Abstract
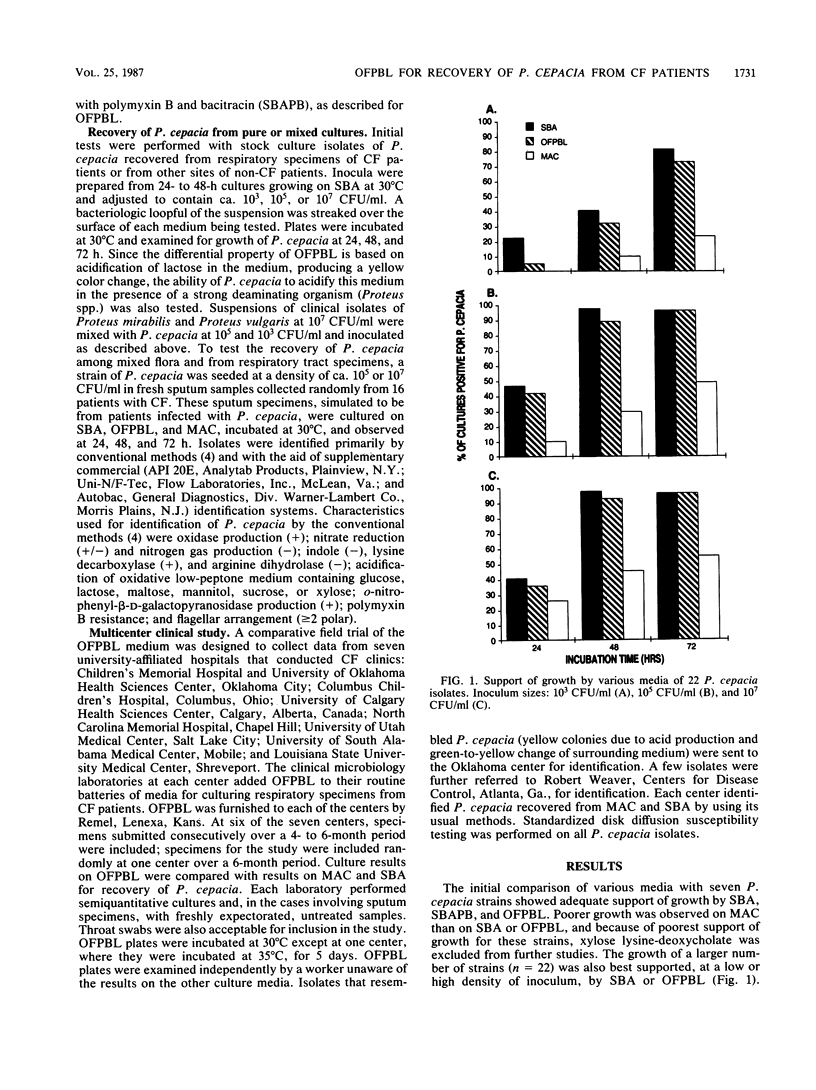
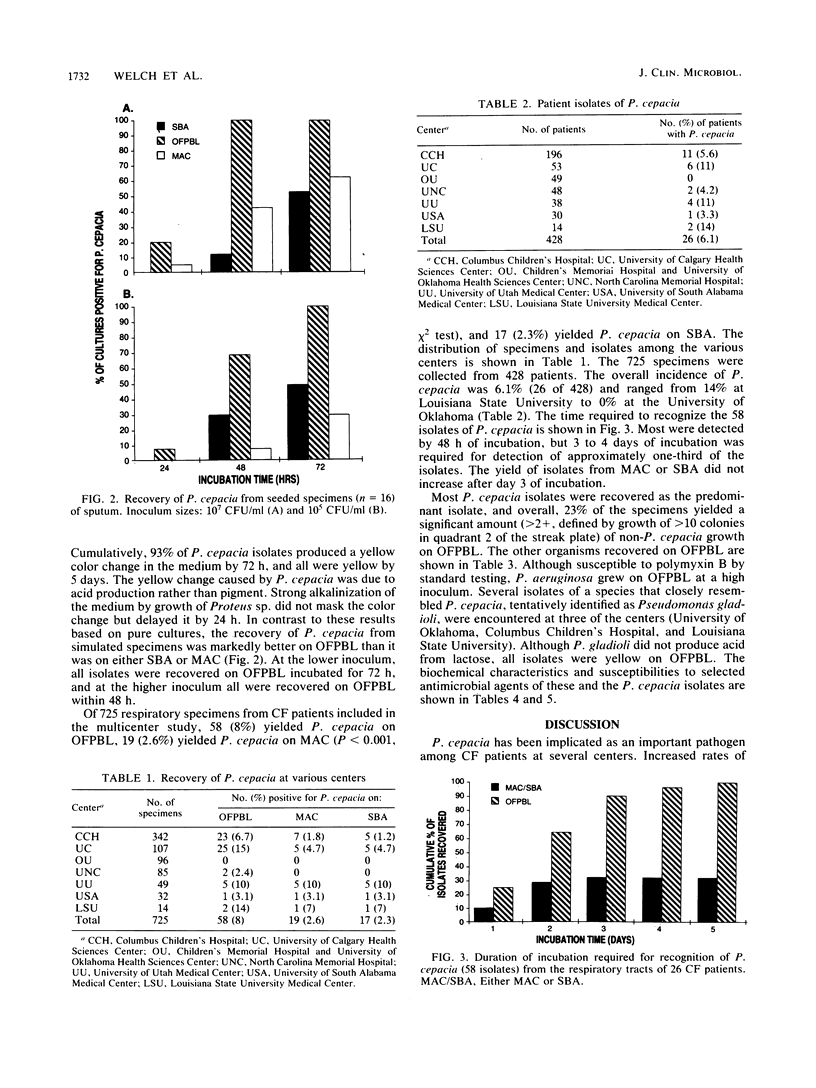
A selective and differential medium, OFPBL (oxidation-fermentation base supplemented with agar, lactose, and two antimicrobial agents), for the isolation of Pseudomonas cepacia from respiratory specimens of patients with cystic fibrosis was developed and tested. Among 725 specimens submitted from seven centers over a 4- to 6-month period, 58 (8%) yielded P. cepacia on OFPBL; only 19 of these were recovered on MacConkey or sheep blood agar (P less than 0.001). No isolate was recovered on MacConkey or sheep blood agar alone. Ranges of recovery rates among centers were 0 to 15% on OFPBL and 0 to 10% on MacConkey or sheep blood agar. Ninety percent of P. cepacia isolates were detected on OFPBL in less than or equal to 3 days. Other nonfermenters and yeasts isolated on OFPBL were distinguished from P. cepacia by failure to acidify the medium. The new medium was clearly superior to MacConkey and sheep blood agars for the isolation of P. cepacia from the respiratory secretions of patients with cystic fibrosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruce M. C., Poncz L., Klinger J. D., Stern R. C., Tomashefski J. F., Jr, Dearborn D. G. Biochemical and pathologic evidence for proteolytic destruction of lung connective tissue in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):529–535. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dees S. B., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Moss C. W. Cellular fatty acid composition of Pseudomonas marginata and closely associated bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1073–1078. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1073-1078.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan P. H., Gage P. A., Bradshaw L. M., Schidlow D. V., DeCicco B. T. Isolation medium for the recovery of Pseudomonas cepacia from respiratory secretions of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):5–8. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.5-8.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Kilian M. Haemophilus from the lower respiratory tract of patients with cystic fibrosis. Scand J Respir Dis. 1976;57(3):103–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isles A., Maclusky I., Corey M., Gold R., Prober C., Fleming P., Levison H. Pseudomonas cepacia infection in cystic fibrosis: an emerging problem. J Pediatr. 