Abstract
A recent outbreak of erythroderma in young children in an Albanian hospital was investigated. The etiology was not established, but Staphylococcus haemolyticus was frequently isolated from the affected children and from staff working in the same unit. Possible relationships among the isolates were investigated by using classical techniques (biotype, antimicrobial susceptibility, and extrachromosomal DNA pattern) and by restriction endonuclease analysis (REA) of total DNA. Control isolates of proven pathogenicity from hospitalized patients in Lyon, France were subjected to the same procedures. Distinct REA patterns were obtained after digestion with two enzymes in 7 of 10 isolates from five affected children. Six distinct patterns were observed in nine isolates from six staff members; two REA patterns from patient isolates and two from staff members were identical, and these were distinguishable by the other markers examined. Only two different REA patterns were found in the pathogenic control isolates despite the use of a third additional enzyme. Again, the isolates with the same REA patterns could be distinguished by their plasmid profile or antimicrobial resistance profile. REA of total DNA used in combination with other markers indicated that the Albanian isolates differed considerably, whereas the French pathogenic isolates showed little variability.
Full text
PDF
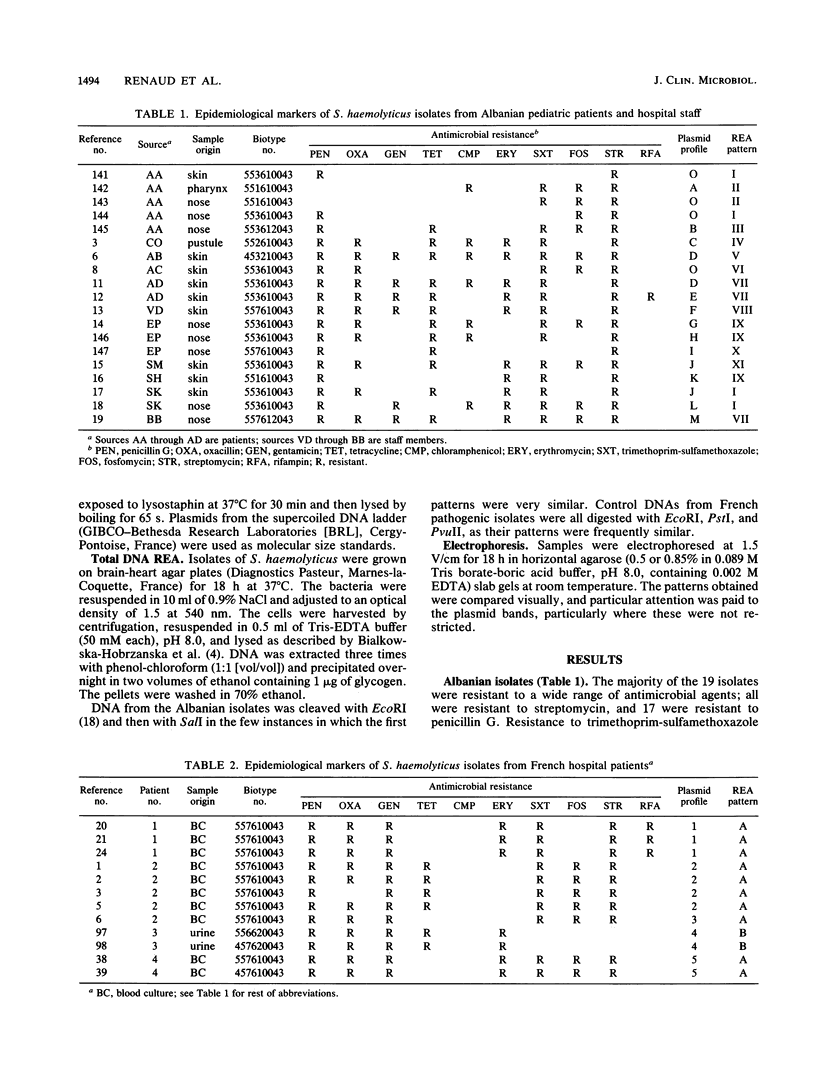
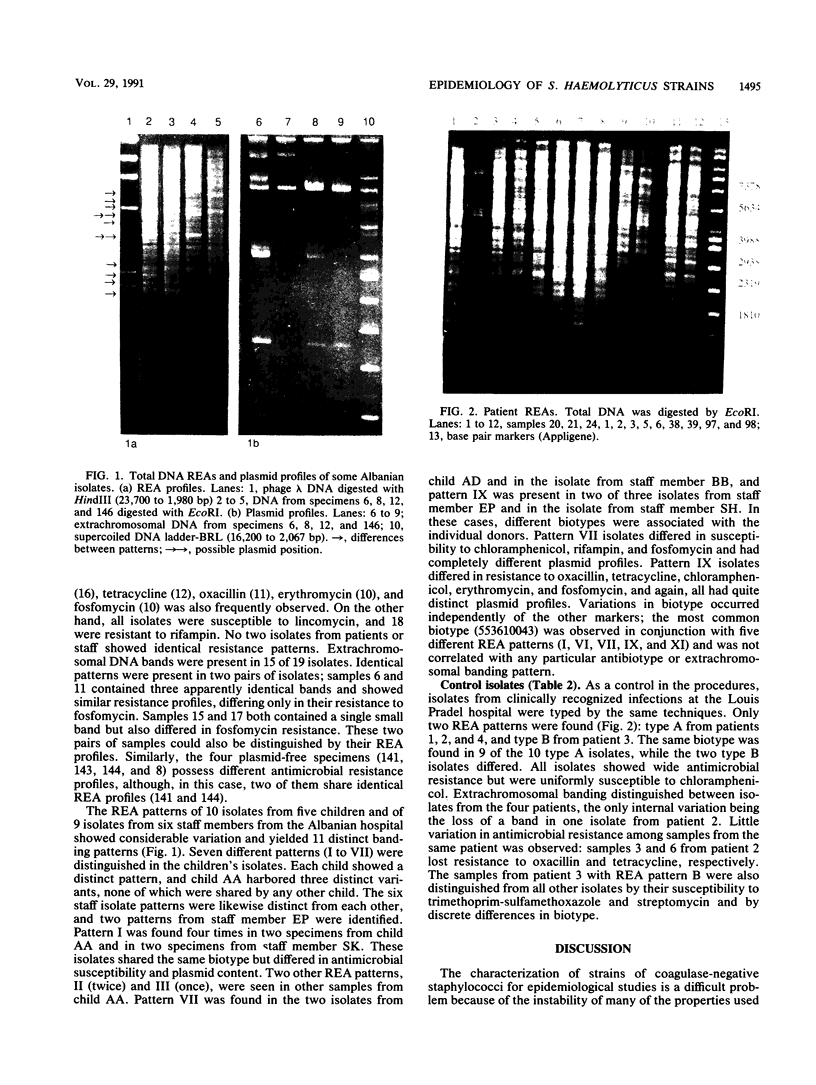


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L. Molecular epidemiology of multiresistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Apr;21 (Suppl 100):133–138. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_c.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldellon C., Mégraud F. Characterization of Micrococcaceae strains isolated from the human urogenital tract by the conventional scheme and a micromethod. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):474–477. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.474-477.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialkowska-Hobrzanska H., Jaskot D., Hammerberg O. Evaluation of restriction endonuclease fingerprinting of chromosomal DNA and plasmid profile analysis for characterization of multiresistant coagulase-negative staphylococci in bacteremic neonates. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):269–275. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.269-275.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun Y., Bes M., Boeufgras J. M., Monget D., Fleurette J., Auckenthaler R., Devriese L. A., Kocur M., Marples R. R., Piemont Y. International collaborative evaluation of the ATB 32 staph gallery for identification of the Staphylococcus species. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1990 Aug;273(3):319–326. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80435-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne J., Brun Y., el Solh N., Delorme V., Mouren C., Bes M., Fleurette J. Characterization of clinically significant isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis from patients with endocarditis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):613–617. