Abstract
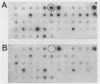
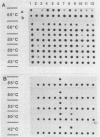
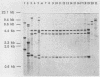
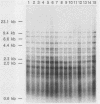
A DNA probe specific for Mycobacterium kansasii was obtained from a plasmid clone library of EcoRI-digested genomic DNA. The probe specifically identified culture-confirmed isolates of M. kansasii and isolates in cultures of environmental water samples. In an attempt to distinguish between isolates of M. kansasii, we used two methods to demonstrate restriction fragment length polymorphisms in the genomic DNA. Both of these methods failed to detect any differences between the isolates. These isolates included the type strain TMC 1201, environmental isolates, and clinical isolates from Australia and the Solomon Islands. This result suggests that the genome of M. kansasii is highly conserved and that genetic divergence within this species in insignificant.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn C. H., Nash D. R., Hurst G. A. Ventilatory defects in atypical mycobacteriosis. A comparison study with tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Mar;113(3):273–279. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altwegg M., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Farmer J. J., 3rd Ribosomal RNA gene restriction patterns provide increased sensitivity for typing Salmonella typhi strains. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):145–149. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey W. C., Brown M., Buechner H. A., Weill H., Ichinose H., Ziskind M. Silico-mycobacterial disease in sandblasters. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Aug;110(2):115–125. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Ullrich A., Raker M. A., Gray A., Dull T. J., Gutell R. R., Noller H. F. Construction and fine mapping of recombinant plasmids containing the rrnB ribosomal RNA operon of E. coli. Plasmid. 1981 Jul;6(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Jr, Nicholson D. P. Pulmonary disease due to Mycobacterium Kansasii. An analysis of some factors affecting prognosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Jan;99(1):73–85. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.99.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. "Opportunist" mycobacteria in England and Wales. Tubercle. 1969 Mar;50(Suppl):78–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J. Chromosomal DNA fingerprinting--a new method of species and strain identification applicable to microbial pathogens. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Oct;30(2):89–99. doi: 10.1099/00222615-30-2-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. C., Raios K., Jackson K., Sievers A., Dwyer B. Differentiation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains by use of a nonradioactive Southern blot hybridization method. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):904–907. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selik R. M., Starcher E. T., Curran J. W. Opportunistic diseases reported in AIDS patients: frequencies, associations, and trends. AIDS. 1987 Sep;1(3):175–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherer R., Sable R., Sonnenberg M., Cooper S., Spencer P., Schwimmer S., Kocka F., Muthuswamy P., Kallick C. Disseminated infection with Mycobacterium kansasii in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Nov;105(5):710–712. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-5-710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker S. A., Fisher J. H., Jones W. D., Jr, Scoggin C. H. Restriction fragment analysis of chromosomal DNA defines different strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Aug;134(2):210–213. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.2.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky E. Nontuberculous mycobacteria and associated diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jan;119(1):107–159. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]