Abstract
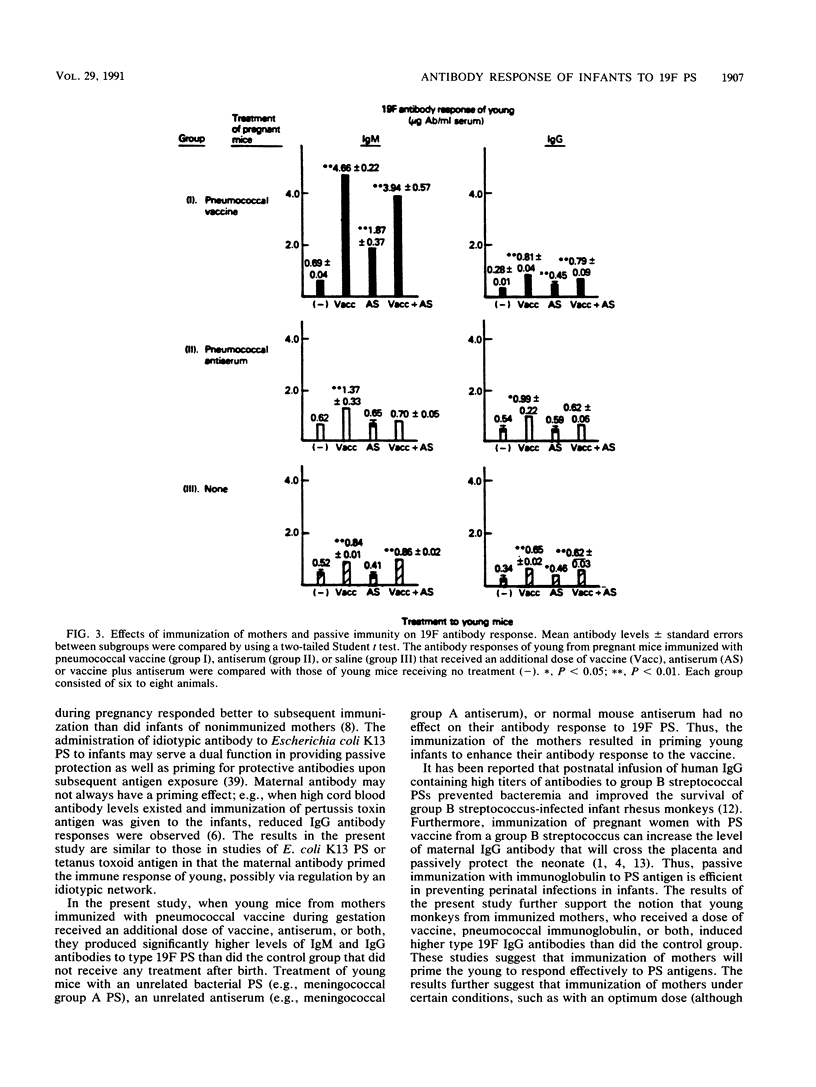
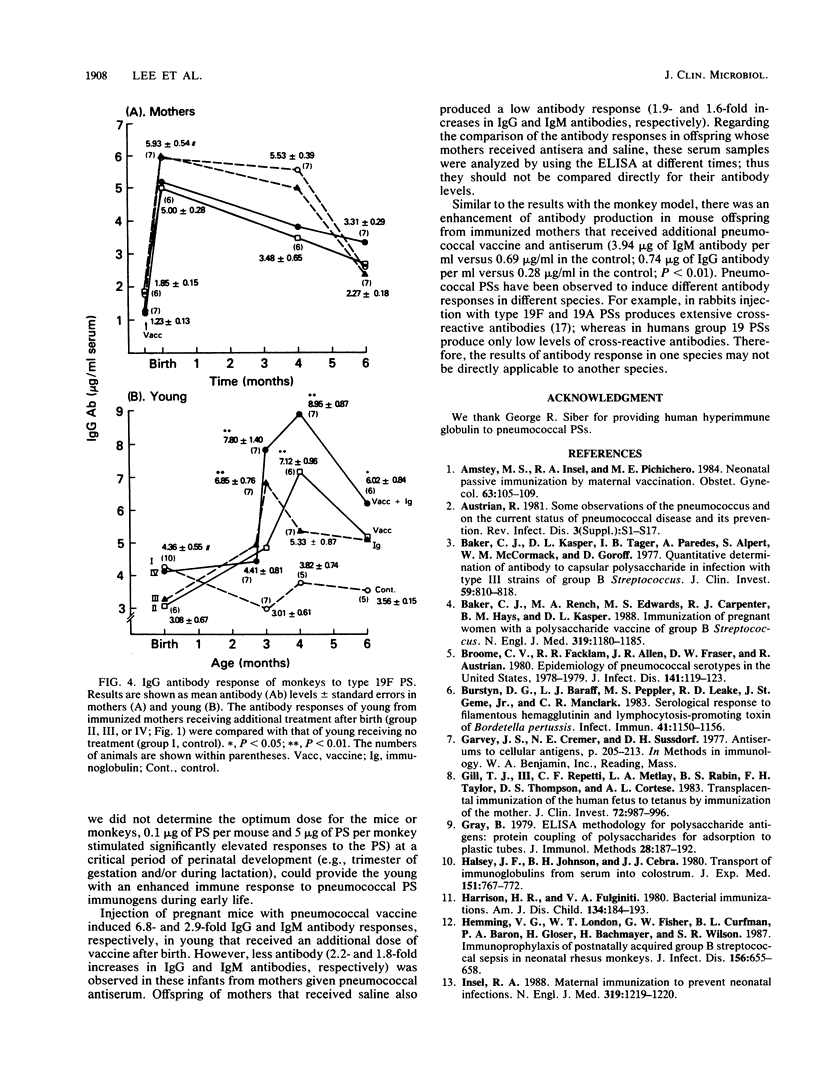
The effect of immunization of mothers on the antibody response of their young to pneumococcal type 19F polysaccharide was studied. When 2-week-old BALB/c mice from mothers immunized with 23-valent pneumococcal vaccine during gestation were given an additional dose of the same vaccine, mouse pneumococcal antiserum, or both, they produced higher titers of antibodies to the 19F polysaccharide (1.87 to 4.66 micrograms of 19F immunoglobulin M [IgM] antibody per ml of serum; 0.45 to 0.81 micrograms of IgG antibody per ml of serum) than the control group that did not receive any treatment after birth (0.69 micrograms of 19F IgM antibody per ml; 0.28 micrograms of 19F IgG antibody per ml) (P less than 0.01). Furthermore, all 11- to 12-week-old monkeys that received an additional dose of 23-valent vaccine, pneumococcal immunoglobulin, or both produced statistically higher titers of IgG antibody to the 19F polysaccharide than did controls at various ages. The titers (micrograms of IgG antibody per milliliter of serum) were as follows: vaccine group, 7.12 +/- 0.96; control group at 4 months of age, 3.82 +/- 0.74 (P less than 0.01); immunoglobulin-treated group, 6.85 +/- 0.76; vaccinated and immunoglobulin-treated group, 7.80 +/- 1.40; control group at 3 months of age, 3.01 +/- 0.61 (P less than 0.01). These results suggest that immunization of mothers under certain conditions, such as with an optimum dose of antigen at a critical period of gestation or postnatal development, could provide young infants with an enhanced antibody response to pneumococcal polysaccharide immunogens.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amstey M. S., Insel R. A., Pichichero M. E. Neonatal passive immunization by maternal vaccination. Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Jan;63(1):105–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austrian R. Some observations on the pneumococcus and on the current status of pneumococcal disease and its prevention. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Mar-Apr;3 (Suppl):S1–17. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.supplement_1.s1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L., Tager IRAB, Paredes A., Alpert S., McCormack W. M., Goroff D. Quantitative determination of antibody to capsular polysaccharide in infection with type III strains of group B Streptococcus. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):810–818. doi: 10.1172/JCI108703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Rench M. A., Edwards M. S., Carpenter R. J., Hays B. M., Kasper D. L. Immunization of pregnant women with a polysaccharide vaccine of group B streptococcus. N Engl J Med. 1988 Nov 3;319(18):1180–1185. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198811033191802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome C. V., Facklam R. R., Allen J. R., Fraser D. W., Austrian R. From the center for disease control. Epidemiology of pneumococcal serotypes in the United States, 1978--1979. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):119–123. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstyn D. G., Baraff L. J., Peppler M. S., Leake R. D., St Geme J., Jr, Manclark C. R. Serological response to filamentous hemagglutinin and lymphocytosis-promoting toxin of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1150–1156. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1150-1156.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill T. J., 3rd, Repetti C. F., Metlay L. A., Rabin B. S., Taylor F. H., Thompson D. S., Cortese A. L. Transplacental immunization of the human fetus to tetanus by immunization of the mother. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):987–996. doi: 10.1172/JCI111071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B. M. ELISA methodology for polysaccharide antigens: protein coupling of polysaccharides for adsorption to plastic tubes. J Immunol Methods. 