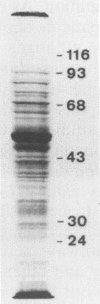
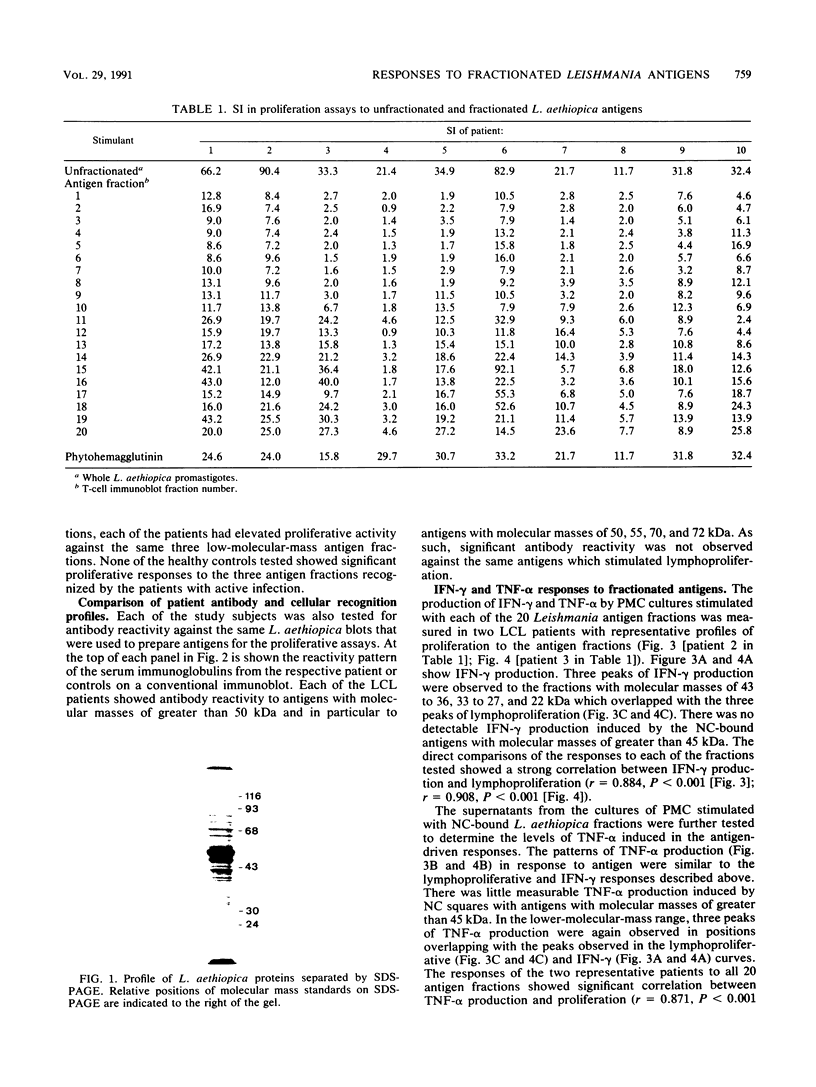
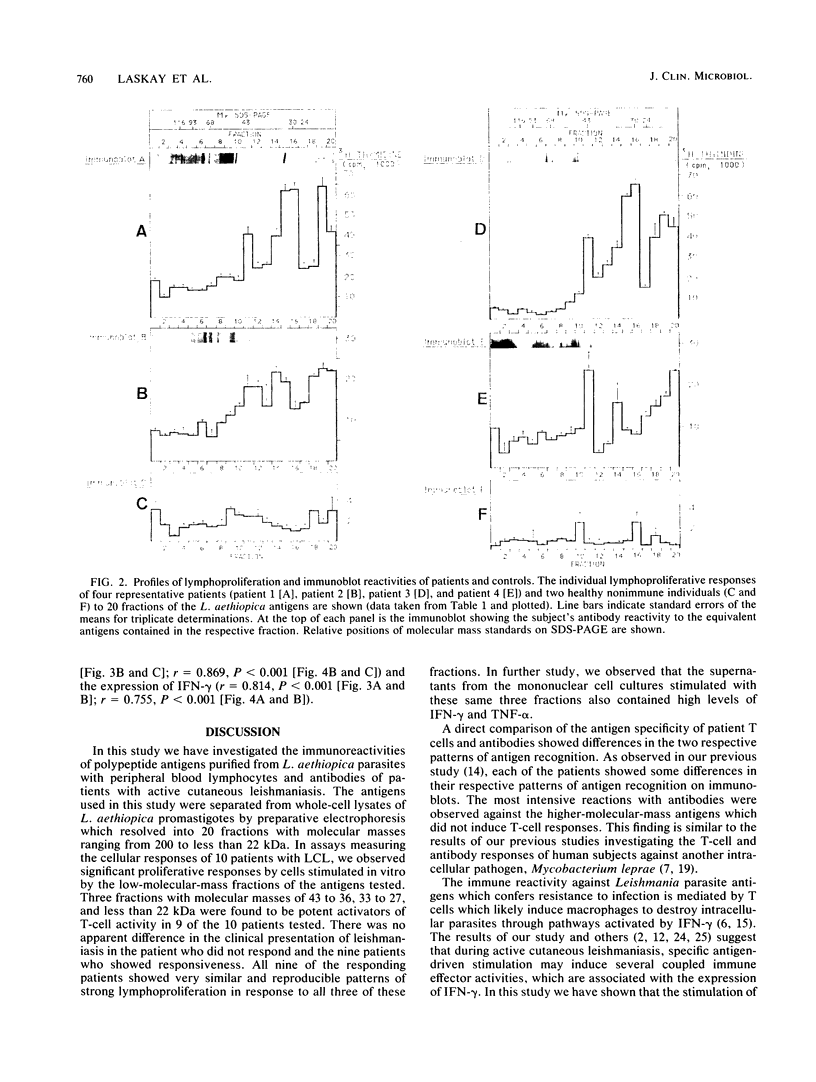
Abstract
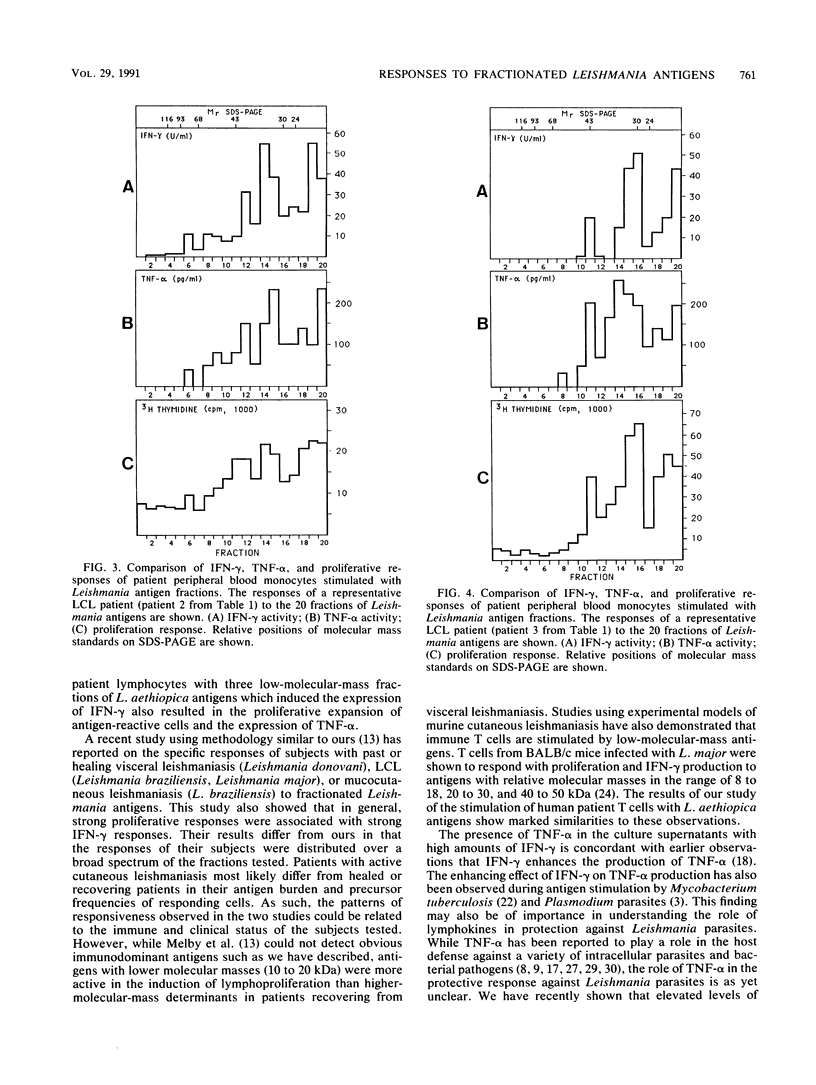
Fractionated antigen preparations of Leishmania aethiopica parasites were used to stimulate the peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with active cutaneous leishmaniasis. In assays measuring lymphocyte proliferation, 9 of 10 patients with similar clinical presentations of infection responded in a similar pattern to the fractionated antigens. Marked proliferation was observed in response to antigen fractions with molecular masses of 43 to 36, 33 to 27, and less than 22 kDa. The induction of relatively high levels of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) was also observed in responses to these same three antigen fractions. In contrast, the proliferative, IFN-gamma, and TNF-alpha responses of patient lymphocytes to antigens with a molecular mass greater than 60 kDa were uniformly low. The results of this study suggest that the antigens of Leishmania parasites, which are recognized by T cells in patients with active cutaneous leishmaniasis, may be partitioned in the lower-molecular-mass antigenic determinants associated with whole-parasite preparations. The observed association between antigen-induced proliferation and IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha production may be indicative of potential disease-limiting immune effector activities which have developed during infection.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akuffo H. O., Fehniger T. E., Britton S. Differential recognition of Leishmania aethiopica antigens by lymphocytes from patients with local and diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis. Evidence for antigen-induced immune suppression. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2461–2466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akuffo H., Schurr E., Andersson G., Yamaneberhan T., Britton S. Responsiveness in diffuse versus local cutaneous leishmaniasis is due to parasite differences. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Dec;26(6):717–721. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. A., Taverne J., Playfair J. H. Malarial parasites induce TNF production by macrophages. Immunology. 1988 Jun;64(2):227–231. