Abstract
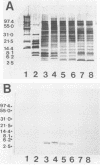
A monoclonal antibody (MAb 4E8C12) specific for Escherichia coli O157:H7 and O26:H11 was produced by immunizing BALB/c mice with a rough strain of E. coli O157:H7. The antibody reacted strongly by a direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with each of 36 strains of E. coli O157:H7. No cross-reactivity was observed with strains of Salmonella spp., Yersinia enterocolitica, Shigella dysenteriae, Proteus spp., Escherichia hermanii, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Campylobacter jejuni, Serratia marcescens, Citrobacter spp., Enterobacter cloacae, Hafnia alvei, Aeromonas hydrophila, and all except five strains of E. coli other than serotype O157:H7 (including strains of serotype O157 but not H7). The E. coli strains (all of serotype O26:H11) that reacted with the antibody were enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) that were isolated from patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome or hemorrhagic colitis and produced verotoxin similar to that of E. coli O157:H7. MAb 4E8C12 belongs to the subclass immunoglobulin G2a and has a kappa light chain. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of outer membrane proteins of E. coli of different serotypes followed by Western immunoblot analysis revealed that MAb 4E8C12 reacted specifically with two proteins of EHEC strains of serotypes O157:H7 and O26:H11 with apparent molecular weights of 5,000 to 6,000. These proteins appeared to be markers specific for EHEC strains of serotypes O157:H7 and O26:H11. This MAb, because of its specificity, may be a useful reagent of an immunoassay for the rapid detection of these types of EHEC isolates in clinical and food specimens.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bopp C. A., Greene K. D., Downes F. P., Sowers E. G., Wells J. G., Wachsmuth I. K. Unusual verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli associated with hemorrhagic colitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1486–1489. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1486-1489.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borczyk A. A., Karmali M. A., Lior H., Duncan L. M. Bovine reservoir for verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lancet. 1987 Jan 10;1(8524):98–98. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91928-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Schoeni J. L. Isolation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from retail fresh meats and poultry. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2394–2396. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2394-2396.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Nikaido H. Outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria. XIX. Isolation from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and use in reconstitution and definition of the permeability barrier. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):381–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.381-390.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Steele B. T., Petric M., Lim C. Sporadic cases of haemolytic-uraemic syndrome associated with faecal cytotoxin and cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in stools. Lancet. 1983 Mar 19;1(8325):619–620. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Xu J. G., Kaper J. B., Lior H., Prado V., Tall B., Nataro J., Karch H., Wachsmuth K. A DNA probe to identify enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli of O157:H7 and other serotypes that cause hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):175–182. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padhye V. V., Zhao T., Doyle M. P. Production and characterisation of monoclonal antibodies to Verotoxins 1 and 2 from Escherichia coli of serotype O 157:H7. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Nov;30(3):219–226. doi: 10.1099/00222615-30-3-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. B., MacLean L., Griffith D. W. Structure of the O-chain polysaccharide of the phenol-phase soluble lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli 0:157:H7. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;64(1):21–28. doi: 10.1139/o86-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard D. R., Johnson W. M., Lior H., Tyler S. D., Rozee K. R. Rapid and specific detection of verotoxin genes in Escherichia coli by the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):540–545. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.540-545.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samadpour M., Liston J., Ongerth J. E., Tarr P. I. Evaluation of DNA probes for detection of Shiga-like-toxin-producing Escherichia coli in food and calf fecal samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1212–1215. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1212-1215.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd E. C., Szabo R. A., Peterkin P., Sharpe A. N., Parrington L., Bundle D., Gidney M. A., Perry M. B. Rapid hydrophobic grid membrane filter-enzyme-labeled antibody procedure for identification and enumeration of Escherichia coli O157 in foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2536–2540. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2536-2540.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Sokolow R., Morris G. K. Laboratory investigation of hemorrhagic colitis outbreaks associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):512–520. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.512-520.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]