Abstract
The intensity and kinetics of the serum polymeric and monomeric immunoglobulin A1 (IgA1) and IgA2 antibody responses to Campylobacter jejuni were analyzed. A rapid and marked serum IgA antibody response involving both the monomeric and polymeric components of IgA was observed after C. jejuni infections. IgA antibodies reached a peak of activity in serum during week 2 after the first symptoms of enteritis, about 10 days before the peak of IgG activity. Polymeric IgA accounted for most of the anti-C. jejuni activity at the peak of the IgA response (median, 90%; range, 44 to 98%) but rapidly disappeared from serum over a few weeks. In contrast, the serum monomeric IgA antibody response was low and was maintained over a prolonged period of time. Anti-C. jejuni IgA detected in the serum of healthy blood donors was mainly monomeric (median, 83%; range, 17 to 94%). In both the patients and the positive controls, IgA1 was the predominant (greater than 85%) subclass involved, even when the IgA antibody response was mainly polymeric. Our results suggest that polymeric IgA antibody responses are linked to a strong or persisting antigenic stimulation or both. Polymeric IgA antibodies appear to be a potential marker of acute C. jejuni infections, and their determination could provide a useful tool for the serological diagnosis of recent C. jejuni infections.
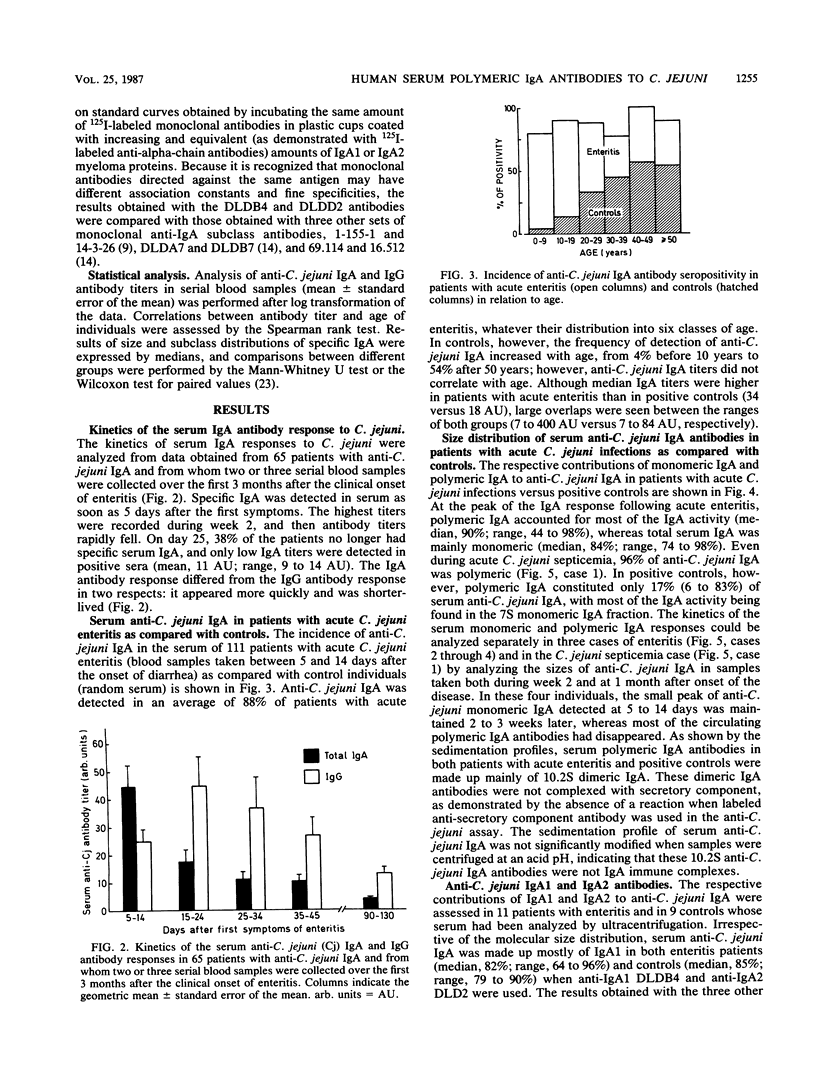
Full text
PDF

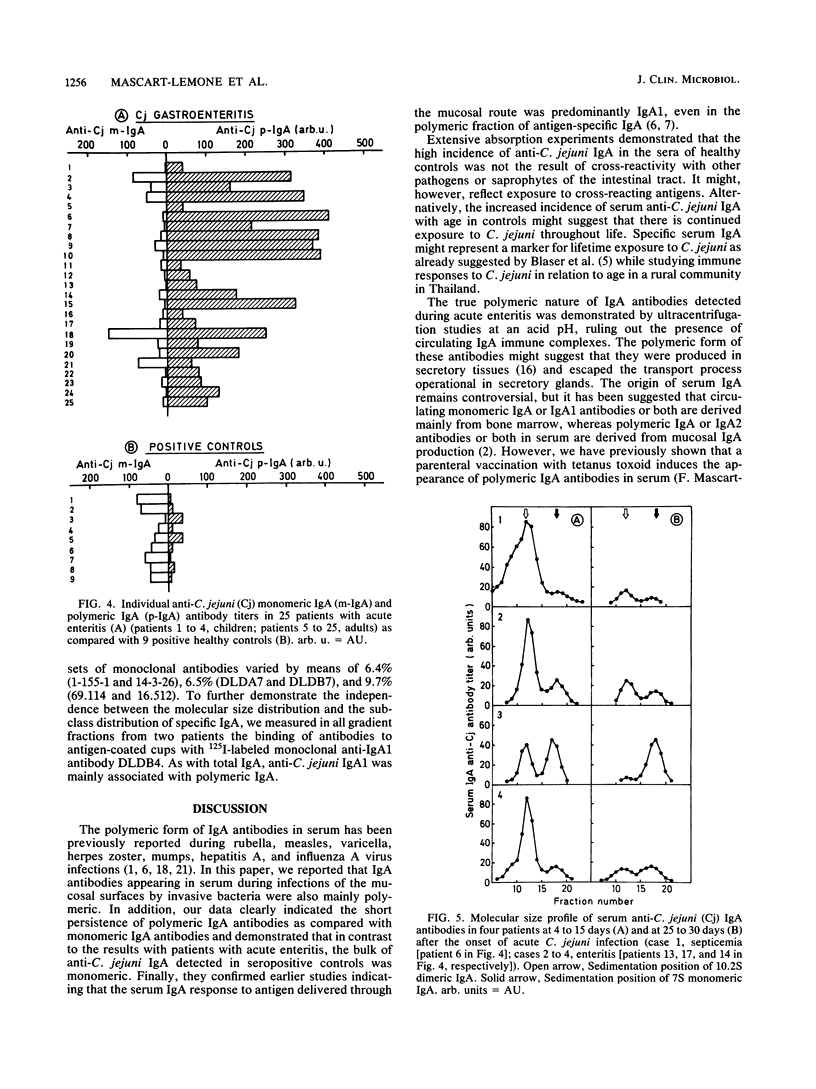

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- André C., Berthoux F. C., André F., Gillon J., Genin C., Sabatier J. C. Prevalence of IgA2 deposits in IgA nephropathies: a clue to their pathogenesis. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 4;303(23):1343–1346. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012043032306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Duncan D. J. Human serum antibody response to Campylobacter jejuni infection as measured in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):292–298. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.292-298.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Reller L. B. Campylobacter enteritis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1444–1452. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Taylor D. N., Echeverria P. Immune response to Campylobacter jejuni in a rural community in Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):249–254. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. A., Murphy B. R., Radl J., Haaijman J. J., Mestecky J. Subclass distribution and molecular form of immunoglobulin A hemagglutinin antibodies in sera and nasal secretions after experimental secondary infection with influenza A virus in humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):259–264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.259-264.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Briles D. E. Lack of IgA subclass restriction in antibody response to phosphorylcholine, beta lactoglobulin and tetanus toxoid. Immunology. 1984 Nov;53(3):419–426. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Kearney J. F., Lawton A. R., 3rd, Cooper M. D. Differentiation of human B cells expressing the IgA subclasses as demonstrated by monoclonal hybridoma antibodies. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2311–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Koopman W. J. Serum IgA1 and IgA2 in normal adults and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and hepatic disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Mar;26(3):390–397. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Dehennin J. P., Vaerman J. P. Influence of molecular size of IgA on its immunoassay by various techniques. II. Solid-phase radioimmunoassays. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(3):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Dive C., Rambaud J. C., Vaerman J. P. IgA subclasses in various secretions and in serum. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):383–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Elkom K. B., Geubel A. P., Hodgson H. F., Dive C., Vaerman J. P. Changes in size, subclass, and metabolic properties of serum immunoglobulin A in liver diseases and in other diseases with high serum immunoglobulin A. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):358–367. doi: 10.1172/JCI110777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Vaerman J. P. Secretory component (SC): preferential binding to heavy (greater than 11S) IgA polymers and IgM in serum, in contrast to predominance of 11S and free SC forms in secretions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Sep;49(3):717–724. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Van Snick J., Vaerman J. P., Conley M. E., Mascart-Lemone F., Bernier G. M. Monoclonal antibodies against isotypic and isoallotypic determinants of human IgA1 and IgA2: fine specificities and binding properties. Mol Immunol. 1986 Apr;23(4):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutteh W. H., Prince S. J., Mestecky J. Tissue origins of human polymeric and monomeric IgA. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):990–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Molecular identification of surface protein antigens of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):675–682. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.675-682.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlino C., Angeretti A., Cavallo R., Negro Ponzi A. IgA specifiche polimeriche nelle infezioni con il virus della parotite. Boll Ist Sieroter Milan. 1985;64(4):335–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., Russell M. W., Jackson S., Brown T. A. The human IgA system: a reassessment. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Jul;40(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosimann J., Jung M., Schär G., Bonifas V., Heinzer I., Brunner S., Hermann G., Lambert R. A. Serologische Diagnose menschlicher Campylobacter-Infektionen. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1981 Jun 6;111(23):846–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negro Ponzi A., Merlino C., Angeretti A., Penna R. Virus-specific polymeric immunoglobulin A antibodies in serum from patients with rubella, measles, varicella, and herpes zoster virus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):505–509. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.505-509.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterom J., den Uyl C. H., Bänffer J. R., Lauwers S., Huisman J., Busschbach A. E., Poelma F. G., Bellemans R. Evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of Campylobacter jejuni antibodies, and comparison with a complement fixation test (CFT). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1985;51(3):321–331. doi: 10.1007/BF02439941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASI T. B., Jr, TAN E. M., SOLOMON A., PRENDERGAST R. A. CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IMMUNE SYSTEM COMMON TO CERTAIN EXTERNAL SECRETIONS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:101–124. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Strober W. Metabolism of immunoglobulins. Prog Allergy. 1969;13:1–110. doi: 10.1159/000385919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