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan C., Moll H., Solbach W., Röllinghoff M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha in combination with interferon-gamma, but not with interleukin 4 activates murine macrophages for elimination of Leishmania major amastigotes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):1131–1135. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P., Chiao J. W. Cellular immunity of mice to Leishmania donovani in vitro: lymphokine-mediated killing of intracellular parasites in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7083–7087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Converse P. J., Ottenhoff T. H., Gebre N., Ehrenberg J. P., Kiessling R. Cellular, humoral, and gamma interferon responses to Mycobacterium leprae and BCG antigens in healthy individuals exposed to leprosy. Scand J Immunol. 1988 May;27(5):515–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Titto E. H., Catterall J. R., Remington J. S. Activity of recombinant tumor necrosis factor on Toxoplasma gondii and Trypanosoma cruzi. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1342–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza I., Männel D., Ruppel A., Falk W., Krammer P. H. Interferon gamma and lymphotoxin or tumor necrosis factor act synergistically to induce macrophage killing of tumor cells and schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):589–594. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G. Immunological regulation and control of experimental leishmaniasis. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1986;28:79–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., O'Hehir R. E., Young D. B. The use of nitrocellulose immunoblots for the analysis of antigen recognition by T lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1988 May 25;110(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y. Regulation of cell-mediated immunity in cutaneous leishmaniasis. Immunol Lett. 1987 Dec;16(3-4):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(87)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melby P. C., Neva F. A., Sacks D. L. Profile of human T cell response to leishmanial antigens. Analysis by immunoblotting. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jun;83(6):1868–1875. doi: 10.1172/JCI114093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengistu G., Akuffo H. O., Yemane-Berhan T., Britton S., Fehniger T. E. Serum antibody specificities to Leishmania aethiopica antigens in patients with localized and diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis. Parasite Immunol. 