Abstract
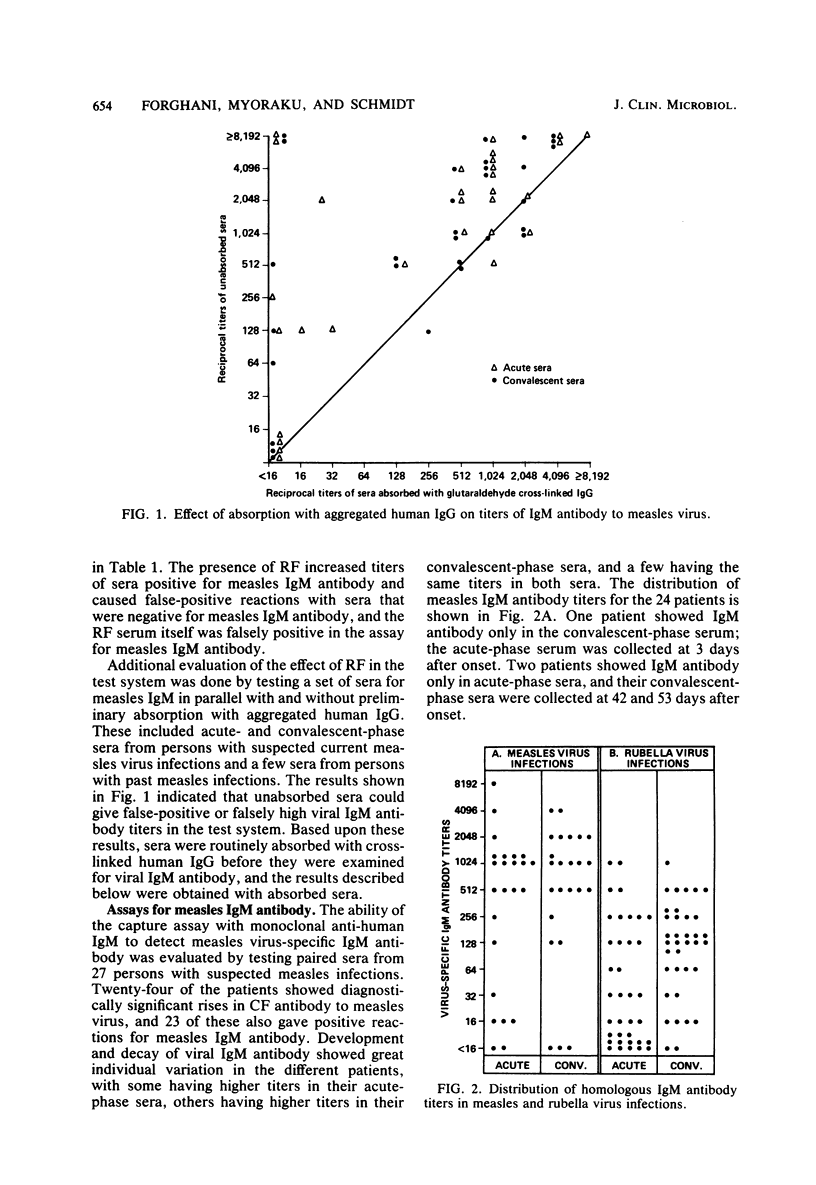
Monoclonal antibodies to human immunoglobulin M (IgM) were used in a four-phase enzyme immunofluorescence "capture" assay for determination of IgM antibodies to measles and rubella viruses. Little or no background reactivity was seen in the test system, and interfering effects of rheumatoid factor were avoided by preabsorption of test sera with aggregated human IgG. Virus-specific IgM antibody was demonstrable in 23 of 24 patients with serological evidence of measles virus infections and in 36 of 36 patients with serological evidence of postnatal rubella infection. A few of the rubella patients did not show IgM antibody until 5 days after onset of illness. The enzyme immunofluorescence assay was able to demonstrate rubella IgM antibody in congenitally infected newborns, whereas indirect immunofluorescence results for virus-specific IgM were negative. Viral IgM antibody was not detected in persons with past infections with the test viruses, in young children without evidence of past infection, or in patients infected with heterotypic viruses, rickettsiae, chlamydiae, or mycoplasmas.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNSTEIN T., JENSEN J. H., WAKSMAN B. H. THE DEVELOPMENT OF A NEUROTROPIC STRAIN OF MEASLES VIRUS IN HAMSTERS AND MICE. J Infect Dis. 1964 Jun;114:265–272. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.3.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbanti-Brodano G., Oyanagi S., Katz M., Koprowski H. Presence of 2 different viral agents in brain cells of patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 May;134(1):230–236. doi: 10.3181/00379727-134-34765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantler S., Evans C. J., Mortimer P. P., Cradock-Watson J. E., Ridehalgh M. K. A comparison of antibody capture radio- and enzyme immunoassays with immunofluorescence for detecting IgM antibody in infants with congenital rubella. J Virol Methods. 1982 Aug;4(6):305–313. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Dennis J., Schmidt N. J. Visual reading of enzyme immunofluorescence assays for human cytomegalovirus antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):704–708. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.704-708.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Myoraku C. K., Schmidt N. J. Production of monoclonal antibodies to human IgM for assay of viral IgM antibodies. J Virol Methods. 1982 Dec;5(5-6):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J. Antigen requirements, sensitivity, and specificity of enzyme immunoassays for measles and rubella viral antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jun;9(6):657–664. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.6.657-664.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Radioimmunoassay of measles virus antigen and antibody in SSPE brain tissue. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Feb;157(2):268–272. doi: 10.3181/00379727-157-40035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo D., Riggs J. L., Schachter J., Emmons R. W. Multiple-antigen slide test for detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies in newborn and infant sera by immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):631–636. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.631-636.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Suggs M. T., Hall E. C. Standardized viral hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition tests. II. Description and statistical evaluation. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):824–833. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.824-833.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaac M., Payne R. A. Antibody class capture assay (ACCA) for rubella-specific IgM antibody. J Med Virol. 1982;10(1):55–64. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890100108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz J. B., Malic A. Rubella-specific IgM detected by an antibody capture assay/ELISA technique. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Dec;34(12):1392–1395. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.12.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer P. P., Tedder R. S., Hamblig M. H., Shafi M. S., Burkhardt F., Schilt U. Antibody capture radioimmunoassay for anti-rubella IgM. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Apr;86(2):139–153. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400068856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen I. R., Antonsdottir A., Evald T., Mordhorst C. H. Detection of measles IgM antibodies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Apr;90(2):153–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Dennis J., Lennette E. H. Comparison of immunofluorescence and immunoperoxidase staining for identification of rubella virus isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jun;7(6):576–583. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.6.576-583.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vejtorp M. Solid phase anti-IgM ELISA for detection of rubella specific IgM antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Apr;89(2):123–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00163_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


