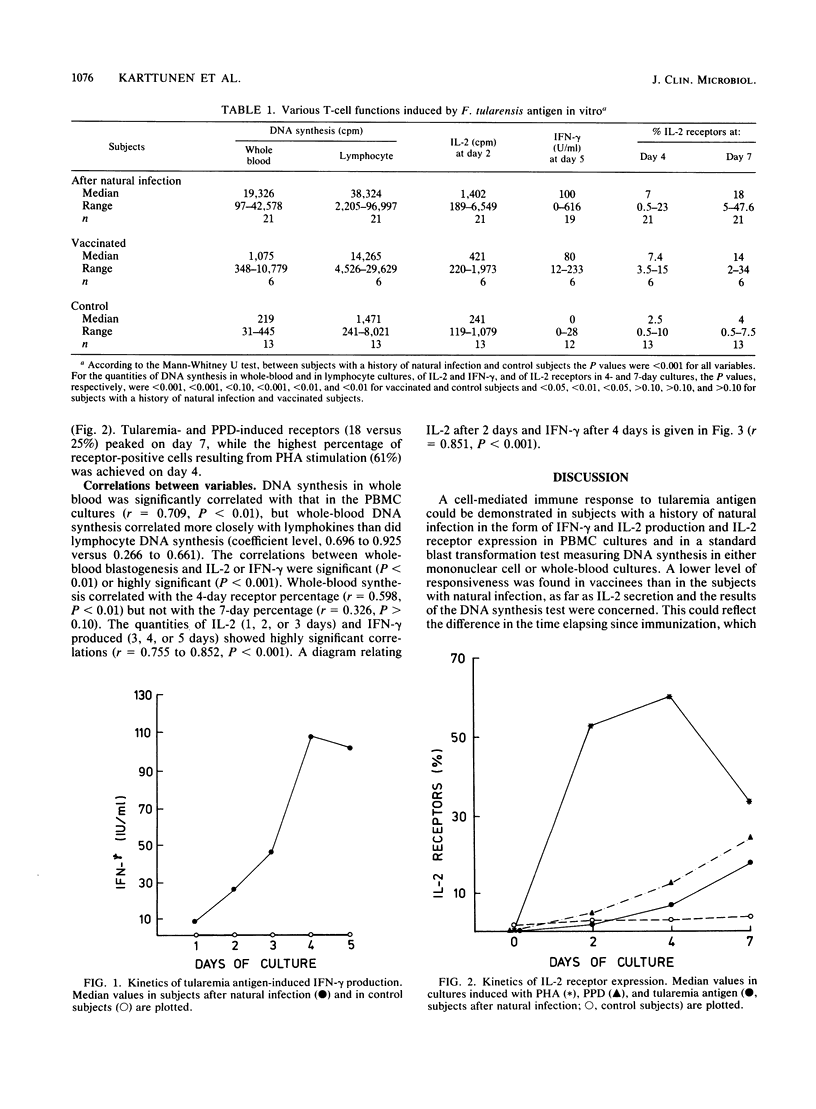
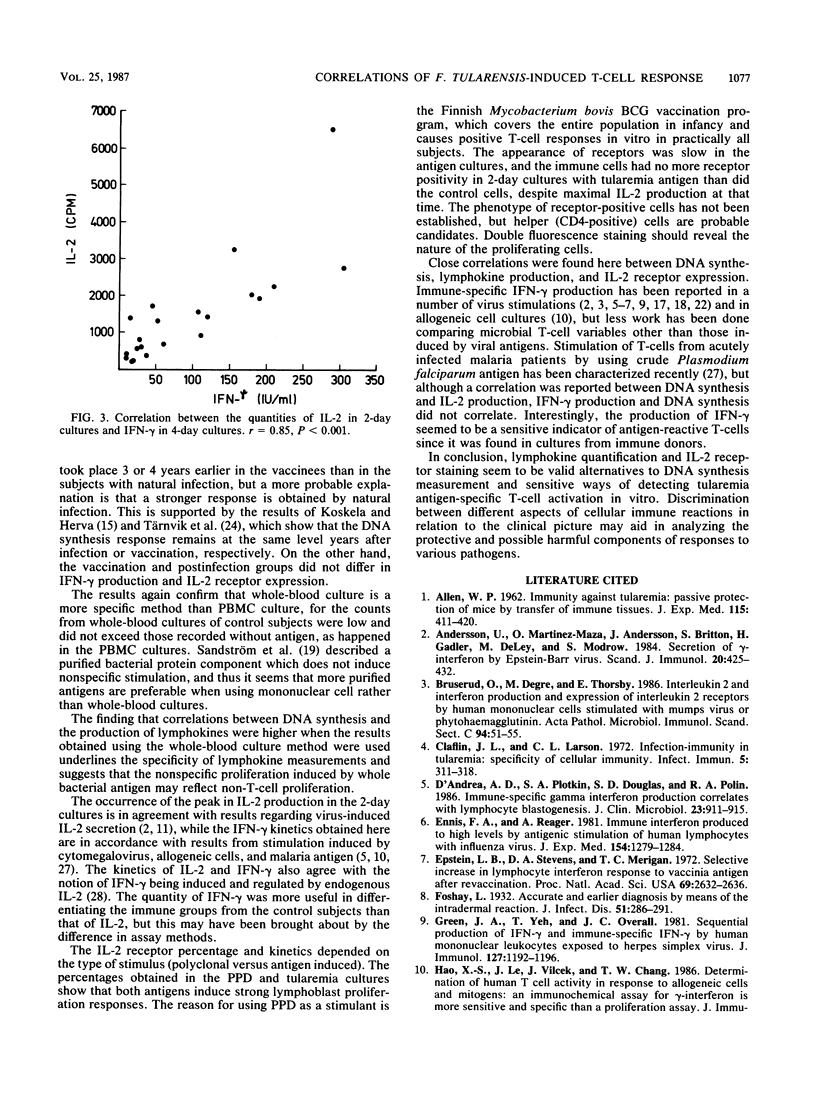
The T-cell response induced by Francisella tularensis antigen in sensitized subjects was characterized in vitro by measuring DNA synthesis in whole-blood and mononuclear cell cultures, interleukin 2 (IL-2) and gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) production, and IL-2 receptor expression. Correlations between these variables were estimated. The strengths of the responses were compared in 21 subjects naturally infected 2 years ago, 6 subjects vaccinated 5 to 6 years ago, and 13 control subjects with no history of infection or vaccination. Subjects with a history of natural infection synthesized more DNA in both whole-blood and mononuclear cell cultures, secreted more IL-2 and IFN-gamma, and expressed more IL-2 receptors than control subjects did. All these responses differed highly significantly (P less than 0.001) from those of the control subjects. The vaccinees exhibited somewhat lower responses than the naturally immunized subjects did, but the vaccinees could be distinguished from the control subjects by their DNA synthesis, receptor expression, and IFN-gamma production (P less than 0.01 to 0.001). The vaccinees showed a lower response, in terms of DNA synthesis and IL-2 secretion (P less than 0.05), than the infected group did but responded in a manner similar to that of this group, with respect to receptor positivity and IFN-gamma secretion (P greater than 0.10). The correlations between all the T-cell functions were good, with highly significant correlations (P less than 0.001) between whole-blood DNA synthesis and IL-2 and IFN-gamma secretion and between the two lymphokines (P less than 0.001). The results not only increase our knowledge of the T-cell response to tularemia antigen but also give an alternative approach to DNA synthesis measurement for the quantitation of T-cell responses. The results for the low-responding sensitized subjects seem to indicate that the parameters were comparable in sensitivity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN W. P. Immunity against tularemia: passive protection of mice by transfer of immune tissues. J Exp Med. 1962 Feb 1;115:411–420. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson U., Martinez-Maza O., Andersson J., Britton S., Gadler H., De Ley M., Modrow S. Secretion of gamma-interferon at the cellular level. Induction by Epstein-Barr virus. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Nov;20(5):425–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb01021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruserud O., Degré M., Thorsby E. Interleukin 2- and interferon-production and expression of interleukin 2 receptors by human mononuclear cells stimulated with mumps virus or phytohaemagglutinin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1986 Apr;94(2):51–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1986.tb02089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claflin J. L., Larson C. L. Infection-immunity in tularemia: specificity of cellular immunity. Infect Immun. 