Abstract
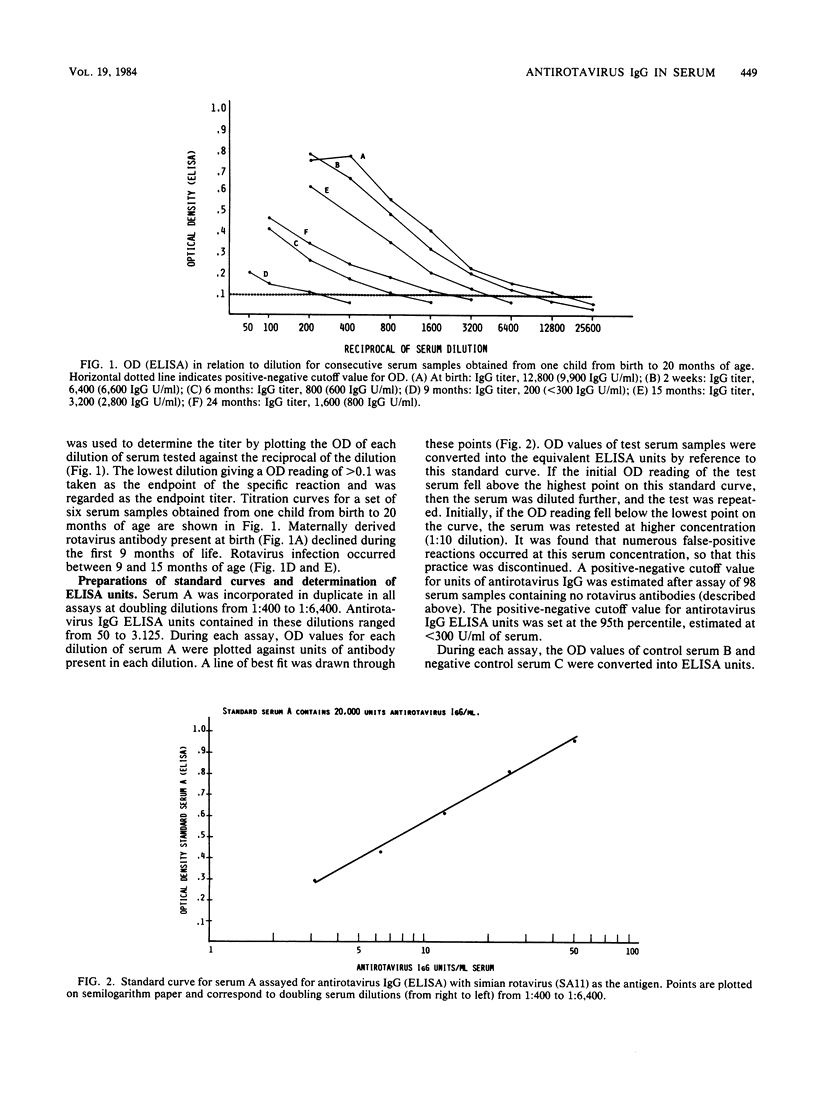
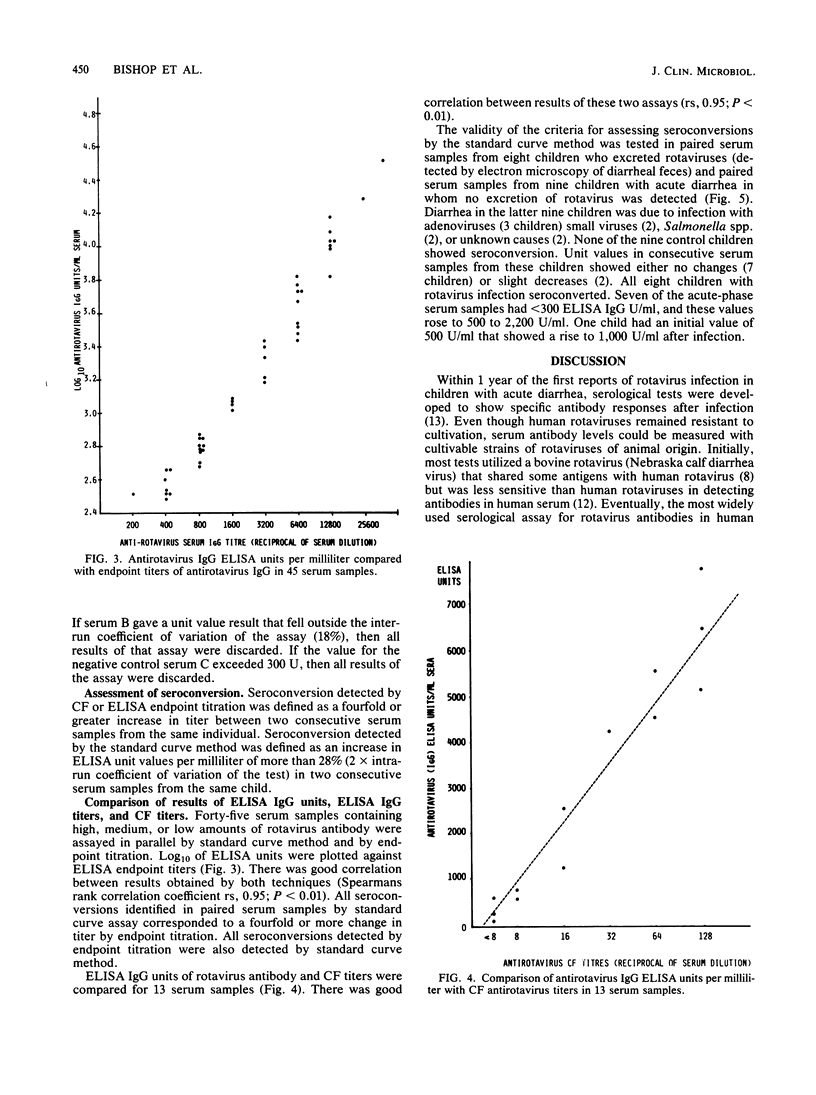
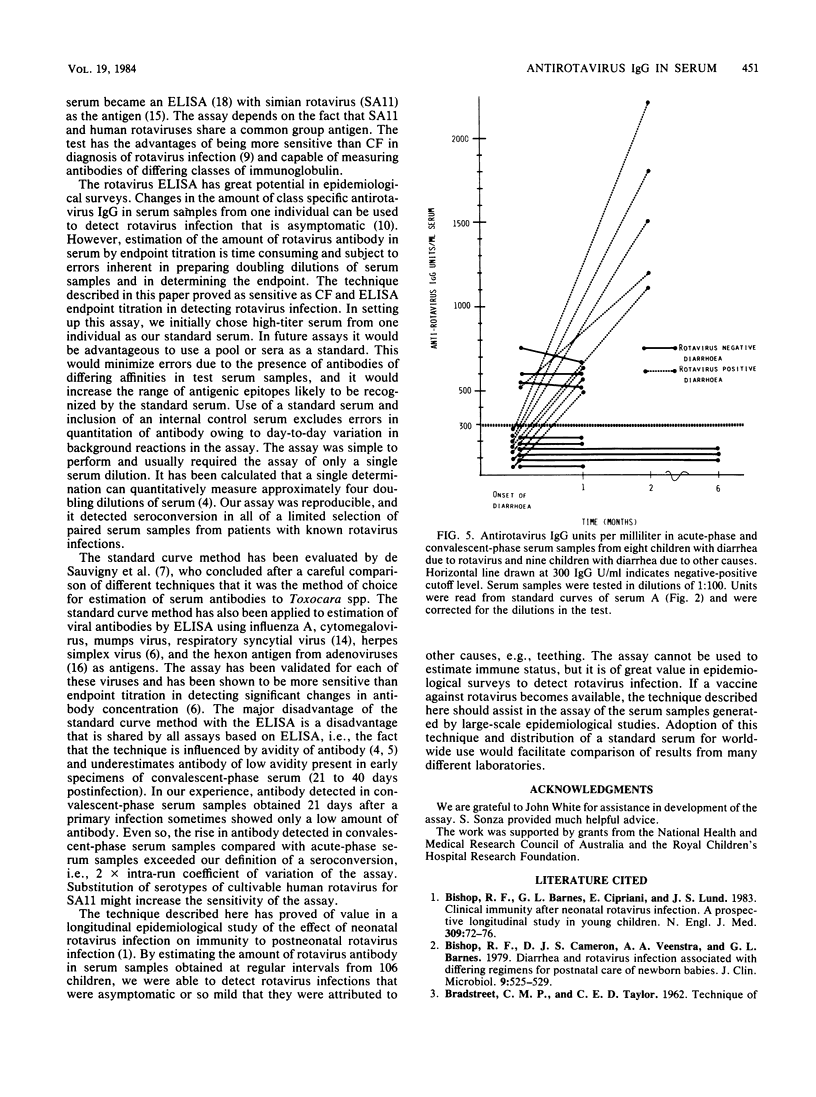
A method for estimating rotavirus immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies by assay of human serum samples at a single serum dilution was studied. Antibody was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The optical density of the reaction with a 1:100 dilution of each serum was expressed as ELISA units of antirotavirus IgG by reference to a standard curve. This standard curve was obtained by incorporation in each assay of five dilutions of a serum containing an arbitrary number of units of antirotavirus IgG. Test serum samples found to contain high amounts of antirotavirus IgG were reassayed at a 1:1,000 dilution. There was good correlation between antirotavirus IgG ELISA units in 45 serum samples and endpoint titers of the same samples (Spearman rank correlation coefficient rs, 0.95). Seroconversion during rotavirus infection was defined as an increase in antirotavirus IgG ELISA units per milliliter of greater than 28% (2 X intra-run coefficient of variation of the assay) in consecutive serum samples from the same child. Paired serum samples from nine children with diarrhea not due to rotavirus infection showed no seroconversions. Paired samples from eight children with rotavirus infection showed seroconversions. Estimation of antirotavirus IgG ELISA units in serum is simple, rapid, reproducible, and economical of serum samples. Standardization of results could be achieved by worldwide distribution of a standard serum. Its use would facilitate epidemiological surveys to evaluate potential rotavirus vaccines.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADSTREET C. M., TAYLOR C. E. Technique of complementfixation test applicable to the diagnosis of virus diseases. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1962 May;21:96–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Barnes G. L., Cipriani E., Lund J. S. Clinical immunity after neonatal rotavirus infection. A prospective longitudinal study in young children. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jul 14;309(2):72–76. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198307143090203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Cameron D. J., Veenstra A. A., Barnes G. L. Diarrhea and rotavirus infection associated with differing regimens for postnatal care of newborn babies. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):525–529. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.525-529.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock S. L., Walls K. W. Evaluation of some of the parameters of the enzyme-linked immunospecific assay. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136 (Suppl):S279–S285. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_2.s279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. E., Feldbush T. L., McGivern P. L., Stewart N. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): a measure of antibody concentration or affinity. Immunochemistry. 1978 Feb;15(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer N. E., Cossen C. K., Hanson C. V., Shell G. R. Evaluation and reporting of enzyme immunoassay determinations of antibody to herpes simplex virus in sera and cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):815–823. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.815-823.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Bryden A. S., Davies H., Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Derrick J. M. Relation between viruses from acute gastroenteritis of children and newborn calves. Lancet. 1974 Jul 13;2(7872):61–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91631-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghose L. H., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Comparison of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitation of rotavirus antibodies with complement fixation in an epidemiological survey. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):268–276. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.268-276.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurwith M., Wenman W., Hinde D., Feltham S., Greenberg H. A prospective study of rotavirus infection in infants and young children. J Infect Dis. 1981 Sep;144(3):218–224. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.3.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gust I. D., Pringle R. C., Barnes G. L., Davidson G. P., Bishop R. F. Complement-fixing antibody response to rotavirus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):125–130. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.125-130.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Cline W. L., Mebus C. A., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., James H. D., Jr, VanKirk D., Chanock R. M. New complement-fixation test for the human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Nebraska calf diarrhea virus used as antigen. Lancet. 1975 May 10;1(7915):1056–1061. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91827-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Rodriguez W. J., Ross S., Cline W. L., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Reoviruslike agent in stools: association with infantile diarrhea and development of serologic tests. Science. 1974 Sep 20;185(4156):1049–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4156.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinikki P. O., Passila S. Quantitative, semiautomated, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for viral antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136 (Suppl):S294–S299. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_2.s294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean B., Sonza S., Holmes I. H. Measurement of immunoglobulin A, G, and M class rotavirus antibodies in serum and mucosal secretions. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):314–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.314-319.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggendorf M., Wigand R., Deinhardt F., Frösner G. G. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for acute adenovirus infection. J Virol Methods. 1982 Feb;4(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenman W. M., Hinde D., Feltham S., Gurwith M. Rotavirus infection in adults. Results of a prospective family study. N Engl J Med. 1979 Aug 9;301(6):303–306. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197908093010604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Kim H. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Immunological response to infection with human reovirus-like agent: measurement of anti-human reovirus-like agent immunoglobulin G and M levels by the method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):540–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.540-546.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Savigny D., Voller A. The communication of ELISA data from laboratory to clinician. J Immunoassay. 1980;1(1):105–128. doi: 10.1080/01971528008055779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