1979;28(1-2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsey J. F., Johnson B. H., Cebra J. J. Transport of immunoglobulins from serum into colostrum. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):767–772. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison H. R., Fulginiti V. A. Bacterial immunizations. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Feb;134(2):184–193. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130140058017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemming V. G., London W. T., Fischer G. W., Curfman B. L., Baron P. A., Gloser H., Bachmayer H., Wilson S. R. Immunoprophylaxis of postnatally acquired group B streptococcal sepsis in neonatal rhesus monkeys. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):655–658. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel R. A. Maternal immunization to prevent neonatal infections. N Engl J Med. 1988 Nov 3;319(18):1219–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198811033191809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. O. The epidemiology of pneumococcal disease in infants and children. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Mar-Apr;3(2):246–253. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.2.246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klugman K. P., Koornhof H. J., Kuhnle V. Clinical and nasopharyngeal isolates of unusual multiply resistant pneumococci. Am J Dis Child. 1986 Nov;140(11):1186–1190. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1986.02140250112045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klugman K. P., Koornhof H. J., Kuhnle V., Miller S. D., Ginsburg P. J., Mauff A. C. Meningitis and pneumonia due to novel multiply resistant pneumococci. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Mar 15;292(6522):730–730. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6522.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy T., Lee C. J., Henrichsen J., Carlo D. J., Stoudt T. M., Robbins J. B. Characterization of the cross-reaction between type 19F(19) and 19A(57) pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides: compositional analysis and immunological relation determined with rabbit typing antisera. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):727–735. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.727-735.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrenson J. B., Klugman K. P., Eidelman J. I., Wasas A., Miller S. D., Lipman J. Fatal infection caused by a multiply resistant type 3 pneumococcus. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1590–1591. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1590-1591.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. J. Bacterial capsular polysaccharides--biochemistry, immunity and vaccine. Mol Immunol. 1987 Oct;24(10):1005–1019. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. J., Lin K. T. Studies on vaccine control and immunogenicity of polysaccharides of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Mar-Apr;3 (Suppl):S51–S60. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.supplement_1.s51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. J. Maternal-foetal interaction, antibody formation, and metabolic response in mice immunized with pneumococcal polysacharides. Immunology. 1980 Sep;41(1):45–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. J., Takaoka Y., Saito T. Maternal immunization and the immune response of neonates to pneumococcal polysaccharides. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 May-Jun;9(3):494–510. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.3.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin K. T., Lee C. J. Immune response of neonates to pneumococcal polysaccharide-protein conjugate. Immunology. 1982 Jun;46(2):333–342. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E. Types of pneumococci found in blood, spinal fluid and pleural exudate during a period of 15 years (1954-1969). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1970;78(3):333–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1970.tb04311.