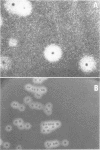
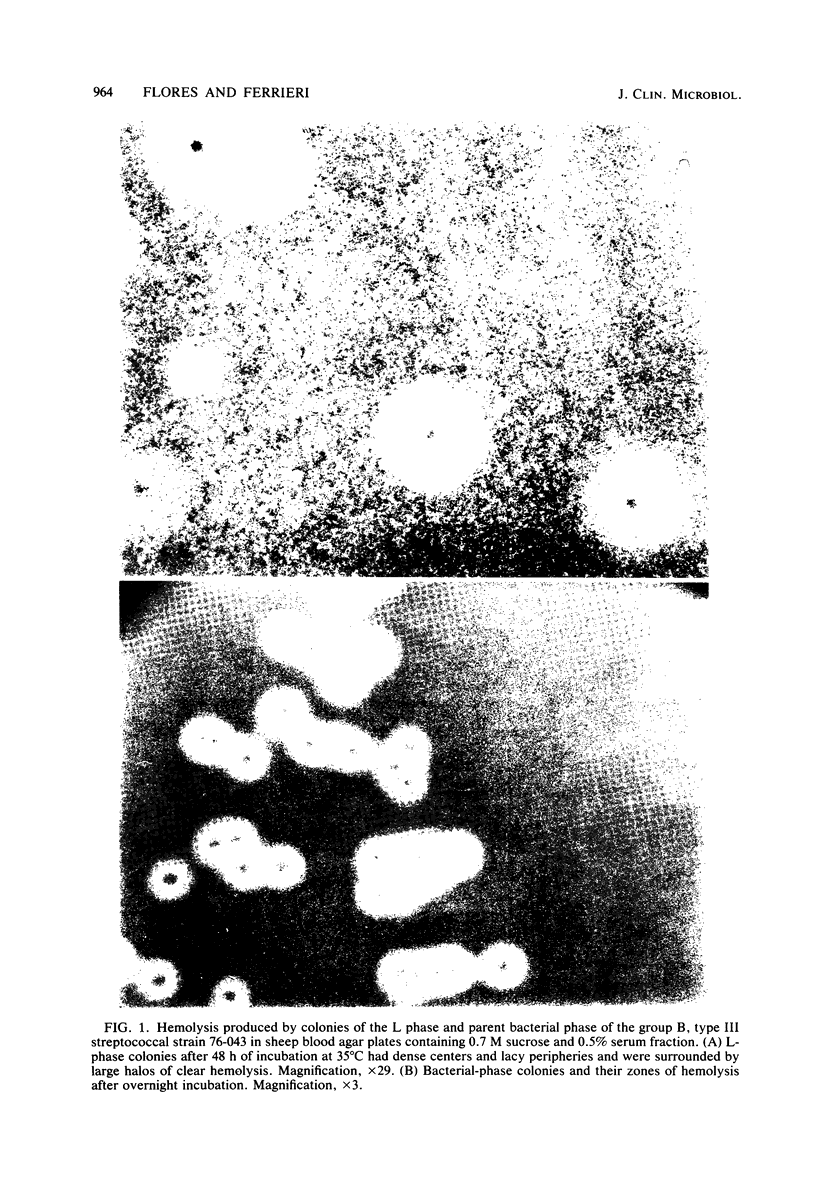
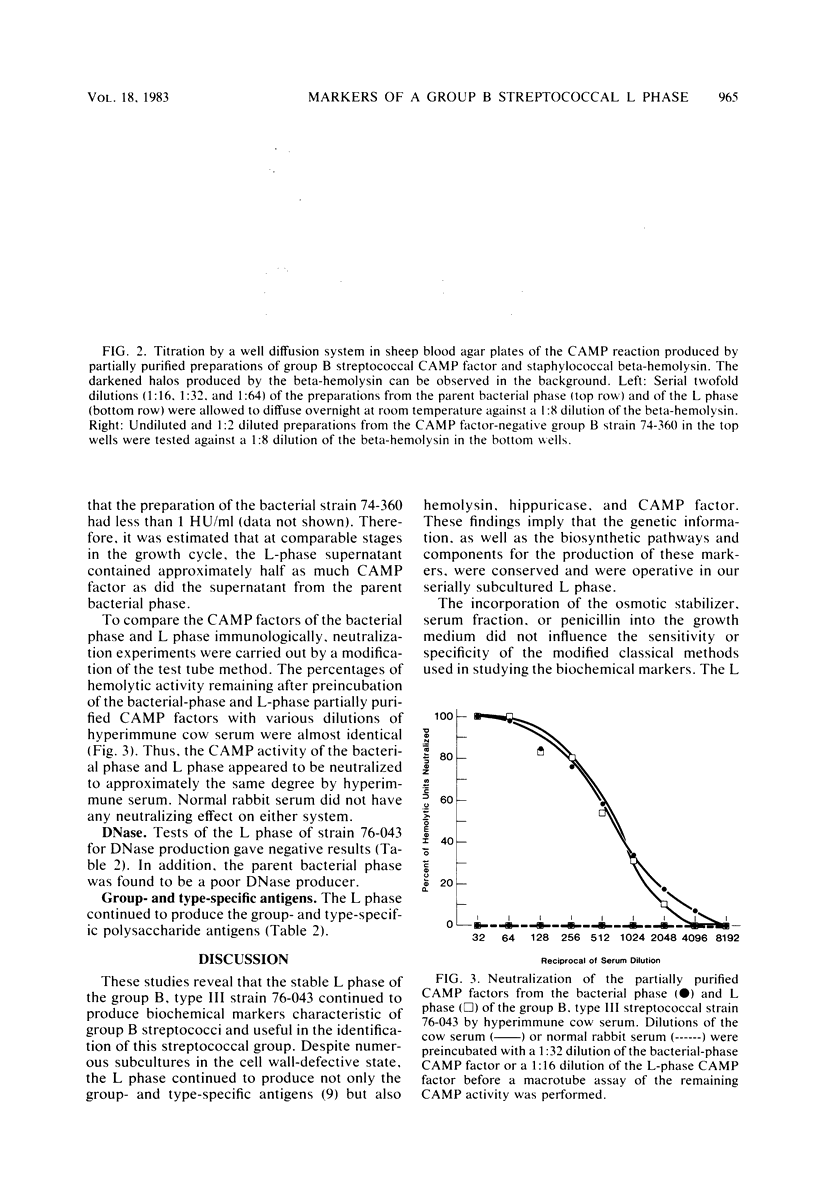
Abstract
The penicillin-induced L phase of growth of the group B, type III streptococcal strain 76-043 was examined for biochemical properties used for the identification of group B streptococci. After numerous serial subcultures in the cell wall-defective state, this stable L phase continued to produce hemolysin, hippuricase, and CAMP factor in addition to the group- and type-specific antigens. Hemolysin production by the L-phase cells was observed on solid and in liquid media containing sheep erythrocytes. Washed whole L-phase cells hydrolyzed hippuric acid. CAMP factor was detected by the characteristic hemolysis produced on blood agar by L-phase cells or filtered culture supernatants. CAMP factor activity was quantitated by an agar well diffusion system and a macrotube assay with partially purified preparations of CAMP factor and staphylococcal beta-hemolysin. Hyperimmune cow serum neutralized the CAMP activity of the L phase and parent bacterial phase to the same degree, suggesting identity of the CAMP factors. Production of hemolysin, hippuricase, and CAMP factor confirmed the bacterial origin of this L phase. Assay for these biological markers could be used to identify L-phase organisms derived from group B streptococci.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S., Kim K. S. Staphylococcal sphingomyelinase (beta-hemolysin). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):292–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Linder R., Avigad L. S. Nature and mechanism of action of the CAMP protein of group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):838–844. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.838-844.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J., Farnsworth R., Wannamaker L. W., Johnson D. W. CAMP factor of group B streptococci: production, assay, and neutralization by sera from immunized rabbits and experimentally infected cows. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):377–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.377-383.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J., Fincham W. J. The effect of streptococcal L-form cultures on lymphocytes. Life Sci. 1969 Apr 15;8(8):357–361. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREIMER E. H., KRAUSE R. M., McCARTY M. Studies of L forms and protoplasts of group A streptococci. I. Isolation, growth, and bacteriologic characteristics. J Exp Med. 1959 Dec 1;110:853–874. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.6.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrieri P., Gray E. D., Wannamaker L. W. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the extracellular nucleases of group B streptococci. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):56–68. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrieri P., Wannamaker L. W., Nelson J. Localization and characterization of the hippuricase activity of group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):747–752. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.747-752.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIJMANS W. Absence of the group-specific and the cell-wall polysaccharide antigen in L-phase variants of group D streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Apr;28:177–179. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-1-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hryniewicz W., Tagg J. R. Bacteriocin production by group a streptococcal L-forms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Dec;10(6):912–914. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.6.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. R., Gooder H. Induction of enterococcal L-forms by the action of lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):686–691. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.686-691.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landman O. E., Spiegelman S. ENZYME FORMATION IN PROTOPLASTS OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Oct 15;41(10):698–704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.10.698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchlewicz B. A., Duncan J. L. Lysis of erythrocytes by a hemolysin produced by a group B Streptococcus sp. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):787–794. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.787-794.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchlewicz B. A., Duncan J. L. Properties of a hemolysin produced by group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):805–813. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.805-813.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J., Ayoub E. M., Wannamaker L. W. Streptococcal anti-desoxyribonuclease B: microtechnique determination. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 May;71(5):867–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARP J. T., HIJMANS W., DIENES L. Examination of the L forms of group A streptococci for the group-specific polysaccharide and M protein. J Exp Med. 1957 Feb 1;105(2):153–159. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A., Willis A. T. Some physiological characters of L forms of Staphylococcus aureus. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(2):359–365. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W. CAMP-disk test for presumptive identification of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):42–45. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.42-45.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]