1990 Sep;12(5):495–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1990.tb00984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Rothermel C. D. Killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani by lymphokine-stimulated human mononuclear phagocytes. Evidence that interferon-gamma is the activating lymphokine. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1172/JCI111107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Fortier A. H., Meltzer M. S., Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Macrophage activation to kill Leishmania major: activation of macrophages for intracellular destruction of amastigotes can be induced by both recombinant interferon-gamma and non-interferon lymphokines. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3505–3511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kato K. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is essential to host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2563–2569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2563-2569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedwin G. E., Svedersky L. P., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. Effect of interleukin 2, interferon-gamma, and mitogens on the production of tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2492–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhoff T. H., Converse P. J., Gebre N., Wondimu A., Ehrenberg J. P., Kiessling R. T cell responses to fractionated Mycobacterium leprae antigens in leprosy. The lepromatous nonresponder defect can be overcome in vitro by stimulation with fractionated M. leprae components. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Apr;19(4):707–713. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisa P., Gennene M., Söder O., Ottenhoff T., Hansson M., Kiessling R. Serum tumor necrosis factor levels and disease dissemination in leprosy and leishmaniasis. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):988–991. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pujol-Borrell R., Todd I., Doshi M., Bottazzo G. F., Sutton R., Gray D., Adolf G. R., Feldmann M. HLA class II induction in human islet cells by interferon-gamma plus tumour necrosis factor or lymphotoxin. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):304–306. doi: 10.1038/326304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Taverne J., Leveton C., Steele J. The role of gamma-interferon, vitamin D3 metabolites and tumour necrosis factor in the pathogenesis of tuberculosis. Immunology. 