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.613-617.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne J., Poitevin-Later F., Renaud F., Fleurette J. Plasmid profiles and genomic DNA restriction endonuclease patterns of 30 independent Staphylococcus lugdunensis strains. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 15;55(1-2):93–97. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90175-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne J., Renaud F., Bes M., Brun Y., Greenland T. B., Freney J., Fleurette J. Instability of characteristics amongst coagulase-negative staphylococci causing endocarditis. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Jun;32(2):115–122. doi: 10.1099/00222615-32-2-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froggatt J. W., Johnston J. L., Galetto D. W., Archer G. L. Antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial isolates of Staphylococcus haemolyticus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):460–466. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill V. J., Selepak S. T., Williams E. C. Species identification and antibiotic susceptibilities of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1314–1319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1314-1319.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruer L. D., Bartlett R., Ayliffe G. A. Species identification and antibiotic sensitivity of coagulase-negative staphylococci from CAPD peritonitis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Jun;13(6):577–583. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.6.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn B. A., Davis C. E., Jr Staphylococcus haemolyticus urinary tract infection in a male patient. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):1055–1057. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.1055-1057.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwantscheff A., Kühnen E., Brandis H. Species distribution of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from clinical sources. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Aug;260(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M., Steele C. Culture of the surfaces of urinary catheters to sample urethral flora and study the effect of antimicrobial therapy. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):902–908. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.902-908.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud F., Freney J., Etienne J., Bes M., Brun Y., Barsotti O., Andre S., Fleurette J. Restriction endonuclease analysis of Staphylococcus epidermidis DNA may be a useful epidemiological marker. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1729–1734. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1729-1734.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., Kaplan R. L., Landau W., Trenholme G. M. Speciation and antibiotic susceptibility patterns of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;1(4):228–232. doi: 10.1007/BF02019713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]