Abstract
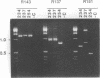
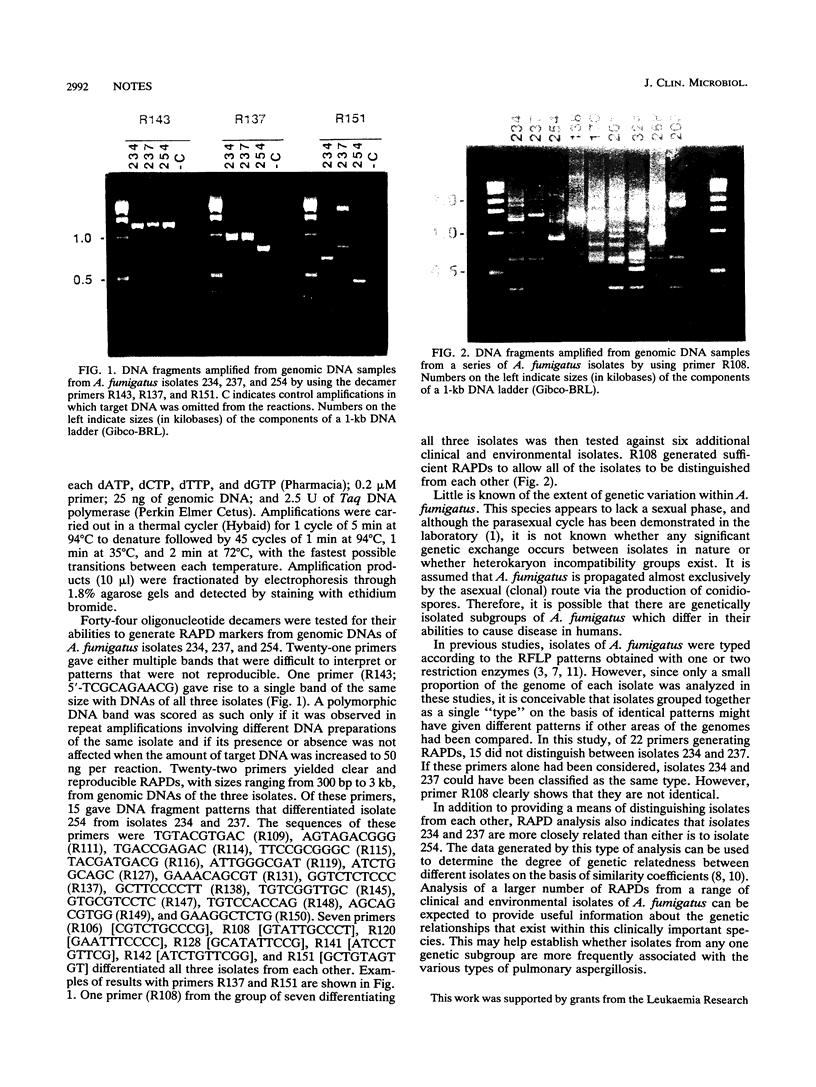
Forty-four oligonucleotide decamers were tested for their abilities to generate randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers from genomic DNAs of three different isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus. Seven primers generated RAPDs that allowed the three isolates to be differentiated; one of the primers also yielded a unique RAPD pattern in each of an additional six fungal isolates, demonstrating the utility of this technique for distinguishing between A. fumigatus isolates.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERG C. M., GARBER E. D. A genetic analysis of color mutants of Aspergillus fumigatus. Genetics. 1962 Sep;47:1139–1146. doi: 10.1093/genetics/47.9.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Vartivarian S. Aspergillosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 May;8(5):413–437. doi: 10.1007/BF01964057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Coke A., Matthews R. C. Restriction endonuclease analysis of Aspergillus fumigatus DNA. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Apr;45(4):324–327. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.4.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Matthews R. C., Clark I., Milne L. J. Immunoblot fingerprinting Aspergillus fumigatus. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Mar 31;118(2):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowhurst R. N., Hawthorne B. T., Rikkerink E. H., Templeton M. D. Differentiation of Fusarium solani f. sp. cucurbitae races 1 and 2 by random amplification of polymorphic DNA. Curr Genet. 1991 Nov;20(5):391–396. doi: 10.1007/BF00317067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning D. W., Clemons K. V., Hanson L. H., Stevens D. A. Restriction endonuclease analysis of total cellular DNA of Aspergillus fumigatus isolates of geographically and epidemiologically diverse origin. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1151–1158. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulik M. M., Brooks A. G. Electrophoretic studies of soluble proteins from Aspergillus spp. Mycologia. 1970 Mar-Apr;62(2):365–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5269–5273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spreadbury C. L., Bainbridge B. W., Cohen J. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms in isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus probed with part of the intergenic spacer region from the ribosomal RNA gene complex of Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Oct;136(10):1991–1994. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-10-1991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Cohen J., Holden D. W. An Aspergillus fumigatus alkaline protease mutant constructed by gene disruption is deficient in extracellular elastase activity. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(12):1663–1671. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00891.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]