1972 Mar;5(3):311–318. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.3.311-318.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Plotkin S. A., Douglas S. D., Polin R. A. Immune-specific gamma interferon production correlates with lymphocyte blastogenesis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):911–915. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.911-915.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis F. A., Meager A. Immune interferon produced to high levels by antigenic stimulation of human lymphocytes with influenza virus. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1279–1289. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. B., Stevens D. A., Merigan T. C. Selective increase in lymphocyte interferon response to vaccinia antigen after revaccination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. A., Yeh T. J., Overall J. C., Jr Sequential production of IFN-alpha and immune-specific IFN-gamma by human mononuclear leukocytes exposed to herpes simplex virus. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1192–1196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilonen J., Salmi A. Detection of antigen-specific cellular immune response by the in vitro production of T-cell growth factor. Scand J Immunol. 1981 May;15(5):521–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karttunen R., Ilonen J., Herva E. Interleukin 2 production in whole blood culture: a rapid test of immunity to Francisella tularensis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):318–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.318-319.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karttunen R., Nurmi T., Ilonen J., Surcel H. M. Cell-mediated immunodeficiency in Down's syndrome: normal IL-2 production but inverted ratio of T cell subsets. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):257–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskela P., Herva E. Cell-mediated and humoral immunity induced by a live Francisella tularensis vaccine. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):983–989. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.983-989.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskela P., Herva E. Cell-mediated immunity against Francisella tularensis after natural infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 1980;12(4):281–287. doi: 10.3109/inf.1980.12.issue-4.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostiala A. A., McGregor D. D., Logie P. S. Tularaemia in the rat. I. The cellular basis on host resistance to infection. Immunology. 1975 May;28(5):855–869. