Abstract
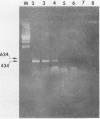
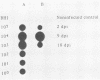
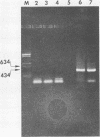
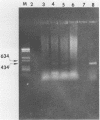
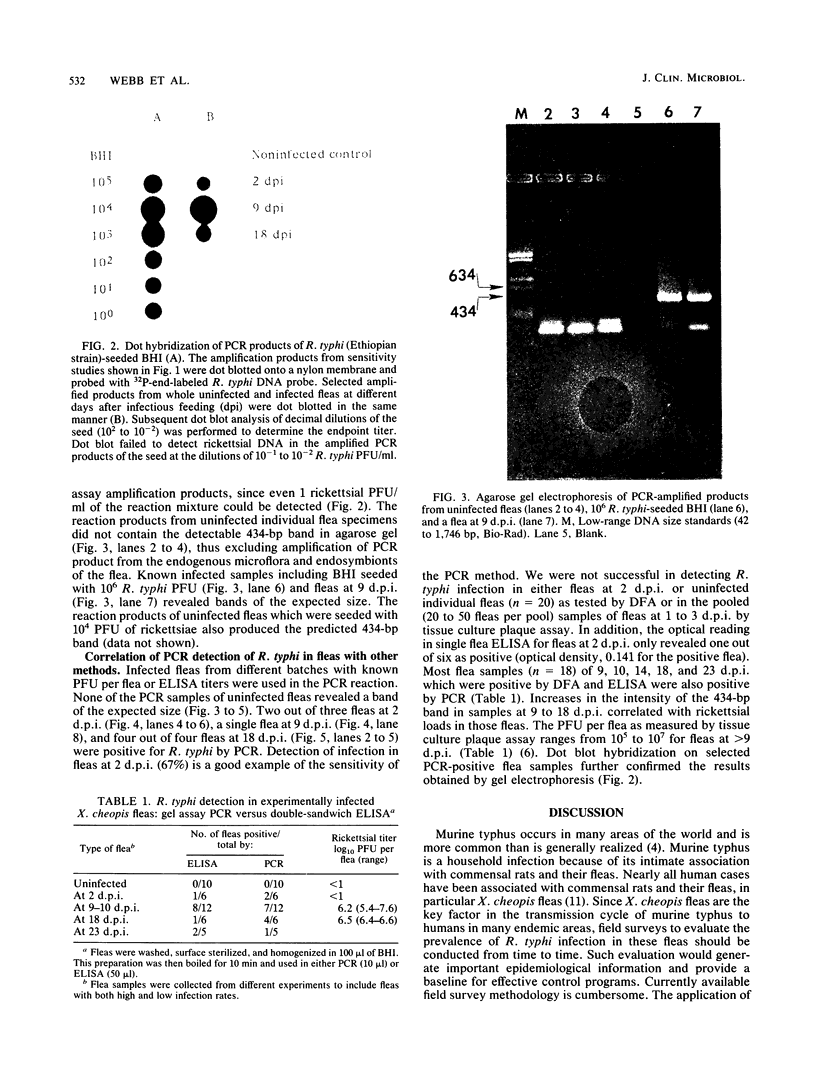
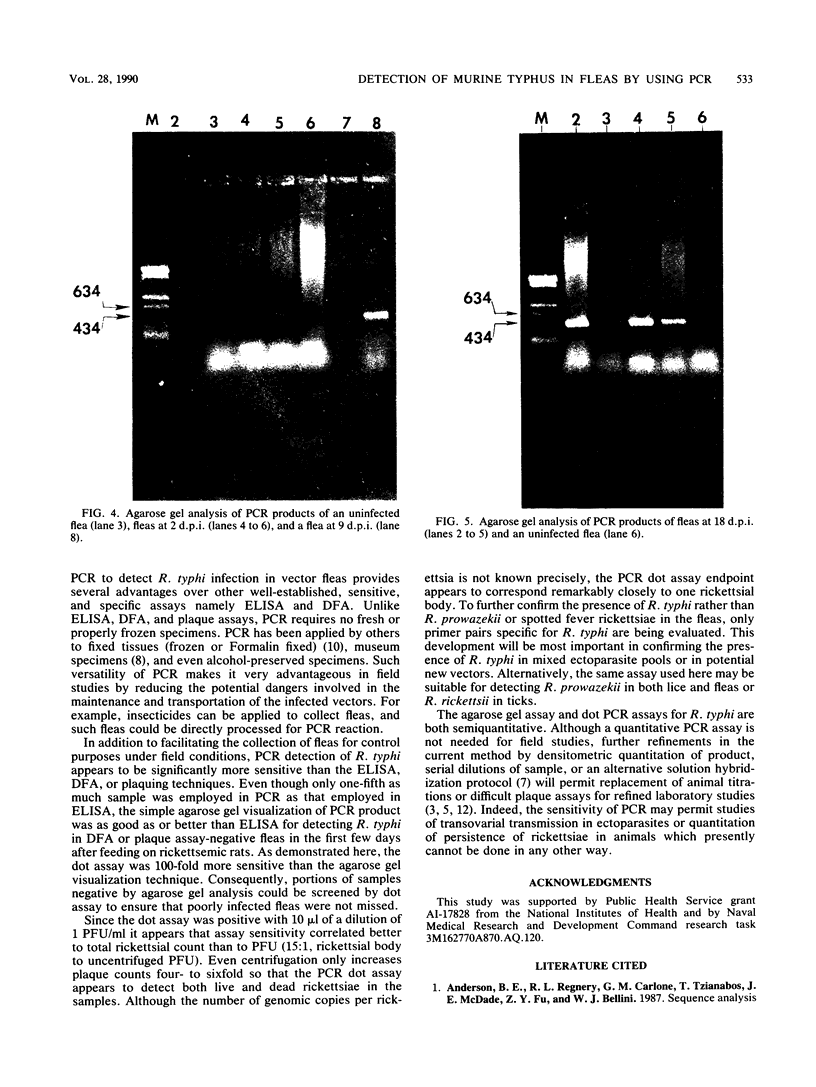
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of DNA was used to detect the etiologic agent of murine typhus, Rickettsia typhi, in experimentally infected adult fleas. A primer pair derived from the 17-kilodalton antigen sequence of typhus and spotted fever group rickettsiae was used to amplify a 434-base-pair (bp) fragment of the genome of the murine typhus rickettsiae. The amplified 17-kilodalton protein antigen-specific sequence was detected in ethidium bromide-stained agarose gels in individual fleas as early as 2 days after exposure to rickettsemic rats (two of six tested). The 434-bp sequence was not detected in uninfected control fleas. A dot hybridization assay used to detect the 434-bp fragment was also specific and about 100-fold more sensitive than the agarose gel PCR assay. Since the PCR assay employed a boiled extract of triturated fleas, both PCR and an antigen capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) could be performed on the same individual flea homogenate. The ELISA identified 12 infected fleas out of 29 randomly selected fleas, compared with 14 specimens which were positive by PCR. The PCR assay detected rickettsiae in samples in which no viable rickettsiae were detected by plaque assay. Like the ELISA, the PCR assay sensitivity was due in part to its suitability for detecting small numbers of both live and dead R. typhi in fleas.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. E., Tzianabos T. Comparative sequence analysis of a genus-common rickettsial antigen gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5199–5201. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5199-5201.