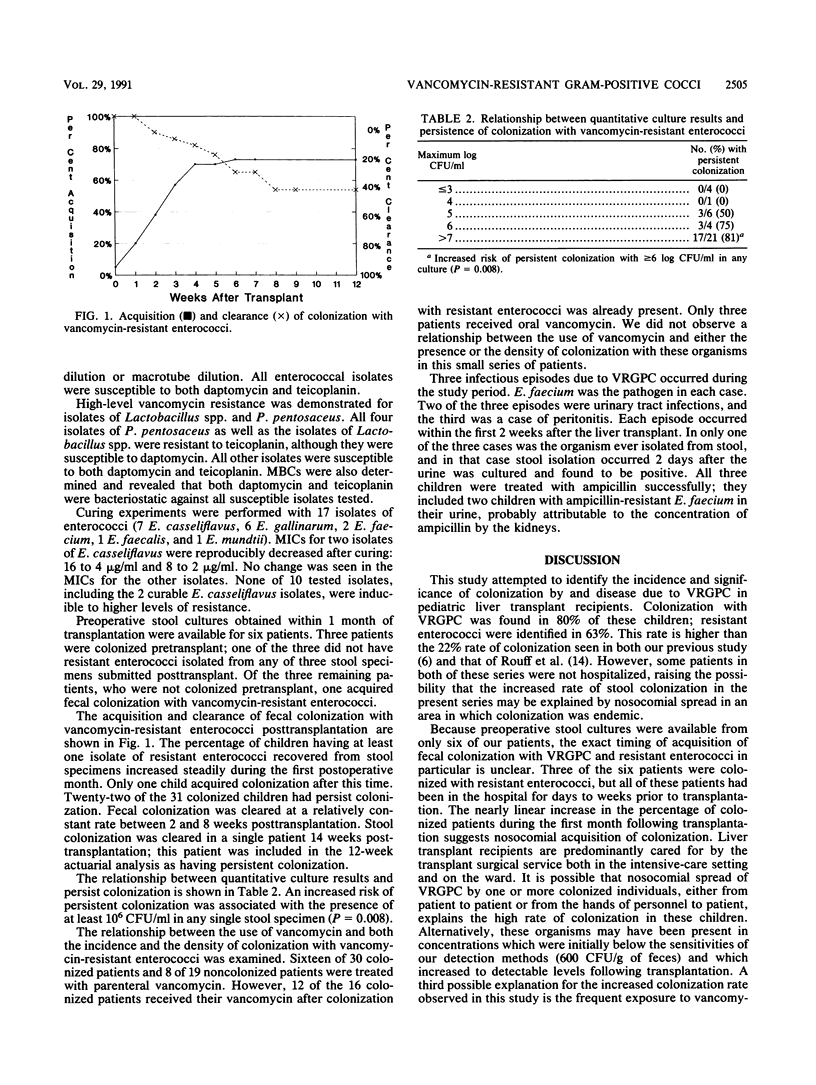
Abstract
Between November 1988 and October 1989, 49 first-time pediatric liver transplant recipients at the Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh were prospectively monitored for the presence of stool colonization and the development of disease caused by vancomycin-resistant gram-positive cocci (VRGPC). Quantitative stool culturing was done on a weekly basis, and cultures were planted onto a selective medium for VRGPC. Isolates for which the MIC was greater than or equal to 8 were considered resistant to vancomycin. Patients were monitored clinically for the development of infection, and their charts were systematically reviewed for the use of antibiotics. Eighty-six isolates were recovered from 36 of the 49 patients. Enterococcal species were isolated from 31 patients and included Enterococcus gallinarum (n = 28), E. casseliflavus (n = 14), E. faecium (n = 9), E. faecalis (n = 2), E. mundtii (n = 2), and E. durans (n = 1). Stool colonization with vancomycin-resistant enterococci was noted to increase steadily during the first month after transplantation. Only 9 of 31 patients demonstrated clearance of these organisms in serial repeat cultures. Additional isolates of VRGPC included Lactobacillus confusus (n = 13), Lactobacillus spp. (n = 12), and Pediococcus pentosaceus (n = 4). Infection due to VRGPC developed in three patients: a urinary tract infection in two and peritonitis in one. E. faecium was the pathogen in each of these cases. The ranges of MICs of vancomycin were 8 to 32 micrograms/ml for all enterococcal isolates and greater than 128 micrograms/ml for Lactobacillus and Pediococcus isolates. All Lactobacillus and Pediococcus isolates were resistant to teicoplanin, although they were susceptible to daptomycin. All other isolates were susceptible to both teicoplanin and daptomycin. This study demonstrates that stool colonization with VRGPC may be a common and early finding among pediatric liver transplant recipients. However, infection appears to be uncommon.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buu-Hoï A., Branger C., Acar J. F. Vancomycin-resistant streptococci or Leuconostoc sp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):458–460. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Collins M. D. Identification of Enterococcus species isolated from human infections by a conventional test scheme. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):731–734. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.731-734.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R., Hollis D., Collins M. D. Identification of gram-positive coccal and coccobacillary vancomycin-resistant bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):724–730. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.724-730.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Wadowsky R. M., Barbadora K. Recovery of vancomycin-resistant gram-positive cocci from children. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):484–488. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.484-488.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman D. J., Gerding D. N. Screening and treatment of infections caused by resistant enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):215–219. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg H. D., Vellozzi E. M., Shapiro J., Rubin L. G. Clinical laboratory challenges in the recognition of Leuconostoc spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):479–483. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.479-483.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufhold A., Ferrieri P. Isolation of Enterococcus mundtii from normally sterile body sites in two patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):1075–1077. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.1075-1077.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusne S., Dummer J. S., Singh N., Iwatsuki S., Makowka L., Esquivel C., Tzakis A. G., Starzl T. E., Ho M. Infections after liver transplantation. An analysis of 101 consecutive cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 1988 Mar;67(2):132–143. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198803000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq R., Derlot E., Duval J., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to vancomycin and teicoplanin in Enterococcus faecium. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jul 21;319(3):157–161. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198807213190307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq R., Derlot E., Weber M., Duval J., Courvalin P. Transferable vancomycin and teicoplanin resistance in Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):10–15. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Elimination of plasmids from several bacterial species by novobiocin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):423–426. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Kuritzkes D. R., Wolfson J. S., Ferraro M. J. Vancomycin-resistant gram-positive bacteria isolated from human sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2064–2068. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2064-2068.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlaes D. M., Bouvet A., Devine C., Shlaes J. H., al-Obeid S., Williamson R. Inducible, transferable resistance to vancomycin in Enterococcus faecalis A256. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Feb;33(2):198–203. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.2.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlaes D. M., Etter L., Gutmann L. Synergistic killing of vancomycin-resistant enterococci of classes A, B, and C by combinations of vancomycin, penicillin, and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):776–779. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlaes D. M., Marino J., Jacobs M. R. Infection caused by vancomycin-resistant Streptococcus sanguis II. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):527–528. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson J. M., Hill B. C., Thornsberry C. Problems with the disk diffusion test for detection of vancomycin resistance in enterococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2140–2142. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2140-2142.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. From penicillin-binding proteins to the lysis and death of bacteria: a 1979 view. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 May-Jun;1(3):434–467. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.3.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trieu-Cuot P., Carlier C., Courvalin P. Conjugative plasmid transfer from Enterococcus faecalis to Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4388–4391. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4388-4391.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S., Knight R. G., Green M., Sahm D. F., Shlaes D. M. Vancomycin susceptibility and identification of motile enterococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Oct;29(10):2335–2337. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.10.2335-2337.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenocur H. S., Smith M. A., Vellozzi E. M., Shapiro J., Isenberg H. D. Odontogenic infection secondary to Leuconostoc species. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1893–1894. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1893-1894.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