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markiewicz Z., Tomasz A. Variation in penicillin-binding protein patterns of penicillin-resistant clinical isolates of pneumococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):405–410. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.405-410.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellander L., Carlsson B., Hanson L. A. Secretory IgA and IgM antibodies to E. coli O and poliovirus type I antigens occur in amniotic fluid, meconium and saliva from newborns. A neonatal immune response without antigenic exposure: a result of anti-idiotypic induction? Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Mar;63(3):555–561. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson M. A., Kruss D. M., Wasil R. E., Metzger W. I. Capsular types and outcome of bacteremic pneumococcal disease in the antibiotic era. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Sep;134(3):505–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst H. F., Spady D. W. Effect of breast-feeding on antibody response to conjugate vaccine. Lancet. 1990 Aug 4;336(8710):269–270. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91802-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M., Kelsoe G., Rajewsky K. Idiotypic regulation by isologous monoclonal anti-idiotope antibodies. Nature. 1981 Mar 19;290(5803):257–259. doi: 10.1038/290257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley I. D., Lehmann D., Alpers M. P., Marshall T. F., Gratten H., Smith D. Pneumococcal vaccine prevents death from acute lower-respiratory-tract infections in Papua New Guinean children. Lancet. 1986 Oct 18;2(8512):877–881. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90409-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Austrian R., Lee C. J., Rastogi S. C., Schiffman G., Henrichsen J., Mäkelä P. H., Broome C. V., Facklam R. R., Tiesjema R. H. Considerations for formulating the second-generation pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide vaccine with emphasis on the cross-reactive types within groups. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1136–1159. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Schneerson R. Polysaccharide-protein conjugates: a new generation of vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):821–832. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein L. J., Goldberg B., Hiernaux J., Stein K. E., Bona C. A. Idiotype-antiidiotype regulation. V. The requirement for immunization with antigen or monoclonal antiidiotypic antibodies for the activation of beta 2 leads to 6 and beta 2 leads to 1 polyfructosan-reactive clones in BALB/c mice treated at birth with minute amounts of anti-A48 idiotype antibodies. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1129–1144. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., Parke J. C., Jr, Bell C., Schlesselman J. J., Sutton A., Wang Z., Schiffman G., Karpas A., Shiloach J. Quantitative and qualitative analyses of serum antibodies elicited in adults by Haemophilus influenzae type b and pneumococcus type 6A capsular polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugates. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.519-528.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyamala G. N., Roberton D. M., Hosking C. S. Human-isotype-specific enzyme immunoassay for antibodies to pneumococcal polysaccharides. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1575–1579. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1575-1579.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Ambrosino D. M., McIver J., Ervin T. J., Schiffman G., Sallan S., Grady G. F. Preparation of human hyperimmune globulin to Haemophilus influenzae b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein K. E., Söderström T. Neonatal administration of idiotype or antiidiotype primes for protection against Escherichia coli K13 infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1001–1011. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


