Abstract
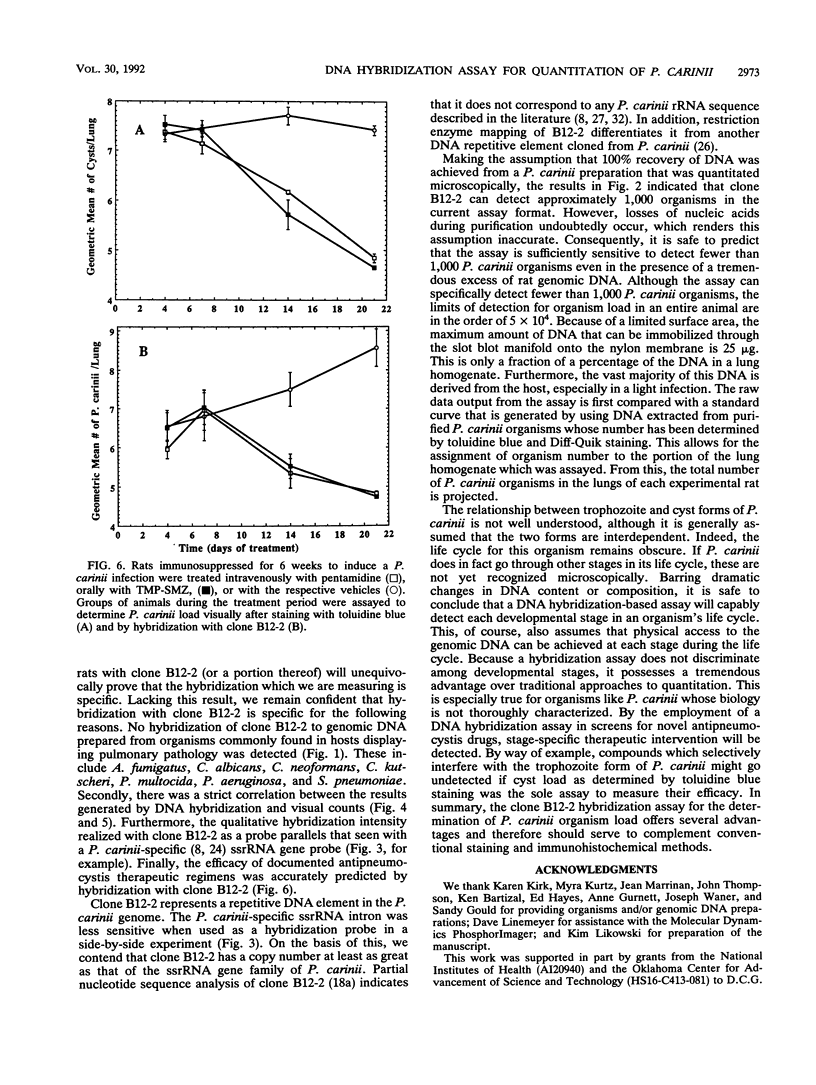
A repetitive genomic DNA clone (B12-2) that specifically hybridizes to Pneumocystis carinii DNA has been identified. No cross-hybridization to genomic DNA prepared from bacteria, other fungi, protozoa, or mammals was observed. Clone B12-2 is multiply represented in the P. carinii genome. By direct hybridization to DNA prepared from the lungs of immunosuppressed rats, the probe can detect the equivalent of fewer than 1,000 P. carinii organisms. A hybridization assay employing clone B12-2 has been developed to quantitate organism load in the rat model for P. carinii. Application of the assay to track the accumulation of organisms during the immunosuppression regimen as well as to monitor the efficacy of two drug therapies used clinically for the treatment of P. carinii pneumonia is described here. The clone B12-2 hybridization assay for the determination of P. carinii organism load possesses several advantageous features and thus should serve to complement conventional staining and immunohistochemical methods.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker R. H., Jr, Suebsaeng L., Rooney W., Alecrim G. C., Dourado H. V., Wirth D. F. Specific DNA probe for the diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1434–1436. doi: 10.1126/science.3513309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Fishman J. A., Durkin M. M., Queener S. F., Smith J. W. Pneumocystis carinii: improved models to study efficacy of drugs for treatment or prophylaxis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in the rat (Rattus spp.). Exp Parasitol. 1990 Jan;70(1):100–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(90)90089-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Fishman J. A., Queener S. F., Durkin M. M., Jay M. A., Smith J. W. New rat model of Pneumocystis carinii infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1100–1102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1100-1102.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Marr J. J., Queener S. F., Klein R. S., Smith J. W. Activity of inosine analogs against Pneumocystis carinii in culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):181–183. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker-Hapak M., Liberator P., Graves D. Detection of human Pneumocystis carinii by the polymerase chain reaction. J Protozool. 1991 Nov-Dec;38(6):191S–194S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHALVARDJIAN A. M., GRAWE L. A. A NEW PROCEDURE FOR THE IDENTIFICATION OF PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII CYSTS IN TISSUE SECTIONS AND SMEARS. J Clin Pathol. 1963 Jul;16:383–384. doi: 10.1136/jcp.16.4.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushion M. T., Ruffolo J. J., Linke M. J., Walzer P. D. Pneumocystis carinii: growth variables and estimates in the A549 and WI-38 VA13 human cell lines. Exp Parasitol. 1985 Aug;60(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4894(85)80021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Kovacs J. A., Masur H., Santi D. V., Elwood H. J., Sogin M. L. Ribosomal RNA sequence shows Pneumocystis carinii to be a member of the fungi. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):519–522. doi: 10.1038/334519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Kwon-Chung K. J. Isolation of the URA5 gene from Cryptococcus neoformans var. neoformans and its use as a selective marker for transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4538–4544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Watanabe J., Nakata K., Fukayama M., Ikeda H. A novel diagnostic method of Pneumocystis carinii. In situ hybridization of ribosomal ribonucleic acid with biotinylated oligonucleotide probes. Lab Invest. 1990 Oct;63(4):576–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Kuhn S., Chaudhary S., Feldman S., Verzosa M., Aur R. J., Pratt C., George S. L. Successful chemoprophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 29;297(26):1419–1426. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712292972602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., McNabb P. C., Makres T. D., Feldman S. Efficacy of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in the prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. K., Foy J. M., Cushion M. T., Stanforth D., Linke M. J., Hendrix H. L., Walzer P. D. Comparison of histologic and quantitative techniques in evaluation of therapy for experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):197–201. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Masur H. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: therapy and prophylaxis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):254–259. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Dawid I. B. Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:727–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pech M., Igo-Kemenes T., Zachau H. G. Nucleotide sequence of a highly repetitive component of rat DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 25;7(2):417–432. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SETHI K. K., SALFELDER K., SCHWARZ J. PULMONARY FUNGUS FLORA IN EXPERIMENTAL PNEUMOCYSTOSIS OF CORTISONE-TREATED RATS. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1964 Dec 15;24:121–129. doi: 10.1007/BF02075554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmatz D. M., Romancheck M. A., Pittarelli L. A., Schwartz R. E., Fromtling R. A., Nollstadt K. H., Vanmiddlesworth F. L., Wilson K. E., Turner M. J. Treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia with 1,3-beta-glucan synthesis inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5950–5954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Edman J. C. A self-splicing intron in the small subunit rRNA gene of Pneumocystis carinii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5349–5359. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer S. L., Hong S. T., Giuntoli D., Stringer J. R. Repeated DNA in Pneumocystis carinii. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jun;29(6):1194–1201. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.6.1194-1201.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer S. L., Stringer J. R., Blase M. A., Walzer P. D., Cushion M. T. Pneumocystis carinii: sequence from ribosomal RNA implies a close relationship with fungi. Exp Parasitol. 1989 May;68(4):450–461. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taft C. S., Stark T., Selitrennikoff C. P. Cilofungin (LY121019) inhibits Candida albicans (1-3)-beta-D-glucan synthase activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Dec;32(12):1901–1903. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.12.1901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Kim C. K., Foy J., Zhang J. L. Furazolidone and nitrofurantoin in the treatment of experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):158–163. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Perl D. P., Krogstad D. J., Rawson P. G., Schultz M. G. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the United States. Epidemiologic, diagnostic, and clinical features. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):83–93. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe J., Hori H., Tanabe K., Nakamura Y. Phylogenetic association of Pneumocystis carinii with the 'Rhizopoda/Myxomycota/Zygomycota group' indicated by comparison of 5S ribosomal RNA sequences. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jan 15;32(2-3):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley M. A., Ivey M. H., Graves D. C. Characterization and cloning of Pneumocystis carinii nucleic acid. J Protozool. 1989 Jan-Feb;36(1):9S–11S. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1989.tb02667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





