Abstract
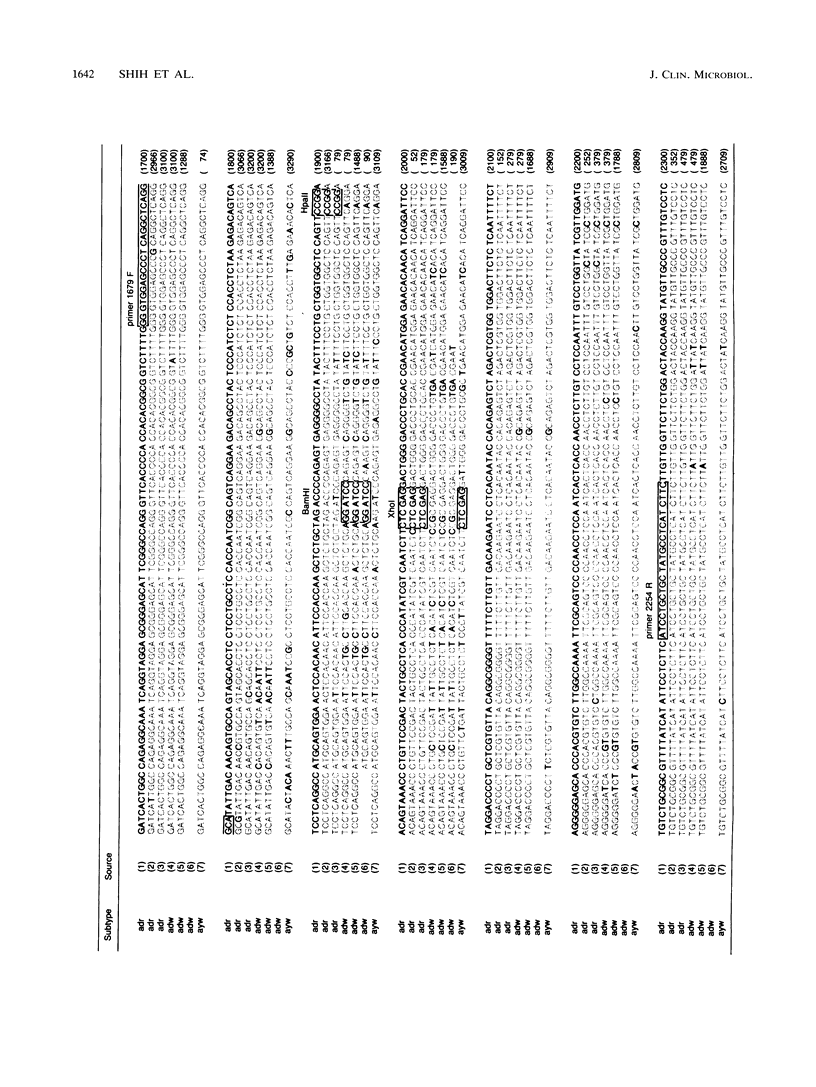
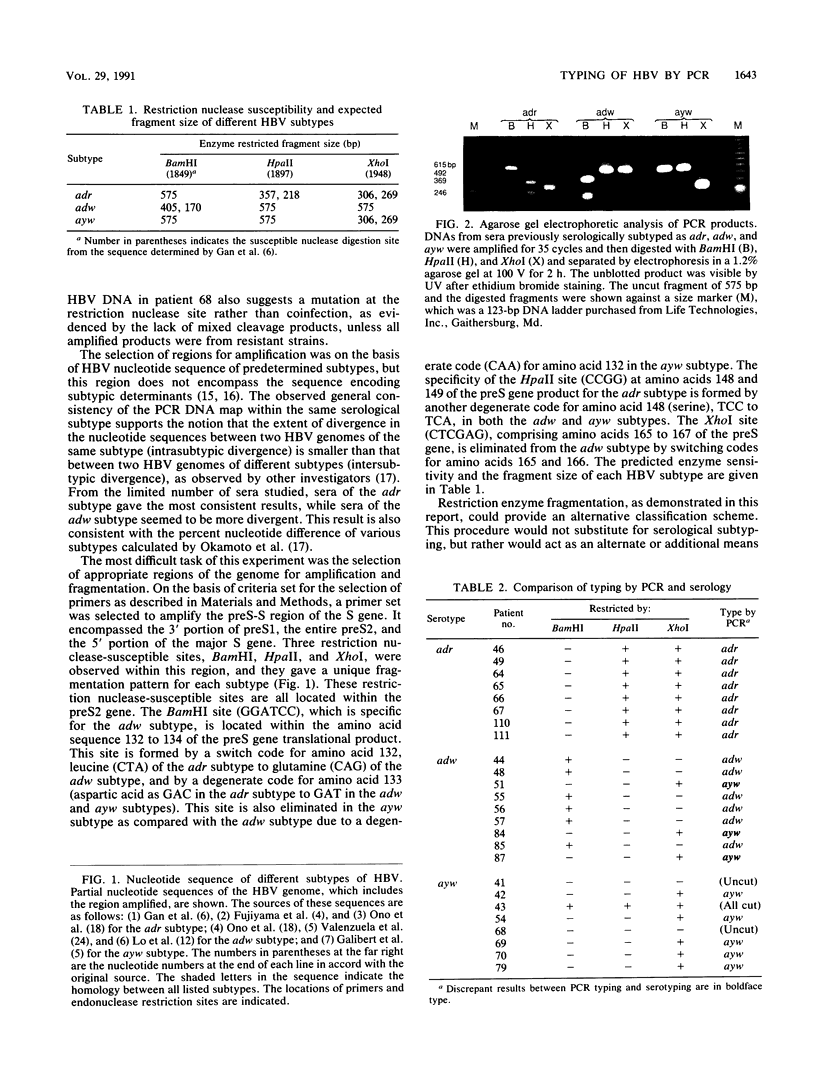
To assess the value of classifying hepatitis B virus (HBV) strains at the genomic level with products from the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), an HBV PCR DNA typing procedure was developed. The design of this method was based on the selective sensitivity of the PCR product to digestion with different restriction endonucleases and on the size of the fragment resulting from a specific nuclease digestion. On the basis of published nucleotide sequences of different HBV subtypes, a set of primers was selected within the preS-S region. One of the primers was 1679F containing 25 nucleotides (5'-GGGTGGAGCCCTCAGGCTCAGGGCA-3'), and the other was 2254R containing 24 nucleotides (5'-GAAGATGAGGCATAGCAGCAGGAT-3'). All of the reactive sera produced the same sized 575-bp identification band. The product was subjected to digestion by a selected panel of restriction endonucleases. By using prototype HBV of known subtype as a model, these restriction nuclease maps of the PCR product were subtype specific. Most adr subtype clinical samples produced predicted PCR DNA restriction nuclease fragmentation in accordance with the nucleotide sequence of the prototype virus. Occasionally, samples of either the adw or the ayw subtype gave discrepant results in which they appeared to be a different subtype or were resistant to the restriction nuclease digestion. This genetic alteration was consistent in the paired specimens from sexual transmission cases. These results show that the described procedures are applicable to HBV strain assessment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bancroft W. H., Mundon F. K., Russell P. K. Detection of additional antigenic determinants of hepatitis B antigen. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):842–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couroucé-Pauty A. M., Plançon A., Soulier J. P. Distribution of HBsAg subtypes in the world. Vox Sang. 1983;44(4):197–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1983.tb01885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama A., Miyanohara A., Nozaki C., Yoneyama T., Ohtomo N., Matsubara K. Cloning and structural analyses of hepatitis B virus DNAs, subtype adr. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4601–4610. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Gerety R. J., Smallwood L. A., Barker L. F. Subtyping of hepatitis B surface antigen and antibody by radioimmunoassay. Gastroenterology. 1977 Feb;72(2):290–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Feinstone S. M., Miller R. H. Rapid and sensitive method for the detection of serum hepatitis B virus DNA using the polymerase chain reaction technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):1930–1933. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.1930-1933.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Miller R. H., Feinstone S. M., Unoura M., Kobayashi K., Hattori N., Purcell R. H. Detection of serum hepatitis B virus DNA in patients with chronic hepatitis using the polymerase chain reaction assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):312–316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koziol D. E., Alter H. J., Kirchner J. P., Holland P. V. The development of HBsAg-positive hepatitis despite the previous existence of antibody to HBsAg. J Immunol. 