Abstract
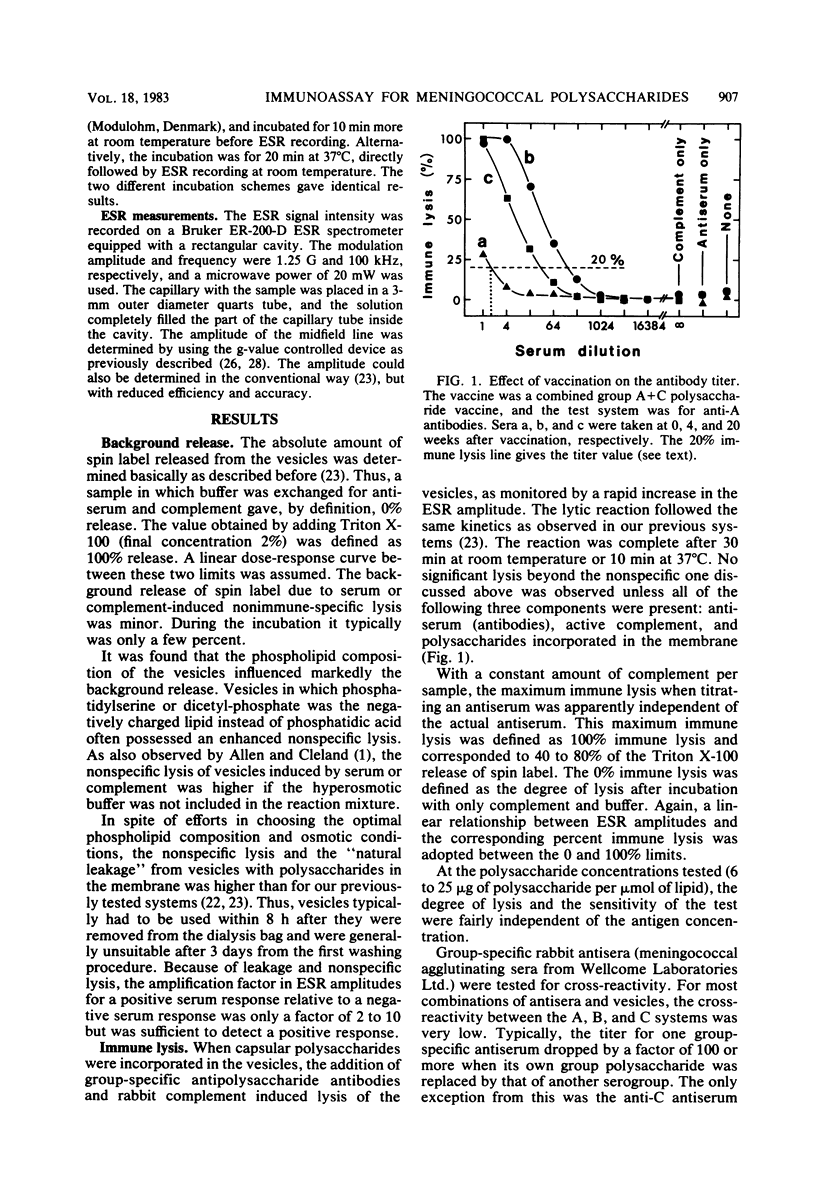
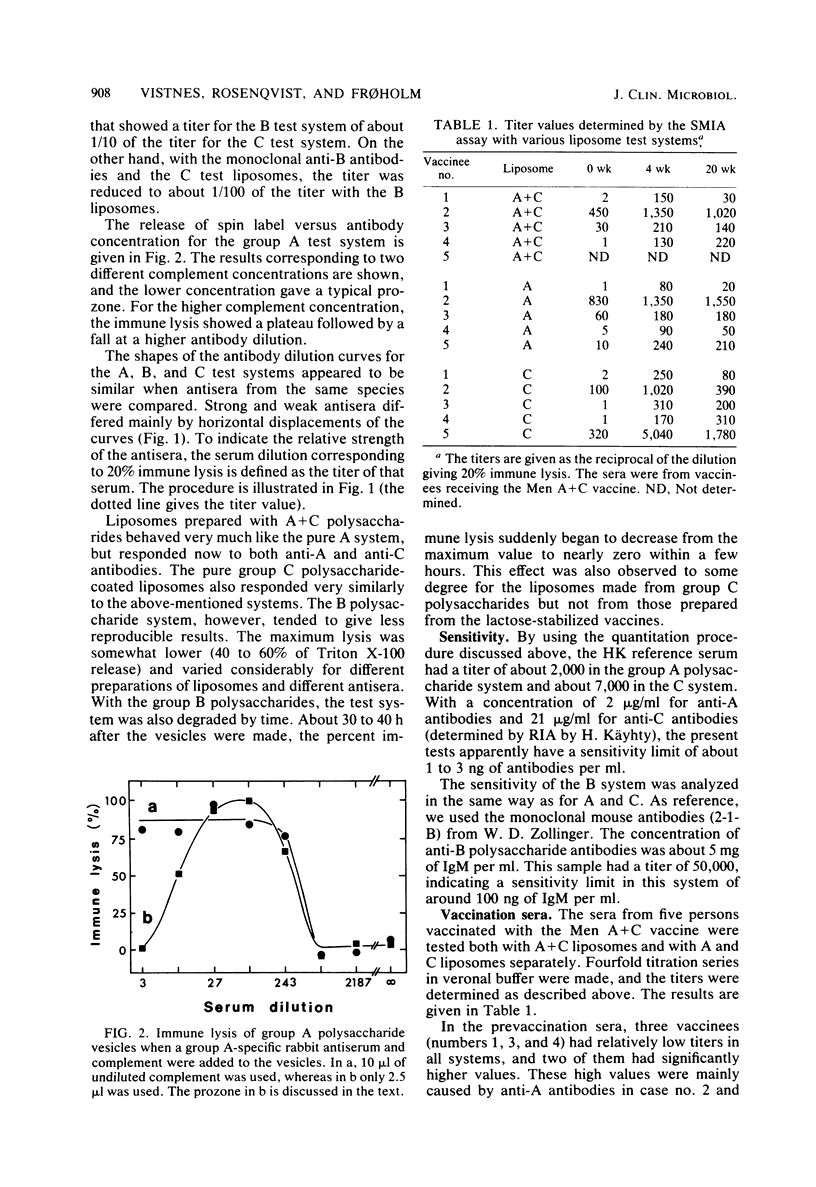
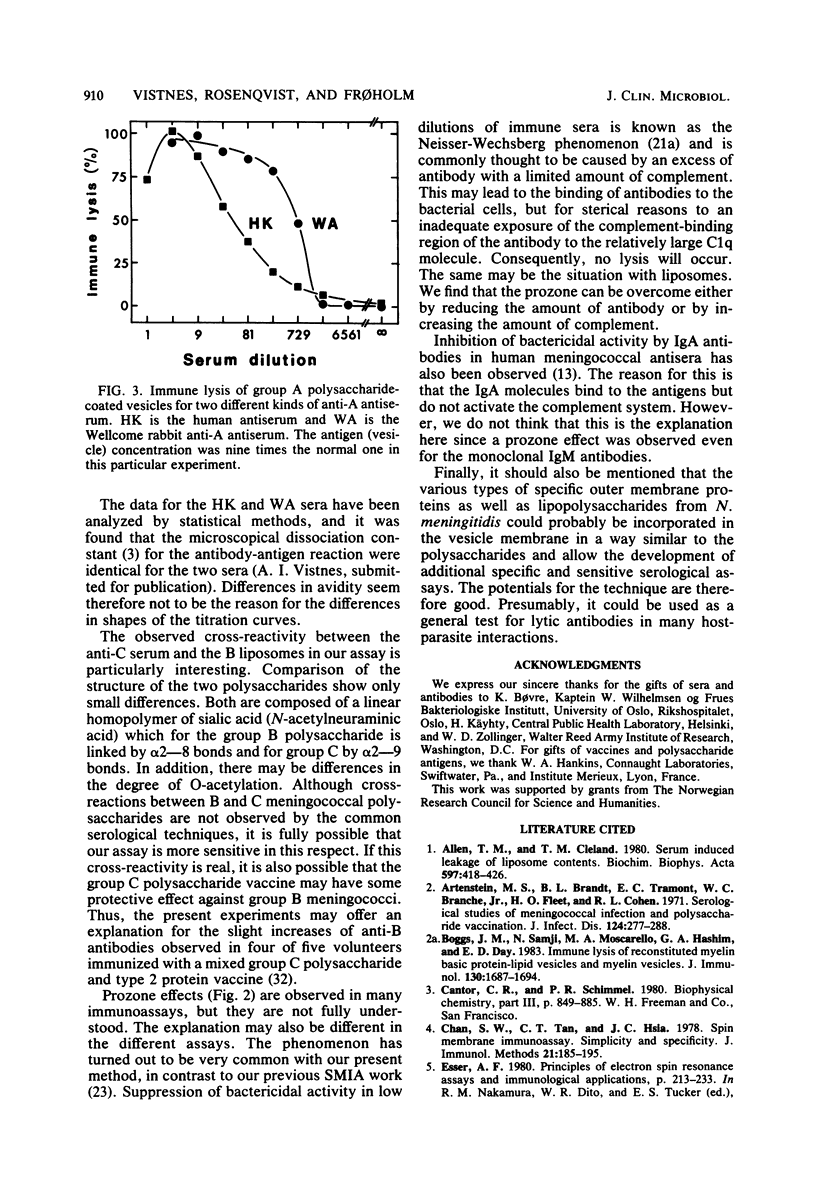
A modified and improved spin membrane immunoassay has been developed for detecting complement-activating antibodies to Neisseria meningitidis capsular polysaccharide antigens. The polysaccharides were incorporated in the membranes of large unilamellar vesicles prepared by the reverse-phase evaporation method and filled with the water-soluble spin label tempocholine chloride. Upon addition of group-specific antisera and complement, the lipid membrane was damaged and the spin label leaked out. This process was monitored by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. A satisfactory assay was developed for polysaccharides of group A and C, whereas in the case of the B system the assay was more labile. The method is rapid and has a sensitivity comparable to that of radioimmunoassay. When studying paired sera from five recruits vaccinated with an A + C polysaccharide vaccine, significant rises in titers to both A and C polysaccharides were observed in all the postvaccination sera.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen T. M., Cleland L. G. Serum-induced leakage of liposome contents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 10;597(2):418–426. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90118-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artenstein M. S., Brandt B. L., Tramont E. C., Branche W. C., Jr, Fleet H. D., Cohen R. L. Serologic studies of meningococcal infection and polysaccharide vaccination. J Infect Dis. 1971 Sep;124(3):277–288. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs J. M., Samji N., Moscarello M. A., Hashim G. A., Day E. D. Immune lysis of reconstituted myelin basic protein--lipid vesicles and myelin vesicles. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1687–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. W., Tan C. T., Hsia J. C. Spin membrane immunoassay: simplicity and specificity. J Immunol Methods. 1978;21(1-2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90235-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Robbins J. D. Protection against group B meningococcal disease. III. Immunogenicity of serotype 2 vaccines and specificity of protection in a guinea pig model. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):629–644. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. I. The role of humoral antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1307–1326. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. II. Development of natural immunity. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1327–1348. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Fraser B. A., Nishimura O., Robbins J. B., Liu T. Y. Lipid on capsular polysaccharides of gram-negative bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8915–8921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Goldschneider I., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. IV. Immunogenicity of group A and group C meningococcal polysaccharides in human volunteers. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1367–1384. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. 3. Preparation and immunochemical properties of the group A, group B, and group C meningococcal polysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1349–1365. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M. Bactericidal activity of meningococcal antisera. Blocking by IgA of lytic antibody in human convalescent sera. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1779–1784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia J. C., Tan C. T. Membrane immunoassay: principle and applications of spin membrane immunoassay. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978;308:139–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb22019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries G. K., McConnell H. M. Immune lysis of liposomes and erythrocyte ghosts loaded with spin label. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1691–1694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C., Haxby J. A., Zopf D. A., Alving C. R., Kinsky C. B. Complement-dependent damage to liposomes prepared from pure lipids and Forssman hapten. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4149–4158. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., McConnell H. M. Inside-outside transitions of phospholipids in vesicle membranes. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 30;10(7):1111–1120. doi: 10.1021/bi00783a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käyhty H. Comparison of passive hemagglutination, bactericidal activity, and radioimmunological methods in measuring antibody responses to Neisseria meningitidis group A capsular polysaccharide vaccine. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):256–263. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.256-263.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käyhty H., Jousimies-Somer H., Peltola H., Mäketä P. H. Antibody response to capsular polysaccharides of groups A and C neisseria meningitidis and Haemophilus influenzae type b during bacteremic disease. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):32–41. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifely M. R., Gilbert A. S., Moreno C. Sialic acid polysaccharide antigens of Neisseria meningitidis and Escherichia coli: esterification between adjacent residues. Carbohydr Res. 1981 Aug 1;94(2):193–203. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)80717-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Zollinger W. D. Measurement of antibodies to meningococcal group B polysaccharide: low avidity binding and equilibrium binding constants. