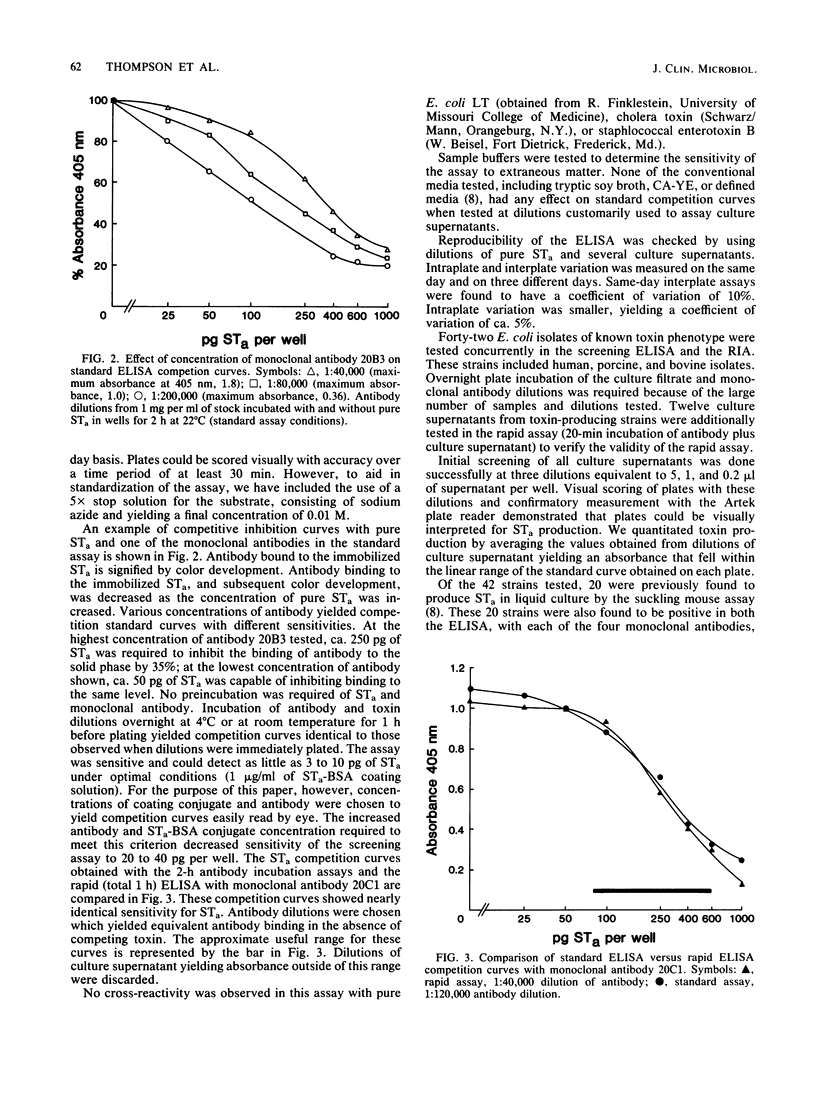
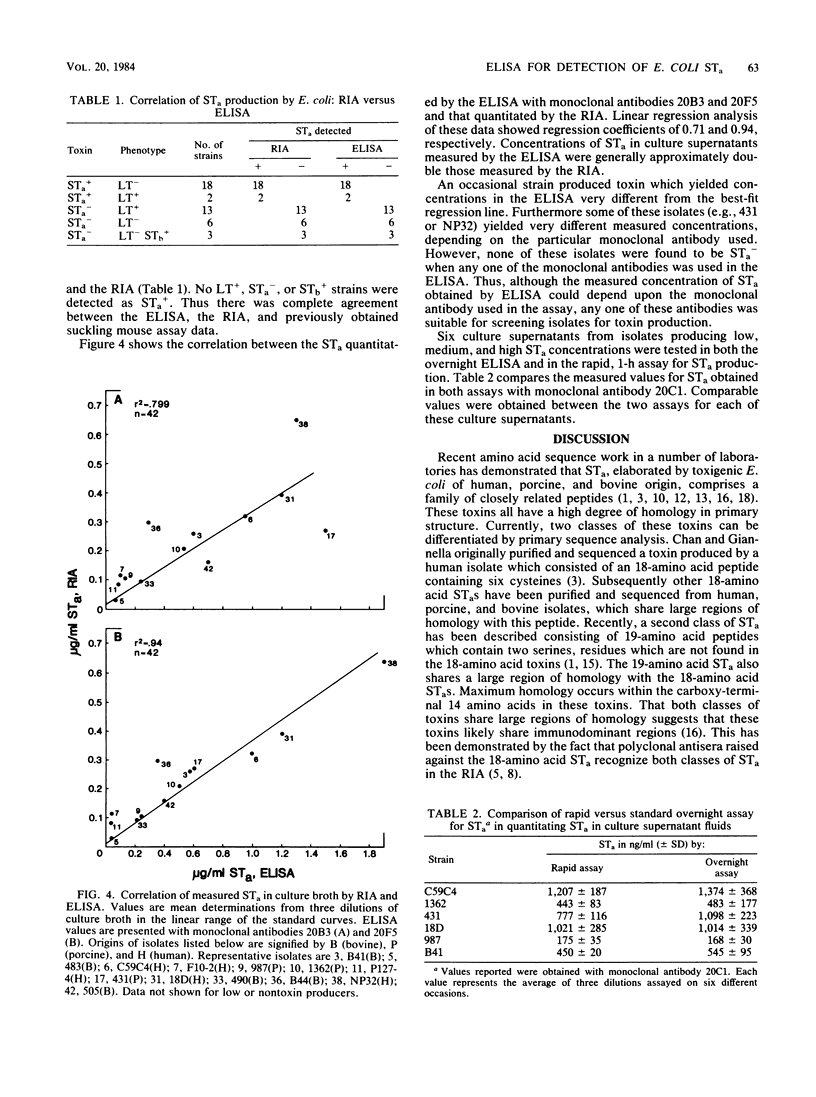
Abstract
We have developed a sensitive and specific competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxins consisting of methanol-soluble, suckling mouse active peptides with similar core sequences (STa) by using monoclonal antibodies prepared against STa purified from a human isolate. The assay can detect 3 to 20 pg of purified STa, depending on the monoclonal antibody used in the assay. The assay is rapid, requiring ca. 1 h to complete. With this competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, we measured STa production by enterotoxigenic E. coli directly in Casamino Acid-yeast extract culture supernatants. The assay was suitable for measuring STa in culture supernatants from human, bovine, and porcine E. coli isolates. No cross-reactivity was observed with heat-labile enterotoxin, cholera toxin, or heat-stable enterotoxin STb, which is a methanol-insoluble peptide(s) active in the ligated pig jejunal loop test. A 100% correlation of toxin production was found by comparing the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with the previously established radioimmunoassay for STa and with suckling mouse activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aimoto S., Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Takeda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Amino-acid sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin produced by human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):257–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Bywater R. J., Cowley C. M., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Biological evaluation of a methanol-soluble, heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice, pigs, rabbits, and calves. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.526-531.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. K., Giannella R. A. Amino acid sequence of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Escherichia coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7744–7746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Frantz J. C., Robertson D. C. Chemical properties of heat-stable enterotoxins produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of different host origins. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.539-548.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Drake K. W., Luttrell M. Development of a radioimmunoassay for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin: comparison with the suckling mouse bioassay. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):186–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.186-192.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman P. E. Production and evaluation of antibody to the heat-stable enterotoxin from a human strain of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Oct;42(4):611–614. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.4.611-614.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazure C., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Lallier R., St-Pierre S. Primary structure determination of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin of porcine origin. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 May;61(5):287–292. doi: 10.1139/o83-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W. Pathogenesis of enteric diseases caused by Escherichia coli. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1974;18(0):179–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Hardy J. W., Hug M. I., Echeverria P., Falkow S. Isolation and nucleotide sequence determination of a gene encoding a heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1167–1174. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1167-1174.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnberg B., Wadström T., Jörnvall H. Structure of a heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a human strain of Escherichia coli. Differences from the toxin of another human strain suggest the presence of compensated amino acid exchanges. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 8;155(2):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80598-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeed A. M., Sriranganathan N., Cosand W., Burger D. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin from bovine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):701–707. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.701-707.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The relationship between two apparently different enterotoxins produced by enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli of porcine origin. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):387–401. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples S. J., Asher S. E., Giannella R. A. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a strain of E. coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4716–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