1987 Oct;62(2):229–234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurr E., Kidane K., Yemaneberhan T., Wunderlich F. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in Ethiopia: I. Lymphocyte transformation and antibody titre. Trop Med Parasitol. 1986 Dec;37(4):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P., Pearce E., Heath S., Sher A. Identification of T-cell-reactive antigens that protect BALB/c mice against Leishmania major. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1987 Sep-Oct;138(5):771–774. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(87)80036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P., Pearce E., Natovitz P., Sher A. Vaccination against cutaneous leishmaniasis in a murine model. II. Immunologic properties of protective and nonprotective subfractions of soluble promastigote extract. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3118–3125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scuderi P., Sterling K. E., Lam K. S., Finley P. R., Ryan K. J., Ray C. G., Petersen E., Slymen D. J., Salmon S. E. Raised serum levels of tumour necrosis factor in parasitic infections. Lancet. 1986 Dec 13;2(8520):1364–1365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer-Avni Y., Wallach D., Sarov I. Inhibition of Chlamydia trachomatis growth by recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2503–2506. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2503-2506.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Kobayashi M., Rosen M., Loudon R., Murphy M., Perussia B. Tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin induce differentiation of human myeloid cell lines in synergy with immune interferon. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1206–1225. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone S. E., Rich E. A., Wallis R. S., Ellner J. J. Expression of tumor necrosis factor in vitro by human mononuclear phagocytes stimulated with whole Mycobacterium bovis BCG and mycobacterial antigens. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3313–3315. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3313-3315.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth J. J., Kierszenbaum F. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor enhances macrophage destruction of Trypanosoma cruzi in the presence of bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):286–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]