Abstract
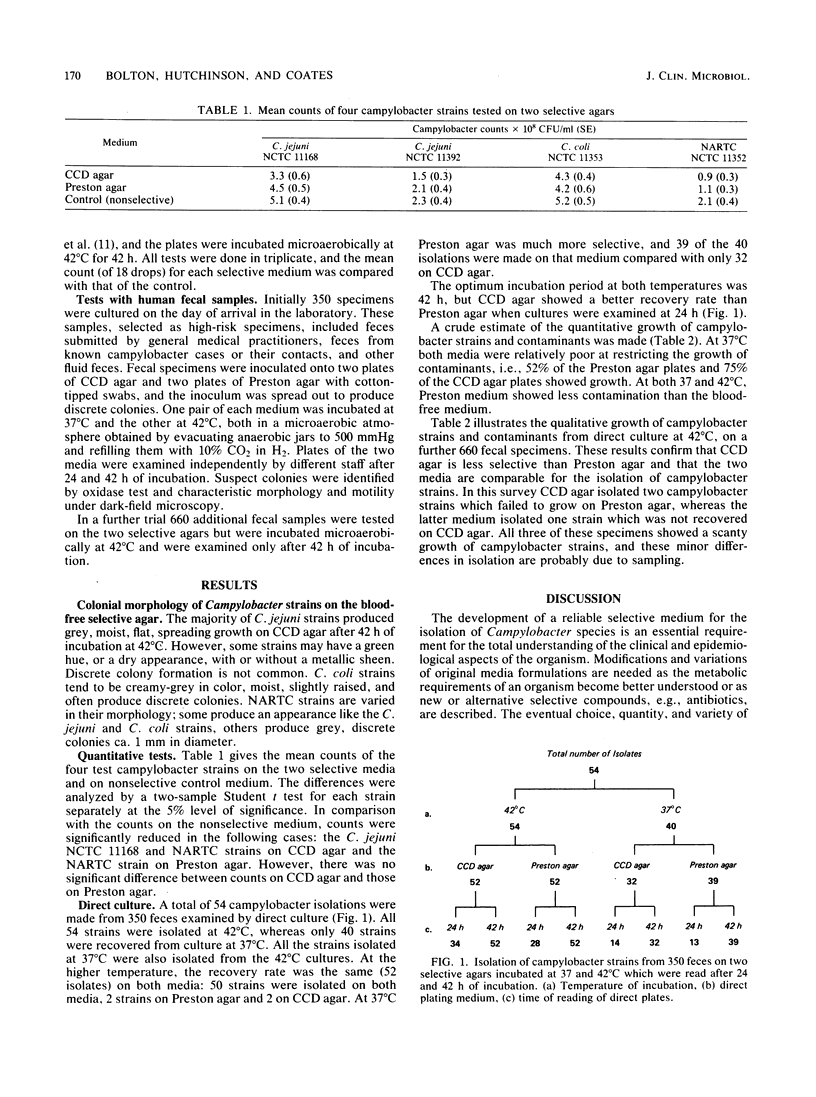
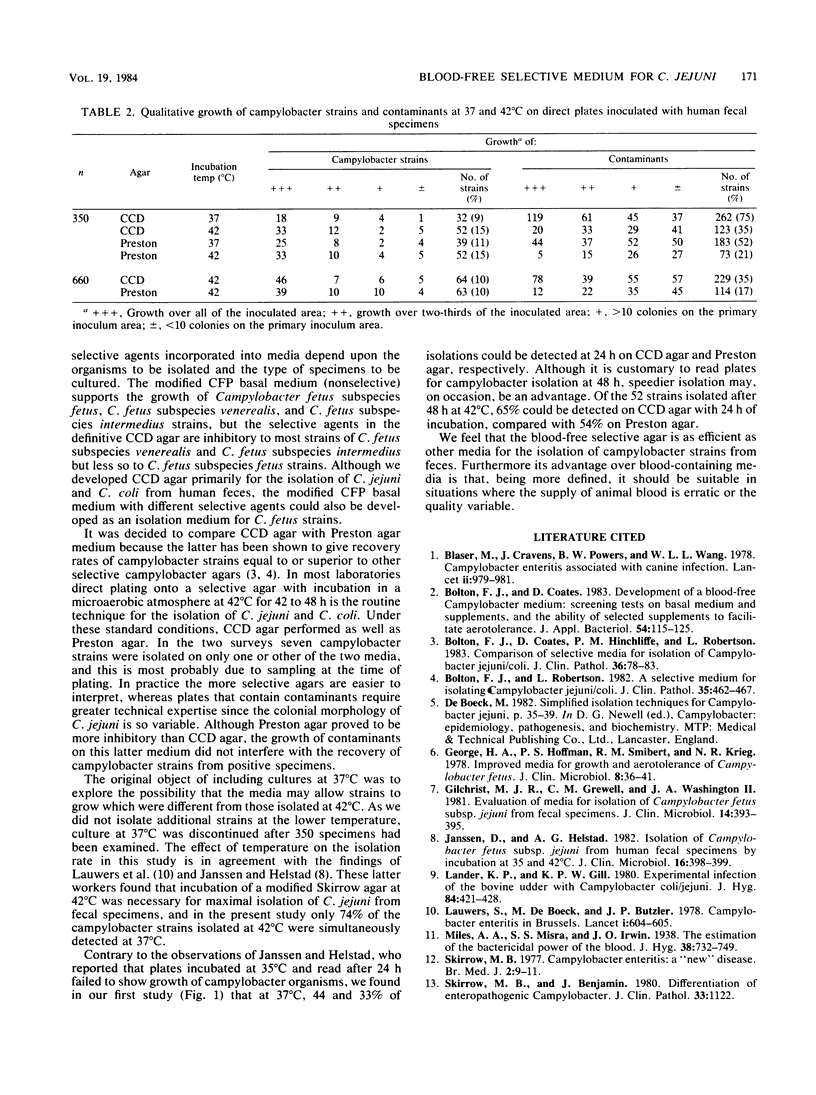
A blood-free selective agar is described which contains charcoal, ferrous sulfate, sodium pyruvate, casein hydrolysates, cefazolin, and sodium deoxycholate (CCD agar). CCD agar was compared with Preston medium for isolation of Campylobacter jejuni from human feces, and isolation rates were similar on both media, but CCD agar was less selective. Temperature studies at 37 and 42 degrees C confirmed that incubation of direct plates at 42 degrees C for 48 h was necessary for maximum isolation of C. jejuni.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M., Cravens J., Powers B. W., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis associated with canine infection. Lancet. 1978 Nov 4;2(8097):979–981. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92541-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton F. J., Coates D. Development of a blood-free Campylobacter medium: screening tests on basal media and supplements, and the ability of selected supplements to facilitate aerotolerance. J Appl Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;54(1):115–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1983.tb01308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton F. J., Coates D., Hinchliffe P. M., Robertson L. Comparison of selective media for isolation of Campylobacter jejuni/coli. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jan;36(1):78–83. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton F. J., Robertson L. A selective medium for isolating Campylobacter jejuni/coli. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Apr;35(4):462–467. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.4.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George H. A., Hoffman P. S., Smibert R. M., Krieg N. R. Improved media for growth and aerotolerance of Campylobacter fetus. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.36-41.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist M. J., Grewell C. M., Washington J. A., 2nd Evaluation of media for isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from fecal specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Oct;14(4):393–395. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.4.393-395.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen D., Helstad A. G. Isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from human fecal specimens by incubation at 35 and 42 degrees C. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):398–399. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.398-399.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander K. P., Gill K. P. Experimental infection of the bovine udder with Campylobacter coli/jejuni. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Jun;84(3):421–428. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauwers S., De Boeck M., Butzler J. P. Campylobacter enteritis in Brussels. Lancet. 1978 Mar 18;1(8064):604–605. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Benjamin J. Differentiation of enteropathogenic Campylobacter. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Nov;33(11):1122–1122. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.11.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