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T. Immune-specific production of gamma interferon in human lymphocyte cultures in response to mumps virus. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):486–492. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.486-492.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen L. E., Jordan G. W., Stevens D. A., Merigan T. C. Lymphocyte interferon production and transformation after Herpes simplex infections in humans. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):728–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandström G., Tärnvik A., Wolf-Watz H., Löfgren S. Antigen from Francisella tularensis: nonidentity between determinants participating in cell-mediated and humoral reactions. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):101–106. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.101-106.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. T-cell growth factor. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:337–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr S. E., Dalton B., Garrabrant T., Paucker K., Plotkin S. A. Lymphocyte blastogenesis and interferon production in adult human leukocyte cultures stimulated with cytomegalovirus antigens. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):17–22. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.17-22.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrjälä H., Herva E., Ilonen J., Saukkonen K., Salminen A. A whole-blood lymphocyte stimulation test for the diagnosis of human tularemia. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):912–915. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORPE B. D., MARCUS S. PHAGOCYTOSIS AND INTRACELLULAR FATE OF PASTEURELLA TULARENSIS. 3. IN VIVO STUDIES WITH PASSIVELY TRANSFERRED CELLS AND SERA. J Immunol. 1965 Apr;94:578–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troye-Blomberg M., Andersson G., Stoczkowska M., Shabo R., Romero P., Patarroyo M. E., Wigzell H., Perlmann P. Production of IL 2 and IFN-gamma by T cells from malaria patients in response to Plasmodium falciparum or erythrocyte antigens in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3498–3504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tärnvik A., Löfgren M. L., Löfgren S., Sandström G., Wolf-Watz H. Long-lasting cell-mediated immunity induced by a live Francisella tularensis vaccine. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):527–530. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.527-530.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tärnvik A., Löfgren S. Stimulation of human lymphocytes by a vaccine strain of Francisella tularensis. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):951–957. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.951-957.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


