Abstract
Ixodes dammini ticks from two northwestern Illinois sites were found to be infected with Borrelia burgdorferi at rates of 19 and 32%. B. burgdorferi isolates, one from each site, had protein and antigenic patterns similar to those of the B-31 strain. An indirect immunofluorescence method proved to be more sensitive than dark-field microscopy in detection of these spirochetes. A modified BSK medium containing rifampin was found to be more efficient for spirochete isolation than unsupplemented BSK medium.
Full text
PDF
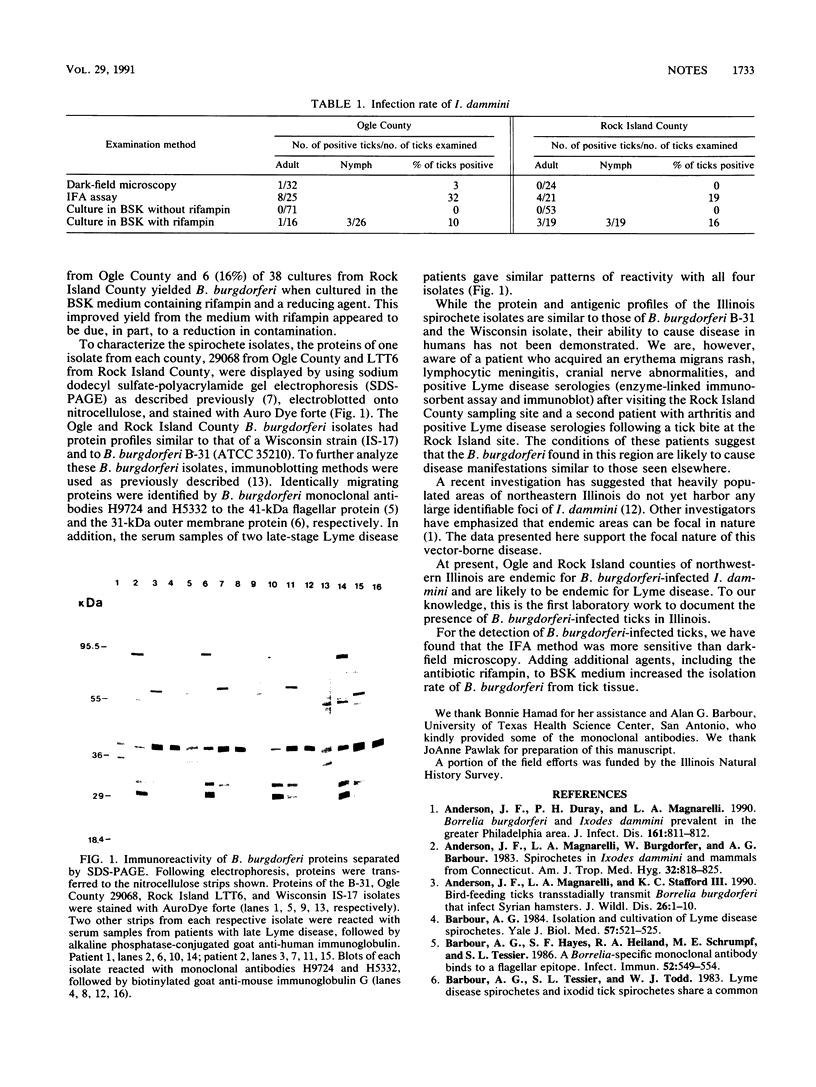

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. F., Duray P. H., Magnarelli L. A. Borrelia burgdorferi and Ixodes dammini prevalent in the greater Philadelphia area. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):811–812. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A., Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G. Spirochetes in Ixodes dammini and mammals from Connecticut. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Jul;32(4):818–824. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A., Stafford K. C., 3rd Bird-feeding ticks transstadially transmit Borrelia burgdorferi that infect Syrian hamsters. J Wildl Dis. 1990 Jan;26(1):1–10. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-26.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Heiland R. A., Schrumpf M. E., Tessier S. L. A Borrelia-specific monoclonal antibody binds to a flagellar epitope. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):549–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.549-554.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett M. L., Hill W. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi strains isolated from Ixodes pacificus ticks in California. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2296–2301. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2296-2301.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouseman J. K., Kitron U., Kirkpatrick C. E., Siegel J., Todd K. S., Jr Status of Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae) in Illinois. J Med Entomol. 1990 Jul;27(4):556–560. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/27.4.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callister S. M., Agger W. A., Schell R. F., Ellingson J. L. Borrelia burgdorferi infection surrounding La Crosse, Wis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2632–2636. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2632-2636.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callister S. M., Case K. L., Agger W. A., Schell R. F., Johnson R. C., Ellingson J. L. Effects of bovine serum albumin on the ability of Barbour-Stoenner-Kelly medium to detect Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):363–365. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.363-365.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callister S. M., Nelson J. A., Schell R. F., Jobe D. A., Bautz R., Agger W. A., Coggins J. Survey for Ixodes spp. and Borrelia burgdorferi in southeastern Wisconsin and northeastern Illinois. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):403–406. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.403-406.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Bankowski M. J., Newton B. J., Benson C. A., Kaplan R., Landau W., Trenholme G. M., Peeples M. E. Detection of antibodies in late Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):1034–1035. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Bartenhagen N. H., Spieler P. N., Newman J. H., Rahn D. W., Hutchinson G. J., Green J., Snydman D. R., Taylor E. The clinical spectrum and treatment of Lyme disease. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):453–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E. Cases of Lyme disease in the United States: locations correlated with distribution of Ixodes dammini. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Nov;91(5):730–733. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



