Abstract
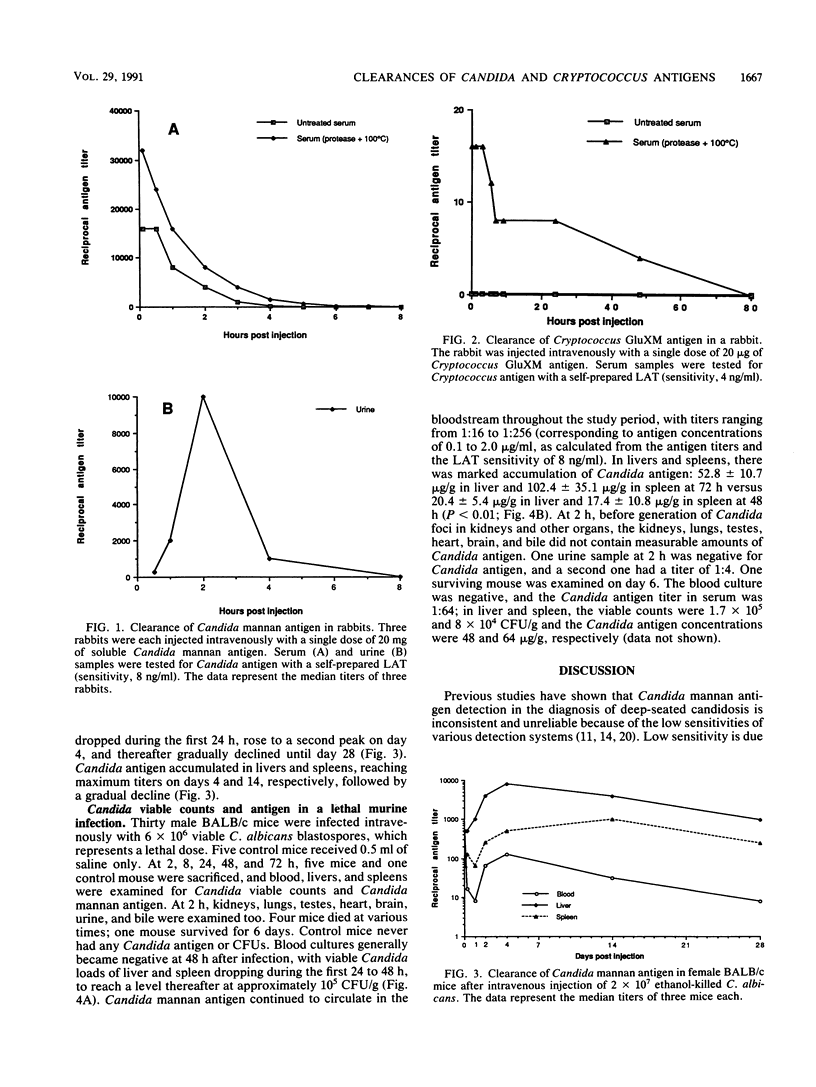
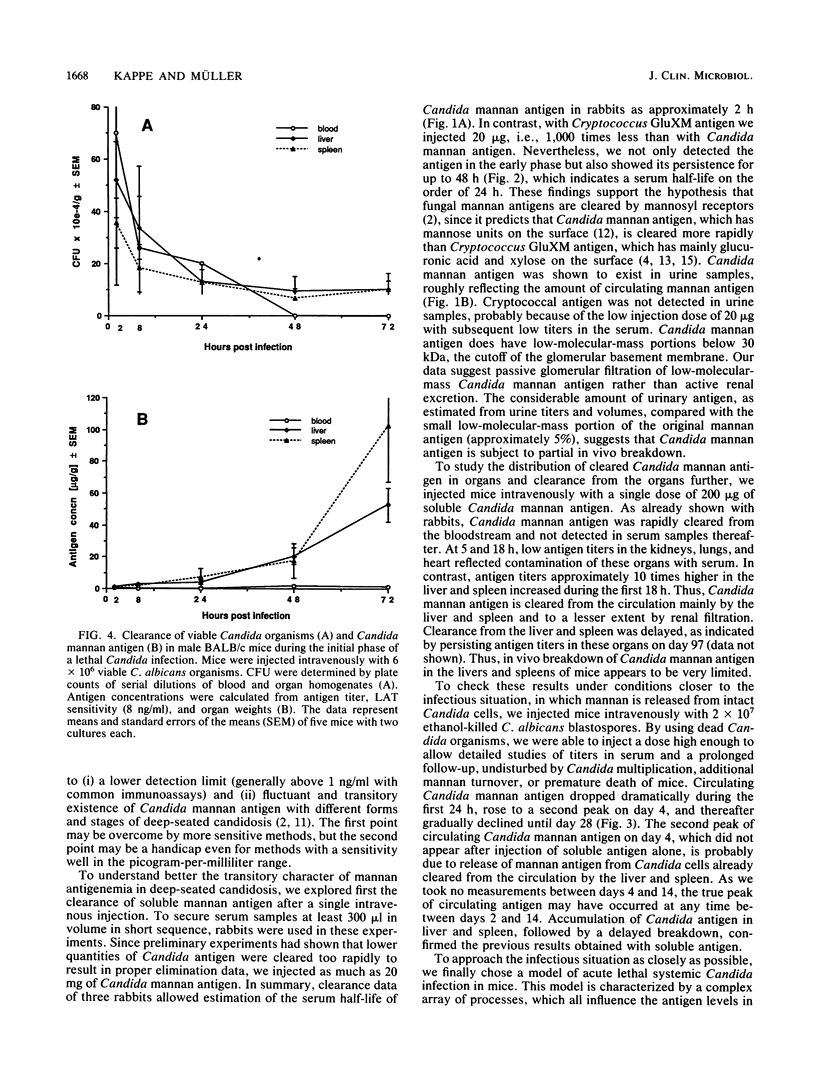
Clearances of mannan antigen from Candida albicans and glucuronoxylomannan antigen from Cryptococcus neoformans were examined in nonimmune rabbits by using self-prepared latex agglutination tests. Injected intravenously, 20 mg of Candida mannan antigen was cleared from the serum with a half-life of approximately 2 h. In contrast, 20 micrograms of Cryptococcus glucuronoxylomannan antigen had a half-life in serum of approximately 24 h. At the latest, 9 h after injection, both antigens were no longer detectable without pretreatment of serum samples with protease and heating to 100 degrees C, thus indicating rapid binding by serum proteins other than immunoglobulins. Candida mannan antigen clearance was also examined in nonimmune mice after intravenous injection of (i) 200 micrograms of Candida mannan antigen, which accumulated in the liver and spleen and persisted for 97 days; (ii) 2 x 10(7) ethanol-killed Candida blastospores, which was accompanied by rapid clearance of mannan from the blood but accumulation of mannan in the liver and spleen and slow clearance from these organs; (iii) 6 x 10(6) viable C. albicans cells (lethal infection), which resulted in a rapid decrease of Candida CFU in the blood, liver, and spleen during the first 8 h, after which blood cultures were negative on day 2 and viable Candida burdens in the liver and spleen persisted at 10(5) CFU/g, whereas Candida mannan antigen continued to circulate in the bloodstream and accumulated in the liver and spleen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardalaye P. C., Nordin J. H. Chemical structure of the galactomannan from the cell wall of Aspergillus niger. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2584–2591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. E., Friedman M. M., Dupont B. Receptor-mediated clearance of Aspergillus galactomannan. J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):1005–1010. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. E. Rapid diagnosis of candidiasis and aspergillosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Mar-Apr;9(2):398–402. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.2.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee A. K., Bennett J. E., Glaudemans C. P. Capsular polysaccharides of Cryptococcus neoformans. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;6(5):619–624. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.5.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burges G., Holley H. P., Virella G. Circulating immune complexes in patients with Candida albicans infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jul;53(1):165–174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosio F. G., Bakaletz A. P. Role of fibronectin on the clearance and tissue uptake of antigen and immune complexes in rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1270–1279. doi: 10.1172/JCI113202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont B., Huber M., Kim S. J., Bennett J. E. Galactomannan antigenemia and antigenuria in aspergillosis: studies in patients and experimentally infected rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):1–11. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Bishburg E., Smith S. M., Kapila R. Cryptococcal infections in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1986 Jul;81(1):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Day L. E., Herman G. A. A human mannose-binding protein is an acute-phase reactant that shares sequence homology with other vertebrate lectins. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1034–1046. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira R. P., Yu B., Niki Y., Armstrong D. Detection of Candida antigenuria in disseminated candidiasis by immunoblotting. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):1075–1078. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.1075-1078.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita S., Matsubara F., Matsuda T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay measurement of fluctuations in antibody titer and antigenemia in cancer patients with and without candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):568–575. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.568-575.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda R., Nishikawa A., Shinoda T., Fukazawa Y. Chemical characterization of capsular polysaccharide from Cryptococcus neoformans serotype A-D. Microbiol Immunol. 1985;29(10):981–991. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1985.tb02962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappe R. Coexistence of free antigens, free antibodies and immune complexes in sera from patients with suspected deep-seated candidosis. Mycoses. 1989 Jan;32(1):24–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1989.tb02165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R. Antigenic structure of Cryptococcus neoformans capsular polysaccharides. Immunol Ser. 1989;47:63–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchinger H., Müller, Takamiya H., Nold B. Immunelektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an Asteroid Bodies in Vaginalmaterial von Candida-Kolpitis-Patientinnen. Mykosen. 1980 Apr;23(4):161–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muro H., Shirasawa H., Maeda M., Nakamura S. Fc receptors of liver sinusoidal endothelium in normal rats and humans. A histologic study with soluble immune complexes. Gastroenterology. 1987 Nov;93(5):1078–1085. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90572-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips P., Dowd A., Jewesson P., Radigan G., Tweeddale M. G., Clarke A., Geere I., Kelly M. Nonvalue of antigen detection immunoassays for diagnosis of candidemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Oct;28(10):2320–2326. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.10.2320-2326.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praaning-van Dalen D. P., de Leeuw A. M., Brouwer A., Knook D. L. Rat liver endothelial cells have a greater capacity than Kupffer cells to endocytose N-acetylglucosamine- and mannose-terminated glycoproteins. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):672–679. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R. T., Horst M. N., Garner R. E., Hudson J., Jenkins P. R., Richardson A. L. Altered hepatic clearance and killing of Candida albicans in the isolated perfused mouse liver model. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2869–2874. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2869-2874.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R. T. The effect of monosaccharides on in situ hepatic trapping of Candida albicans. Mycopathologia. 1988 Nov;104(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00436931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. E., Leaning M. S., Summerfield J. A. Uptake and processing of glycoproteins by rat hepatic mannose receptor. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):E690–E698. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.5.E690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheat L. J., Kohler R. B., Tewari R. P. Diagnosis of disseminated histoplasmosis by detection of Histoplasma capsulatum antigen in serum and urine specimens. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jan 9;314(2):83–88. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198601093140205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