1976 Dec;117(6):2260–2262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouvier G. L. The heterogeneity of Australia antigen. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jun;123(6):671–675. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.6.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. J., Chen M. L., Chien M. L., Lee Y. H. Characteristics of pre-S2 region of hepatitis B virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):382–388. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Takezawa Y., Maeda T. Difference of subtypes of hepatitis B surface antigen between asymptomatic carriers and patients with chronic liver diseases. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1980 Nov;132(3):367–368. doi: 10.1620/tjem.132.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Imai M., Kametani M., Nakamura T., Mayumi M. Genomic heterogeneity of hepatitis B virus in a 54-year-old woman who contracted the infection through materno-fetal transmission. Jpn J Exp Med. 1987 Aug;57(4):231–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Imai M., Tsuda F., Tanaka T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Point mutation in the S gene of hepatitis B virus for a d/y or w/r subtypic change in two blood donors carrying a surface antigen of compound subtype adyr or adwr. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3030–3034. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3030-3034.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Omi S., Wang Y., Itoh Y., Tsuda F., Tanaka T., Akahane Y., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. The loss of subtypic determinants in alleles, d/y or w/r, on hepatitis B surface antigen. Mol Immunol. 1989 Feb;26(2):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Tsuda F., Sakugawa H., Sastrosoewignjo R. I., Imai M., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Typing hepatitis B virus by homology in nucleotide sequence: comparison of surface antigen subtypes. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2575–2583. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Onda H., Sasada R., Igarashi K., Sugino Y., Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA; subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1747–1757. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Sattler F., Robinson W. S. Restriction endonuclease cleavage map and location of unique features of the DNA of hepatitis B virus, subtype adw2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4664–4668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiers V., Nakajima E., Kremsdorf D., Mack D., Schellekens H., Driss F., Goudeau A., Wands J., Sninsky J., Tiollais P. Transmission of hepatitis B from hepatitis-B-seronegative subjects. Lancet. 1988 Dec 3;2(8623):1273–1276. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92891-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich P. P., Bhat R. A., Seto B., Mack D., Sninsky J., Vyas G. N. Enzymatic amplification of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum compared with infectivity testing in chimpanzees. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):37–43. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




