Abstract
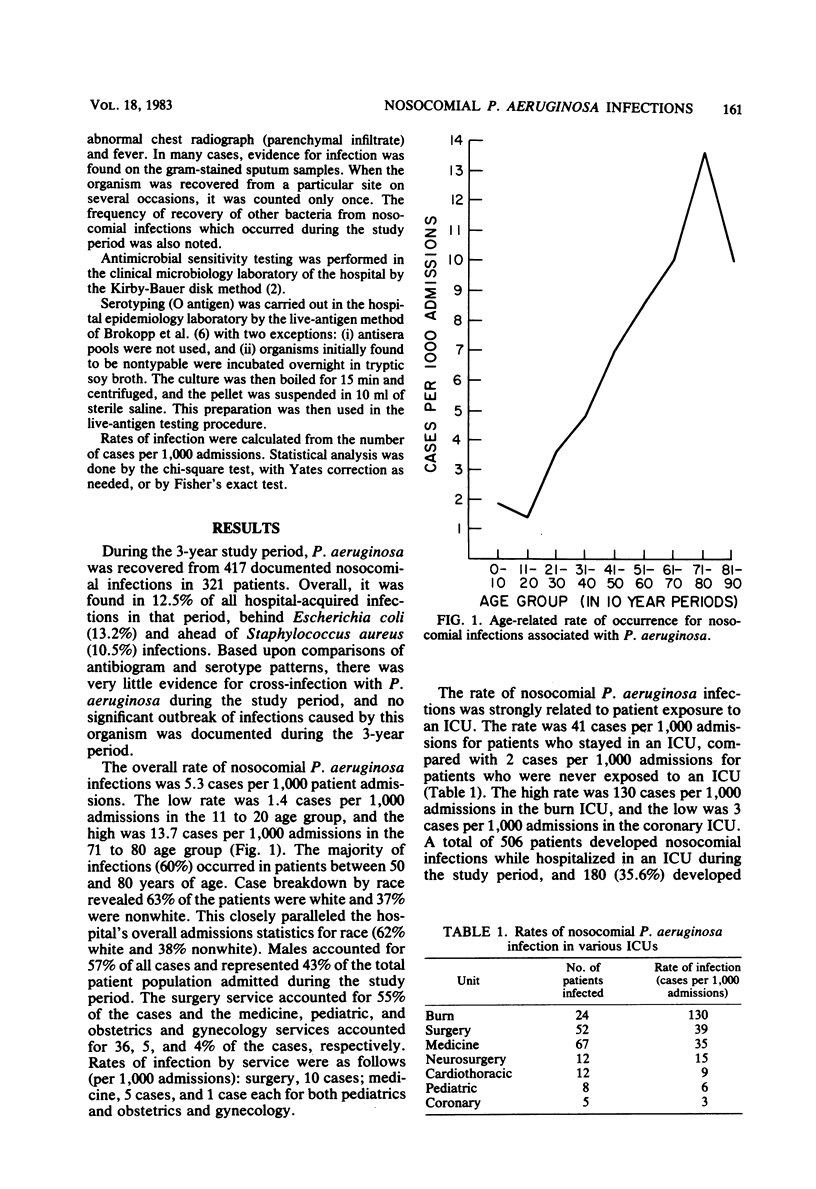
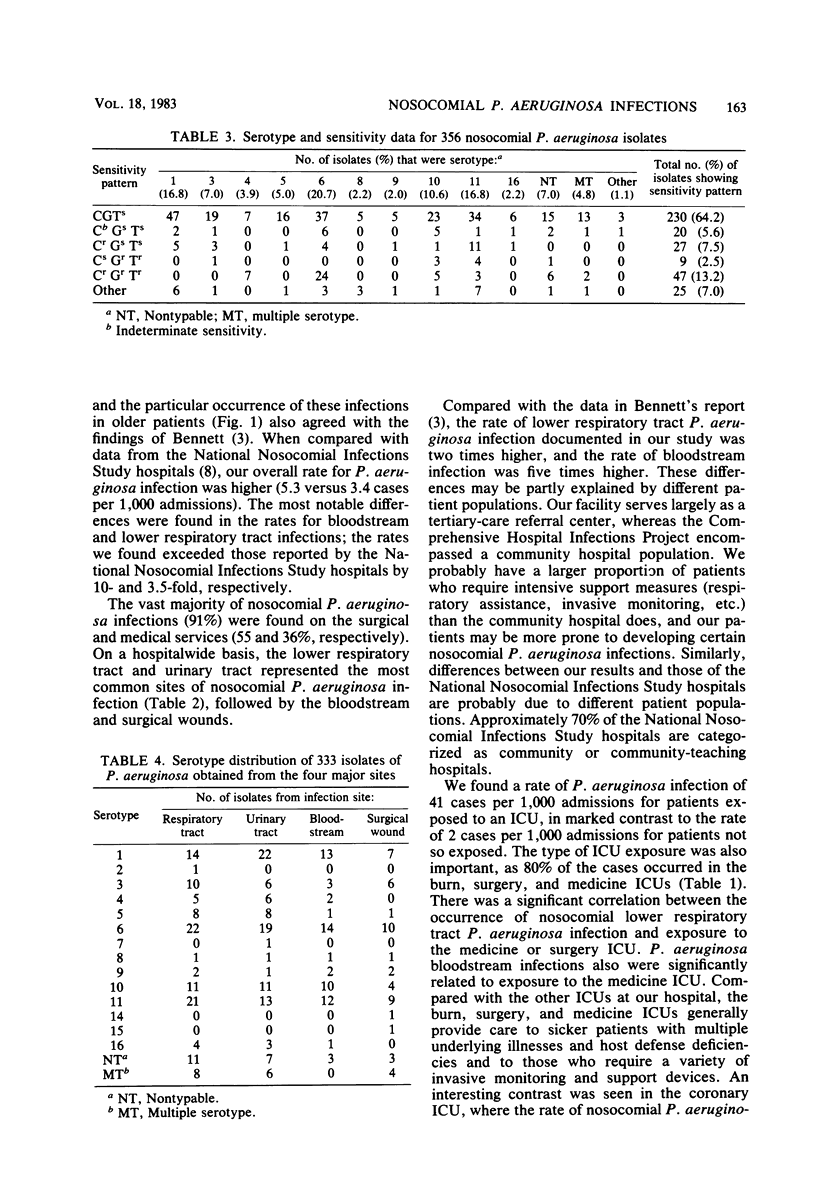
During a 3-year study period in a university teaching hospital, 417 nosocomial infections associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa were documented in 321 patients. The overall rate of P. aeruginosa nosocomial infection was 5.3 cases per 1,000 patients. Residence on the surgery or medicine service, advanced patient age, and exposure to the burn, surgery, or medicine intensive care units correlated with higher rates of infection. The most common sites for P. aeruginosa infection were the lower respiratory tract, urinary tract, blood stream, and surgical wounds. Nosocomial P. aeruginosa lower respiratory tract and blood stream infections were significantly associated with exposure to certain intensive care units, whereas P. aeruginosa urinary tract infections more commonly occurred on the neurology and neurosurgery services. Results of live antigen serotyping showed that serotype 6 was most common, followed by serotypes 1 and 11. Serotype 6 correlated with resistance to carbenicillin, gentamicin, and tobramycin, and serotype 11 correlated with resistance to carbenicillin. Two-thirds of the isolates tested were sensitive to carbenicillin, gentamicin, and tobramycin, but 13.2% were resistant to all three of these drugs. P. aeruginosa isolates resistant to all three drugs were associated with urinary tract infections.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore R. S., Dobek A. S., Stark F. R., Artenstein M. S. Clinical and epidemiological correlates of Pseudomonas typing. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S53–S59. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. V. Nosocomial infections due to Pseudomonas. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S4–S7. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobo R. A., Newton E. J., Jones L. F., Farmer L. H., Farmer J. J., 3rd Nursery outbreak of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: epidemiological conclusions from five different typing methods. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):414–420. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.414-420.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P. Epidemiological studies of Pseudomonas species in patients with leukemia. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Aug;260(2):82–89. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197008000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brokopp C. D., Gomez-Lus R., Farmer J. J., 3rd Serological typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: use of commercial antisera and live antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):640–649. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.640-649.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Weinstein R. A., Zierdt C. H., Brokopp C. D. Hospital outbreaks caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: importance of serogroup O11. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):266–270. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.266-270.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick M. R., Cluff L. E. Pseudomonas bacteremia. Review of 108 cases. Am J Med. 1976 Apr;60(4):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90716-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger B. E., Craven D. E., Carling P. C., McCabe W. R. Gram-negative bacteremia. III. Reassessment of etiology, epidemiology and ecology in 612 patients. Am J Med. 1980 Mar;68(3):332–343. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legakis N. J., Aliferopoulou M., Papavassiliou J., Papapetropoulou M. Serotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in clinical specimens in relation to antibiotic susceptibility. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):458–463. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.458-463.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Reynolds H. Y., Carbone P. P. Pseudomonas pneumonia. A retrospective study of 36 cases. Am J Med. 1973 Aug;55(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