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arango-Jaramillo S., Farhang-Azad A., Wisseman C. L., Jr Experimental infection with Rickettsia mooseri and antibody response of adult and newborn laboratory rats. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Sep;33(5):1017–1025. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. F. Epidemiology of murine typhus. Annu Rev Entomol. 1990;35:553–569. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.35.010190.003005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson M. E., Azad A. F., Dasch G. A., Webb L., Olson J. G. Detection of murine typhus infected fleas with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 May;40(5):521–528. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.40.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farhang Azad A., Traub R. Transmission of murine typhus rickettsiae by Xenopsylla cheopis, with notes on experimental infection and effects of temperature. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 May;34(3):555–563. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G. H., Huang D. P., Manak M. M. A sensitive nonisotopic hybridization assay for HIV-1 DNA. Anal Biochem. 1989 Feb 15;177(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Higuchi R. G., Wilson A. C. Ancient DNA and the polymerase chain reaction. The emerging field of molecular archaeology. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9709–9712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata D. K., Arnheim N., Martin W. J. Detection of human papilloma virus in paraffin-embedded tissue using the polymerase chain reaction. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):225–230. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub R., Wisseman C. L. The ecology of murine typhus-a critical review. Trop Dis Bull. 1978 Apr;75(4):237–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. The biology of rickettsiae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:345–370. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]