1984 Feb;104(2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80993-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maduri-Traczewski M., L'Heureux C., Escalona L., Macone A., Goldmann D. Facilitated detection of antibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas in cystic fibrosis sputum using homogenized specimens and antibiotic-containing media. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 Nov;5(4):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKevitt A. I., Woods D. E. Characterization of Pseudomonas cepacia isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):291–293. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.291-293.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tablan O. C., Carson L. A., Cusick L. B., Bland L. A., Martone W. J., Jarvis W. R. Laboratory proficiency test results on use of selective media for isolating Pseudomonas cepacia from simulated sputum specimens of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):485–487. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.485-487.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tablan O. C., Chorba T. L., Schidlow D. V., White J. W., Hardy K. A., Gilligan P. H., Morgan W. M., Carson L. A., Martone W. J., Jason J. M. Pseudomonas cepacia colonization in patients with cystic fibrosis: risk factors and clinical outcome. J Pediatr. 1985 Sep;107(3):382–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80511-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Klinger J. D., Stern R. C. Pseudomonas cepacia colonization among patients with cystic fibrosis. A new opportunist. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 May;131(5):791–796. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.5.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K., Roberts M. C., Owens L., Fife M., Smith A. L. Selective media for the quantitation of bacteria in cystic fibrosis sputum. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Apr;17(2):113–119. doi: 10.1099/00222615-17-2-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Thompson S. T. Selective medium for Pseudomonas cepacia containing 9-chloro-9-(4-diethylaminophenyl)-10-phenylacridan and polymyxin B sulfate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):743–746. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.743-746.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


