Abstract
A current concept of the serological response to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection in humans is that antibodies to core antigens (p55, p24, and p15) are detectable earlier during initial stages of antibody production than antibodies against envelope antigens (gp160, gp120, and gp41). Comparative studies of Western blot (immunoblot), radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA), and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) during initial antibody production are limited to case reports and have not resolved the issue. Thirty of the 37 participants who are part of a prospective study had at least one specimen that was negative for anti-gp41 but had one or more other bands on Western blot. Twenty-seven of these 30 specimens were reactive for anti-gp120/160 in the RIPA. Of the same 30 specimens, kits from Bionetics identified 2 (7%), ElectroNucleonics 4 (13%), Abbott 13 (43%), Du Pont 25 (83%), and Genetic Systems 25 (83%). All participants had evidence of serological progression by Western blot, including a gp41 band, on subsequent visits; the ELISA kits of all manufacturers identified these later specimens with greater accuracy. These data show that the RIPA detects anti-envelope antibodies that may be not detectable by Western blot and that the production of anti-envelope antibodies approximately parallels the production of anti-core antibodies. The false-negative results by ELISA would permit transmission of HIV by blood transfusion from donors in early stages of infection. The sensitivity of licensed ELISA kits should be improved to identify antibody as soon as possible after infection.
Full text
PDF

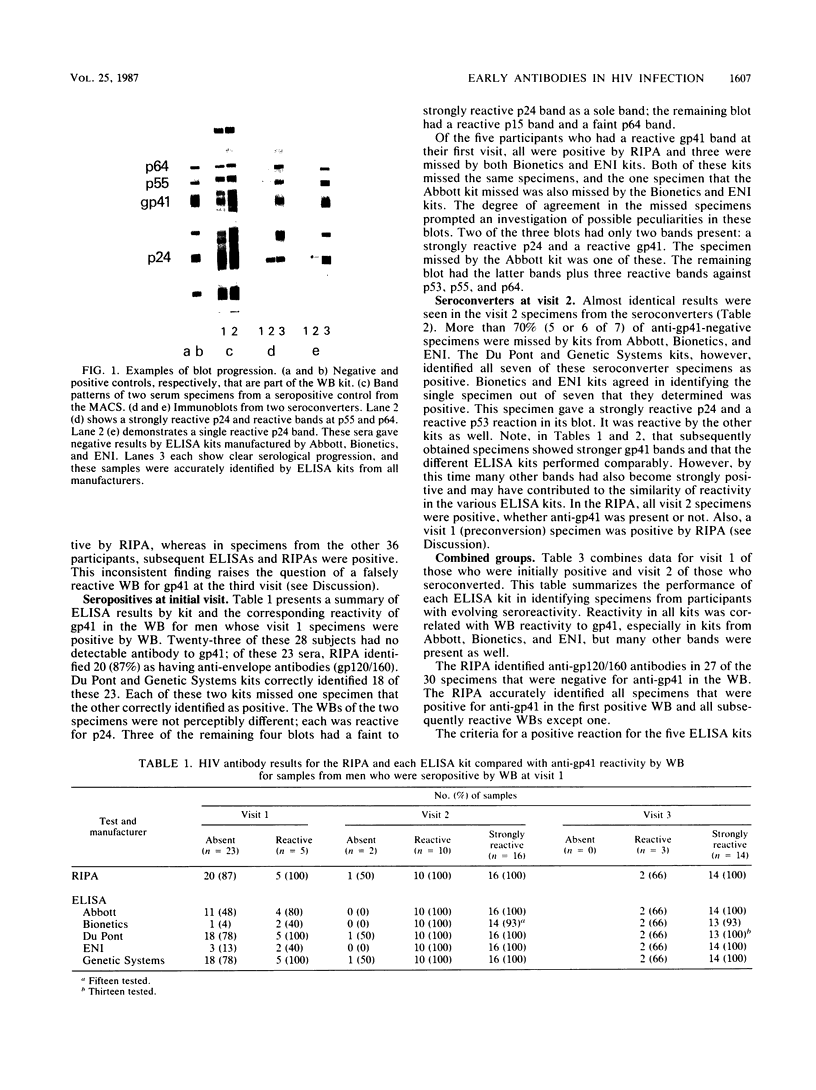
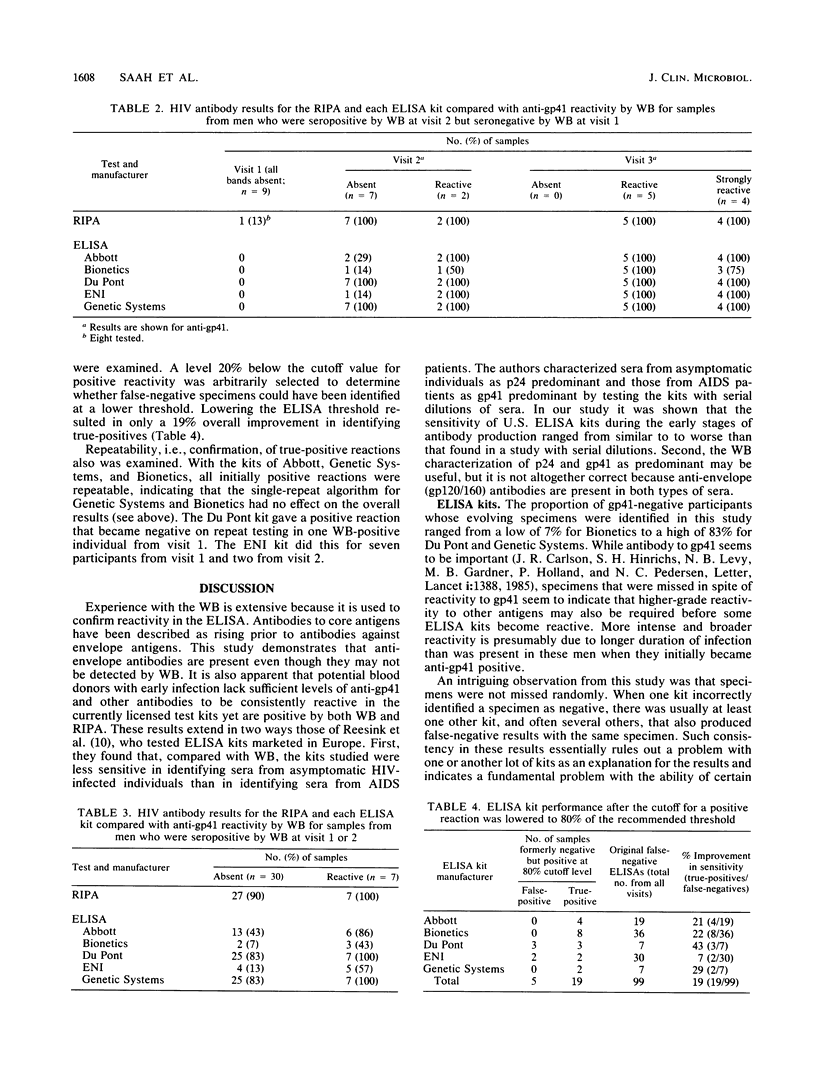


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barin F., McLane M. F., Allan J. S., Lee T. H., Groopman J. E., Essex M. Virus envelope protein of HTLV-III represents major target antigen for antibodies in AIDS patients. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1094–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.2986291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggar R. J., Melbye M., Ebbesen P., Alexander S., Nielsen J. O., Sarin P., Faber V. Variation in human T lymphotropic virus III (HTLV-III) antibodies in homosexual men: decline before onset of illness related to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Oct 12;291(6501):997–998. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6501.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban J. I., Shih J. W., Tai C. C., Bodner A. J., Kay J. W., Alter H. J. Importance of western blot analysis in predicting infectivity of anti-HTLV-III/LAV positive blood. Lancet. 1985 Nov 16;2(8464):1083–1086. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90683-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Shearer G. M., Kaplan M., Haynes B. F., Palker T. J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reesink H. W., Lelie P. N., Huisman J. G., Schaasberg W., Gonsalves M., Aaij C., Winkel I. N., van der Does J. A., Hekker A. C., Desmyter J. Evaluation of six enzyme immunoassays for antibody against human immunodeficiency virus. Lancet. 1986 Aug 30;2(8505):483–486. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarngadharan M. G., Popovic M., Bruch L., Schüpbach J., Gallo R. C. Antibodies reactive with human T-lymphotropic retroviruses (HTLV-III) in the serum of patients with AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):506–508. doi: 10.1126/science.6324345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüpbach J., Haller O., Vogt M., Lüthy R., Joller H., Oelz O., Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Gallo R. C. Antibodies to HTLV-III in Swiss patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS and in groups at risk for AIDS. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 31;312(5):265–270. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501313120502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulstrup J. C., Skaug K., Figenschau K. J., Orstavik I., Bruun J. N., Petersen G. Sensitivity of western blotting (compared with ELISA and immunofluorescence) during seroconversion after HTLV-III infection. Lancet. 1986 May 17;1(8490):1151–1152. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91862-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