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2172–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel L. H., Gustafson L., Larsen L. J. Re-examination of the Neisser-Wechsberg (antibody prozone) phenomenon. Immunology. 1969 Oct;17(4):525–533. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenqvist E., Michaelsen T. E., Vistnes A. I. Effect of streptolysin O and digitonin on egg lecithin/cholesterol vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 16;600(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenqvist E., Vistnes A. I. Immune lysis of spin label loaded liposomes incorporating cardiolipin; a new sensitive method for detecting anticardiolipin antibodies in syphilis serology. J Immunol Methods. 1977;15(2):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F., Jr, Papahadjopoulos D. Procedure for preparation of liposomes with large internal aqueous space and high capture by reverse-phase evaporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4194–4198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan C. T., Chan S. W., Hsia J. C. Membrane immunoassay: a spin membrane immunoassay for thyroxine. Methods Enzymol. 1981;74(Pt 100):152–161. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)74010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei R., Alving C. R., Richards R. L., Copeland E. S. Liposome spin immunoassay: a new sensitive method for detecting lipid substances in aqueous media. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Dec;9(2):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyle F. A., Artenstein M. S., Brandt B. L., Tramont E. C., Kasper D. L., Altieri P. L., Berman S. L., Lowenthal J. P. Immunologic response of man to group B meningococcal polysaccharide vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):514–521. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Boslego J. W. A general approach to standardization of the solid-phase radioimmunoassay for quantitation of class-specific antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1981;46(2):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E., Altieri P., Berman S., Lowenthal J., Artenstein M. S. Safety and immunogenicity of a Neisseria meningitidis type 2 protein vaccine in animals and humans. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jun;137(6):728–739. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.6.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E., Griffiss J. M., Altieri P., Berman S. Complex of meningococcal group B polysaccharide and type 2 outer membrane protein immunogenic in man. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):836–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI109383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E. Importance of complement source in bactericidal activity of human antibody and murine monoclonal antibody to meningococcal group B polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):257–264. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.257-264.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


