Abstract
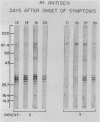
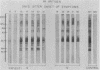
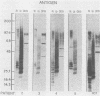
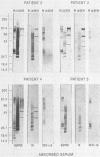
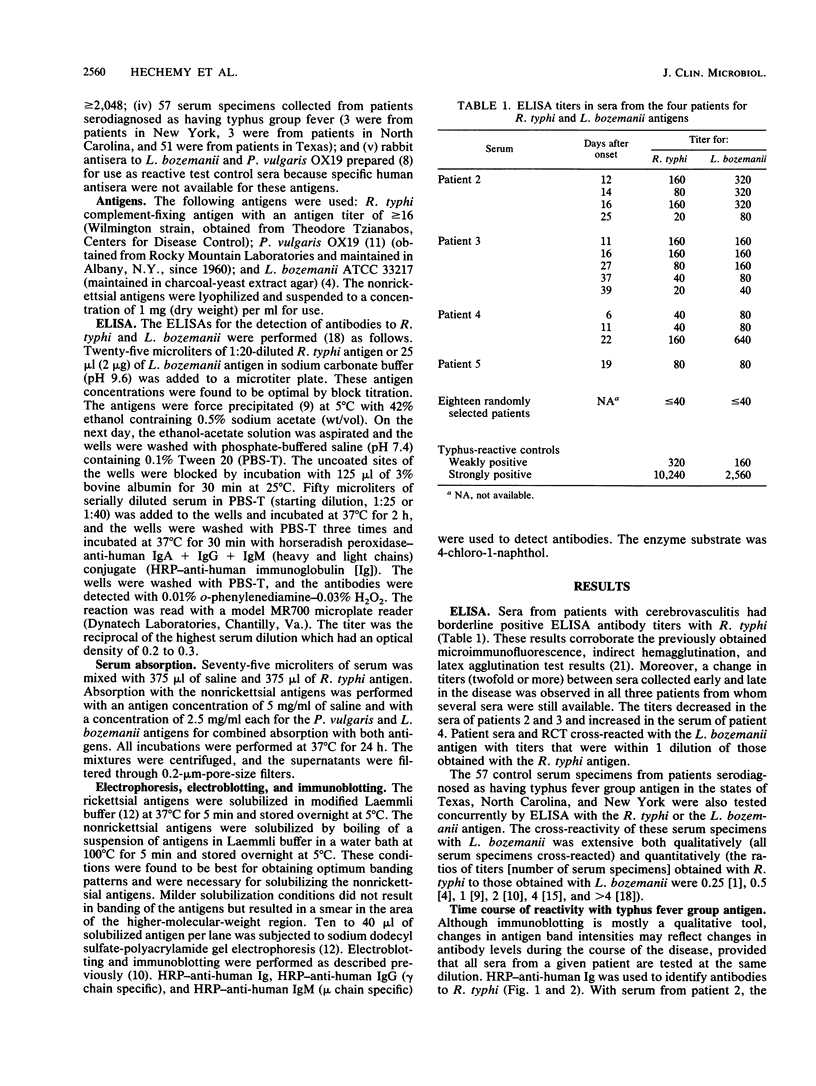
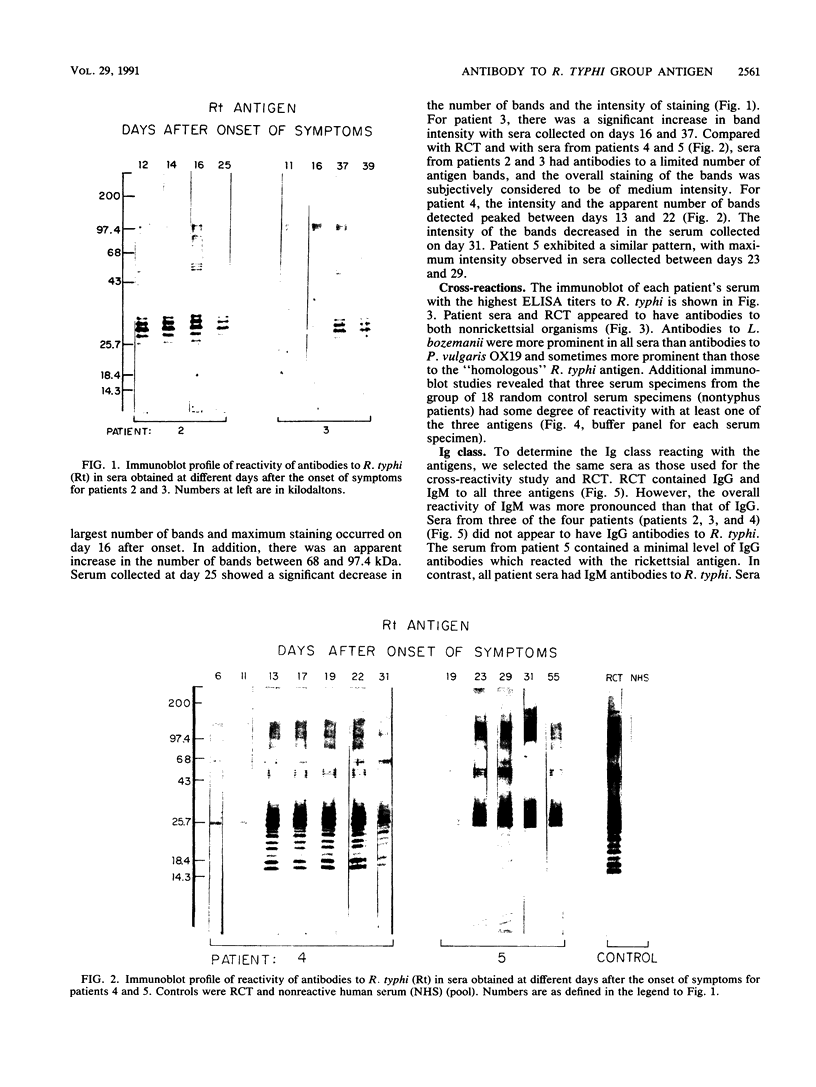
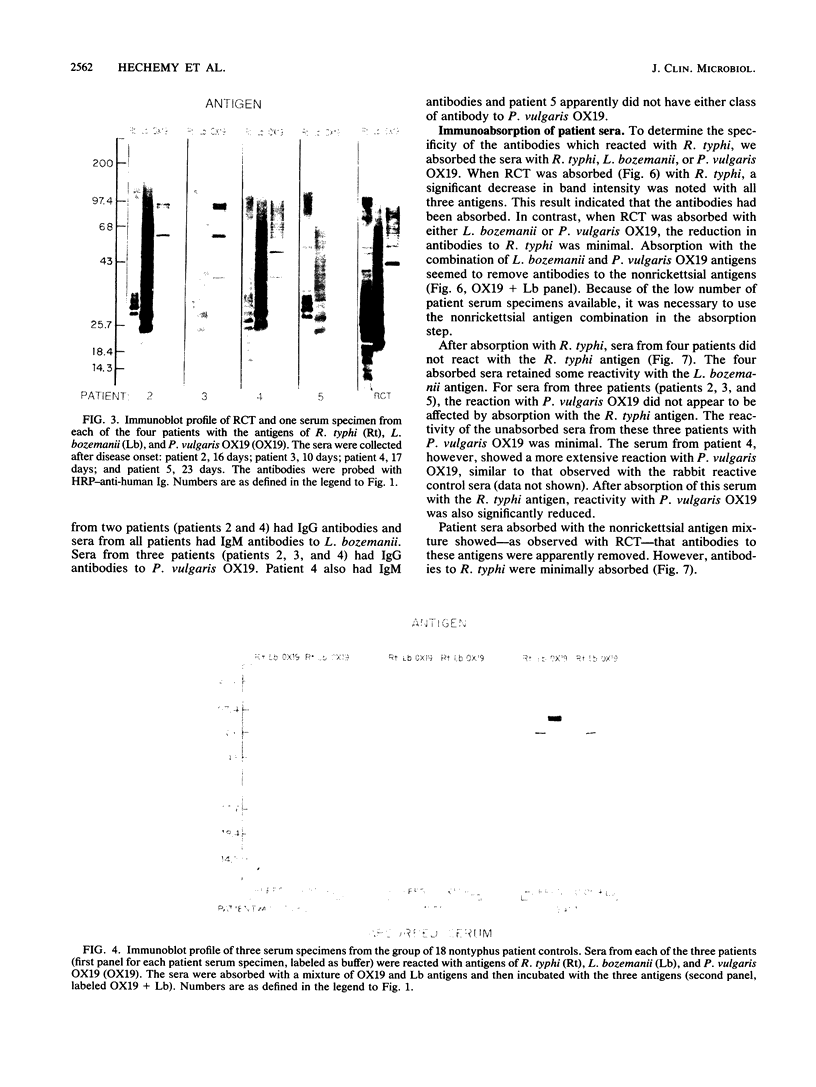
In 1986, an unusual syndrome of acute febrile cerebrovasculitis in the Piedmont Region of Virginia was reported. All patients had encephalopathy and prior exposure to both a sylvan environment and flea-infested animals. The initial serological studies suggested a rickettsial origin, corroborating clinical, epidemiological, and histopathological findings. Sera from four of five patients were subsequently studied by immunoblotting. Unabsorbed and absorbed sera were tested with electrophoresed and electroblotted Rickettsia typhi, Legionella bozemanii, and Proteus vulgaris OX19 antigens. The unabsorbed sera reacted with all three antigens. The P. vulgaris- and L. bozemanii-absorbed sera reacted with R. typhi only and without significantly less intensity. In contrast, the reactivity of R. typhi-absorbed sera was significantly lower with all three antigens. These results indicate that these patients had specific antibodies to a typhus group antigen. Although our findings suggest that a rickettsia of the typhus group may have caused this syndrome, no definitive diagnosis could be achieved because a rickettsial organism was not isolated.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duma R. J., Sonenshine D. E., Bozeman F. M., Veazey J. M., Jr, Elisberg B. L., Chadwick D. P., Stocks N. I., McGill T. M., Miller G. B., Jr, MacCormack J. N. Epidemic typhus in the United States associated with flying squirrels. JAMA. 1981 Jun 12;245(22):2318–2323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein D. B., Kemp A., Dawson J. E., Greene N. R., Redus M. A., Fields D. H. Human ehrlichiosis: prospective active surveillance in febrile hospitalized patients. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):803–809. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein D. B., McDade J. E. Acute febrile cerebrovasculitis. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Nov;105(5):802–803. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-5-802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Comparison of immunoblotting and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using different antigen preparations for diagnosing early Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):790–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechemy K. E., Fox J., Samsonoff W. A., Anacker R., Silverman D., Eisemann C., Green I. S. Production of antibody to and cellular localization of erythrocyte-sensitizing substance from Rickettsia rickettsii. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):377–384. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.377-384.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechemy K. E., Stevens R. W., Sasowski S., Michaelson E. E., Casper E. A., Philip R. N. Discrepancies in Weil-Felix and microimmunofluorescence test results for Rocky Mountain spotted fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):292–293. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.292-293.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechemy K., Stevens R. W., Gaafar H. A. Detection of Escherichia coli antigens by a latex agglutination test. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):306–311. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.306-311.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E., Shepard C. C., Redus M. A., Newhouse V. F., Smith J. D. Evidence of Rickettsia prowazekii infections in the United States. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Mar;29(2):277–284. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterman J. V., Eisemann C. S. Rickettsial indirect hemagglutination test: isolation of erythrocyte-sensitizing substance. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):189–196. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.189-196.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Boldur I., Goldwasser R. A., Kahana H., Kazak R., Keysary A., Pik A. Serological cross-reactions between Rickettsia typhi, Proteus vulgaris OX19, and Legionella bozemanii in a series of febrile patients. Isr J Med Sci. 1986 Oct;22(10):745–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Cain B. G., Olmstead P. M. Laboratory diagnosis of Rocky Mountain spotted fever by immunofluorescent demonstration of Rickettsia in Cutaneous lesions. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;69(6):619–623. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.6.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R. P., Hayden F. G., Gröschel D. H., Salata R. A., Young W. S., Greenlee J. E., Newman S., Miller P. J., Hechemy K. E., Burgdorfer W. Acute febrile cerebrovasculitis: a syndrome of unknown, perhaps rickettsial, cause. Ann Intern Med. 1986 May;104(5):606–615. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-104-5-606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westfall H. N., Goldwasser R. A., Weiss E., Hussong D. Prevalence of antibodies to Legionella species in a series of patients in Israel. Isr J Med Sci. 1986 Feb;22(2):131–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]