Abstract
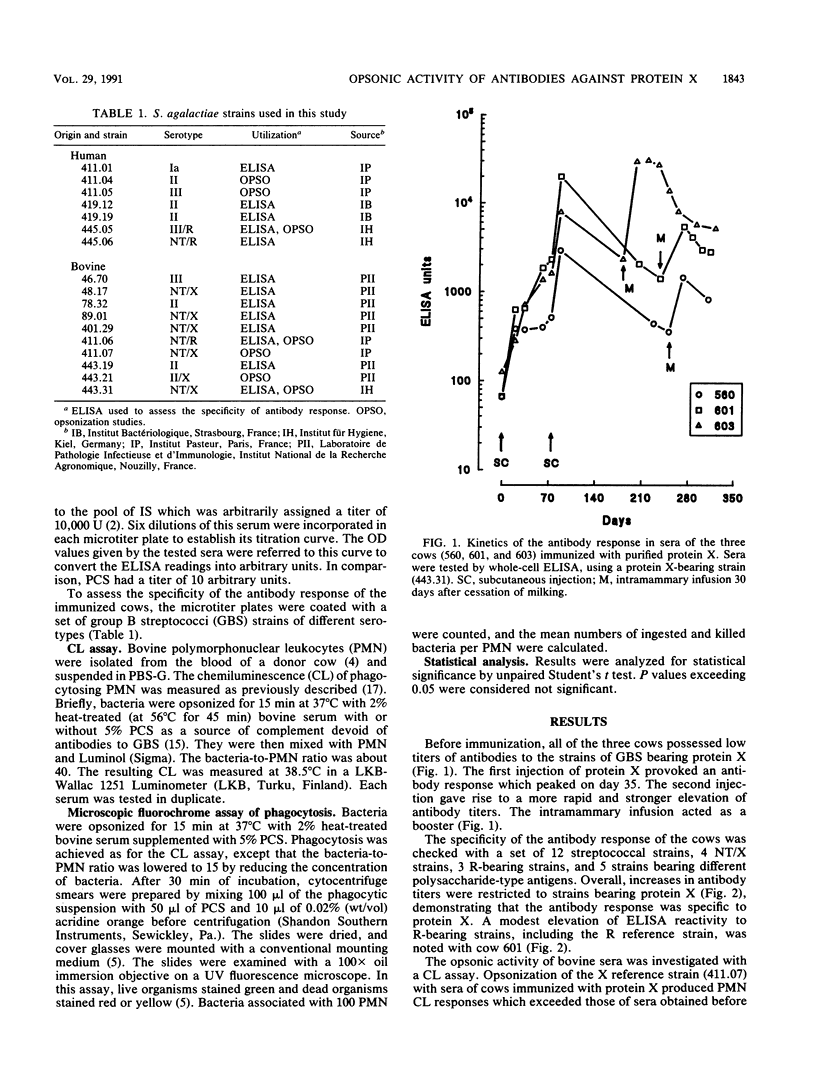
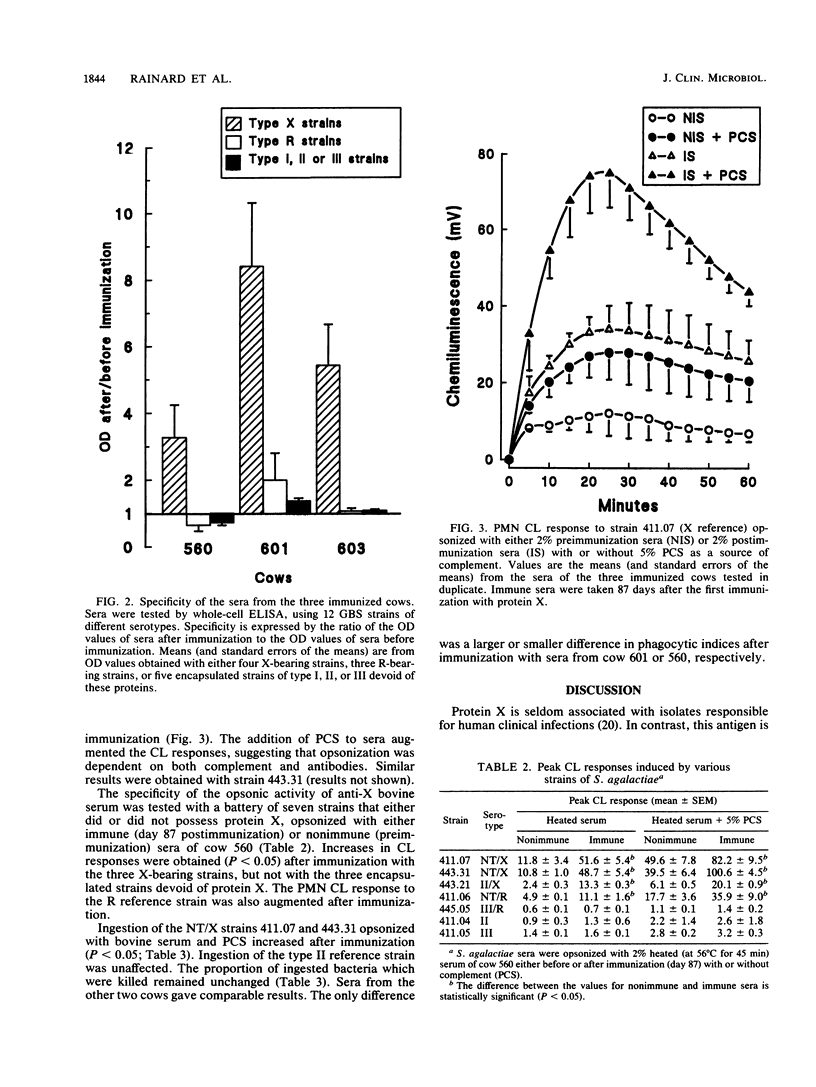
Protein X of Streptococcus agalactiae is a surface protein frequently associated with strains isolated from cases of mastitis of dairy cows. By immunizing cows with purified protein X, we obtained an antibody response which was restricted to X-bearing strains of S. agalactiae in a whole-cell enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. This response resulted in an increase in the opsonic activity of serum for strains bearing protein X, as assessed through the augmentation of the chemiluminescence response of phagocytosing polymorphonuclear cells and through an increased ingestion of bacteria, although the proportion of ingested bacteria which were killed (about 60%) remained unchanged. Protein X behaved as a target of opsonins and, as such, could be a protective antigen worth incorporating in a vaccine against S. agalactiae mastitis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. J., Webb B. J., Kasper D. L., Edwards M. S. The role of complement and antibody in opsonophagocytosis of type II group B streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):47–54. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL S. G., NORCROSS N. L. ANTIBODIES AGAINST STREPTOCOCCUS AGALACTIAE IN THE COLOSTRUM OF FIRST-CALF HEIFERS. Am J Vet Res. 1964 Jul;25:993–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn W., Hansmann C., Federlin K. An improved fluorochrome microassay for the detection of living and non-living intracellular bacteria in human neutrophils. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Nov 7;83(2):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen N. E. Distribution of serotypes of group-B streptococci in herds and cows within an area of Denmark. Acta Vet Scand. 1980;21(3):354–366. doi: 10.1186/BF03546867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen N. E. Production and evaluation of antisera for serological type determination of group-B streptococci by double diffusion in agarose gel. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Apr;87B(2):77–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautrou Y., Rainard P., Poutrel B., Zygmunt M. S., Vénien A., Dufrenoy J. Purification of the protein X of Streptococcus agalactiae with a monoclonal antibody. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 May 15;64(2-3):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90584-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. R., Wright C. L. Streptococcus agalactiae serotypes in the south west of Scotland. Vet Rec. 1984 Oct 27;115(17):439–439. doi: 10.1136/vr.115.17.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTISON I. H., MATTHEWS P. R., HOWELL D. G. The type classification of group-B streptococci, with special reference to bovine strains apparently lacking in type polysaccharide. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jan-Apr;69(1-2):51–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Kim Y. K., Ferrieri P. Effect of differences in antibody and complement requirements on phagocytic uptake and intracellular killing of "c" protein-positive and -negative strains of type II group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1243–1251. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1243-1251.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainard P. Assessment of phagocytosis of plastic adherent group B streptococci by ELISA quenching. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Oct 4;113(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90389-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainard P., Lautrou Y., Poutrel B. Ingestion and killing of Streptococcus agalactiae by bovine granulocytes in the presence of natural opsonins. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Sep;18(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutra L., Rainard P., Poutrel B. Phagocytosis of mastitis isolates of Staphylococcus aureus and expression of type 5 capsular polysaccharide are influenced by growth in the presence of milk. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Oct;28(10):2253–2258. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.10.2253-2258.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner B., Wagner M., Kubin V., Rýc M. Immunoelectron microscopic study of the location of group-specific and protein type-specific antigens of group B streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 May;118(1):95–105. doi: 10.1099/00221287-118-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W. Comparison of streptococcal R antigens. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):669–670. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.669-670.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W. Group B streptococcal infection in humans. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:41–57. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


