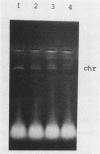
Abstract
A female patient suffered a typical attack of typhoid fever due to a lactose-negative, fully susceptible Salmonella typhi strain. During convalescence she became febrile, and a lactose-fermenting S. typhi strain resistant to ampicillin, chloramphenicol, tetracycline, and trimethoprim was isolated from blood culture. This isolated was shown to harbor a plasmid which cotransferred lactose fermentation and antibiotic resistance.
Full text
PDF

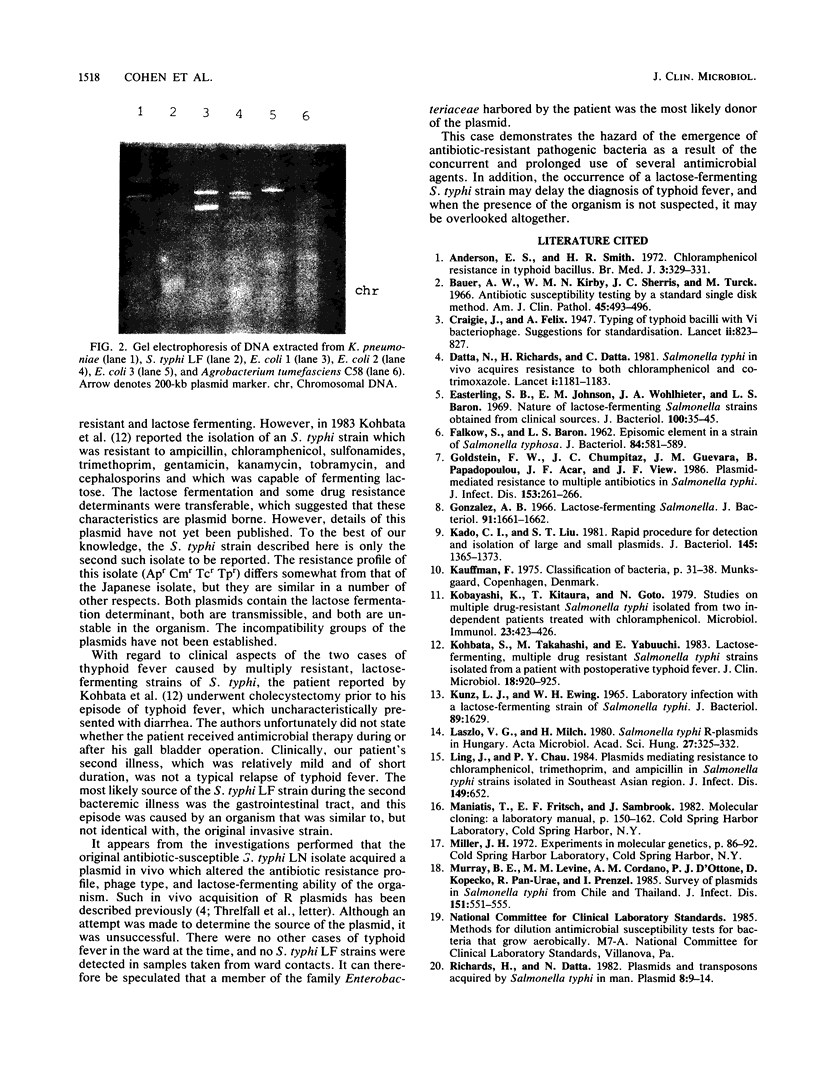
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. S., Smith H. R. Chloramphenicol resistance in the typhoid bacillus. Br Med J. 1972 Aug 5;3(5822):329–331. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5822.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Richards H., Datta C. Salmonella typhi in vivo acquires resistance to both chloramphenicol and co-trimoxazole. Lancet. 1981 May 30;1(8231):1181–1183. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92350-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easterling S. B., Johnson E. M., Wohlhieter J. A., Baron L. S. Nature of lactose-fermenting Salmonella strains obtained from clinical sources. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):35–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.35-41.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S., Baron L. S. EPISOMIC ELEMENT IN A STRAIN OF SALMONELLA TYPHOSA. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84(3):581–589. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.581-589.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein F. W., Chumpitaz J. C., Guevara J. M., Papadopoulou B., Acar J. F., Vieu J. F. Plasmid-mediated resistance to multiple antibiotics in Salmonella typhi. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):261–266. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez A. B. Lactose-fermenting Salmonella. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1661–1662. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1661-1662.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNZ L. J., EWING W. H. LABORATORY INFECTION WITH A LACTOSE-FERMENTING STRAIN OF SALMONELLA TYPHI. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1629–1629. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1629-1629.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Kitaura T., Goto N., Nakaya R. Studies on multiple drug-resistant Salmonella typhi isolated from two independent patients treated with chloramphenicol. Microbiol Immunol. 1979;23(5):423–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1979.tb00480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohbata S., Takahashi M., Yabuuchi E. Lactose-fermenting, multiple drug-resistant Salmonella typhi strains isolated from a patient with postoperative typhoid fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):920–925. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.920-925.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling J., Chau P. Y. Plasmids mediating resistance to chloramphenicol, trimethoprim, and ampicillin in Salmonella typhi strains isolated in the Southeast Asian region. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):652–652. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- László V. G., Milch H. Salmonella typhi R-plasmids in Hungary. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1980;27(4):325–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Levine M. M., Cordano A. M., D'Ottone K., Jayanetra P., Kopecko D., Pan-Urae R., Prenzel I. Survey of plasmids in Salmonella typhi from Chile and Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):551–555. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards H., Datta N. Plasmids and transposons acquired by Salmonella typhi in man. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]