Abstract
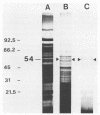
A Western blot (immunoblot) assay is presented for the diagnosis of nocardiosis with a specific immunodominant 54-kilodalton (kDa) antigen purified from a culture filtrate of Nocardia asteroides by immunoaffinity chromatography. The chromatography column was prepared with immunoglobulin G obtained from sera from patients with lepromatous leprosy. Unbound solutes consisted of specific, partially purified N. asteroides antigens, primarily a 54-kDa band, accompanied by two others of 31 and 62 kDa. The Western blot technique was applied to detecting the immunologic response to nocardiae. Immunodetection was performed according to the biotin-avidin system, which greatly improved the detection of antibodies even in immunosuppressed hosts. Each of 16 serum samples from immunosuppressed or immunocompetent patients infected with N. asteroides reacted with the 54-kDa band, and two reacted with the 31- and 62-kDa bands. Each of the serum specimens obtained from patients with mycetoma caused by Nocardia brasiliensis or Rhodococcus rhodochrous reacted with the 54-kDa band. There was no reaction to either the 54- or the 31-kDa antigen with all serum samples obtained from patients with tuberculosis, except one, with all serum samples obtained from patients with leprosy, or with all sera obtained from healthy controls. The 54-kDa protein is a candidate to be used as a probe to study the humoral immunologic response to nocardiae.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair J. C., Beck A. C., Apfelbaum R. I., Baringer J. R. Nocardial cerebral abscess in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1987 May;44(5):548–550. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520170074026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angeles A. M., Sugar A. M. Identification of a common immunodominant protein in culture filtrates of three Nocardia species and use in etiologic diagnosis of mycetoma. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2278–2280. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2278-2280.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angeles A. M., Sugar A. M. Rapid diagnosis of nocardiosis with an enzyme immunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1987 Feb;155(2):292–296. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.2.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baily G. G., Neill P., Robertson V. J. Nocardiosis: a neglected chronic lung disease in Africa? Thorax. 1988 Nov;43(11):905–910. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.11.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Burnside J., Edwards B., Causey W. Nocardial infections in the United States, 1972-1974. J Infect Dis. 1976 Sep;134(3):286–289. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.3.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumer S. O., Kaufman L. Microimmunodiffusion test for nocardiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):308–312. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.308-312.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. H. The double dialysis method of producing farmer's lung antigens. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Apr;79(4):683–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtz H. A., Lavery D. P., Kapila R. Actinomycetales infection in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Feb;102(2):203–205. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-2-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys D. W., Crowder J. G., White A. Serological reactions to Nocardia antigens. Am J Med Sci. 1975 May-Jun;269(3):323–326. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197505000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra S. K., Gordon R. E., Barnett D. A. Identification of nocardiae and streptomycetes of medical importance. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):728–736. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.728-736.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajki K., Brehmer W., Hammer H. J., Fischer W., Daus H., Mauch H. Analysis of the soluble cytoplasmic components of Mycobacteria and Nocardia by crossed immunoelectrofocusing. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1982 Mar;251(3):389–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severo L. C., Petrillo V. F., Coutinho L. M. Actinomycetoma caused by Rhodococcus spp. Mycopathologia. 1987 Jun;98(3):129–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00437647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainhouse J. Z., Pier A. C., Stevens D. A. Complement fixation antibody test for human nocardiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Nov;8(5):516–519. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.5.516-519.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson G. L., Stinson E. B., Egger M. J., Remington J. S. Nocardial infections in the immunocompromised host: A detailed study in a defined population. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):492–507. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugar A. M., Schoolnik G. K., Stevens D. A. Antibody response in human nocardiosis: identification of two immunodominant culture-filtrate antigens derived from Nocardia asteroides. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):895–901. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Zaatari F. A., Reiss E., Yakrus M. A., Bragg S. L., Kaufman L. Monoclonal antibodies against isoelectrically focused Nocardia asteroides proteins characterized by the enzyme-linked immunoelectro-transfer blot method. Diagn Immunol. 1986;4(2):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]