Abstract
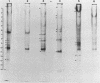
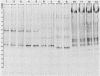
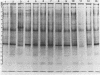
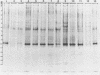
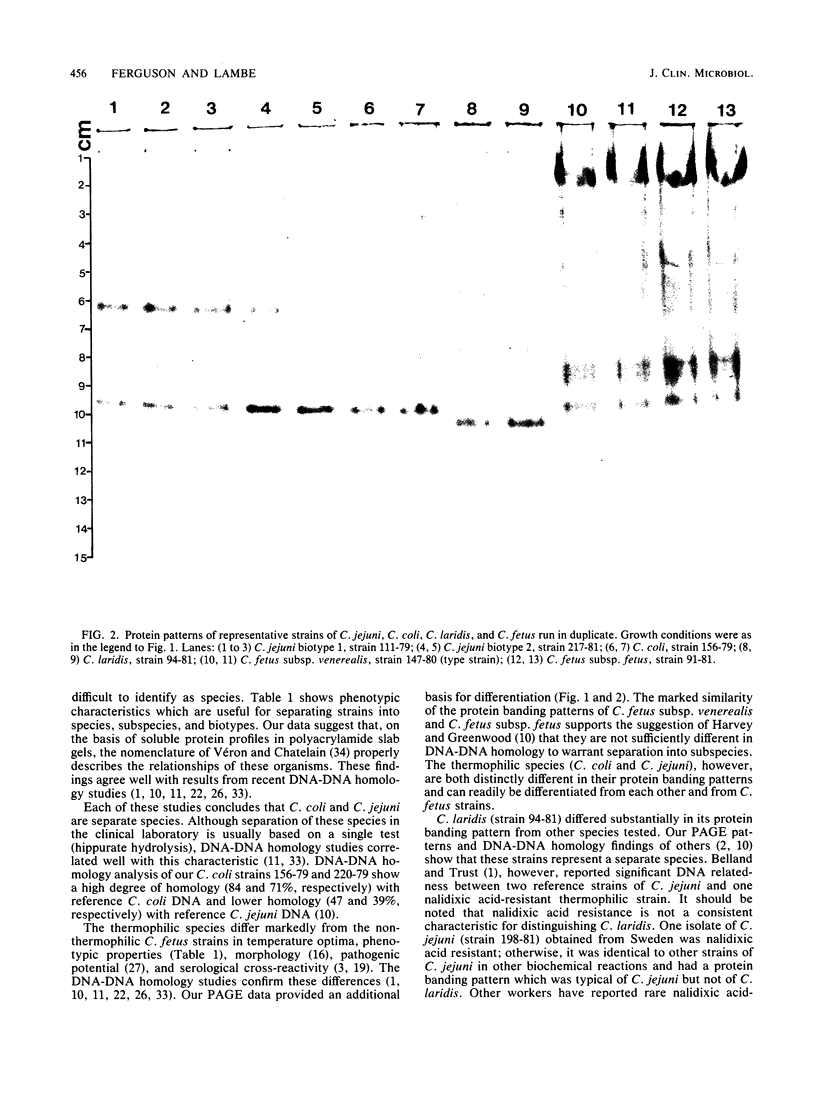
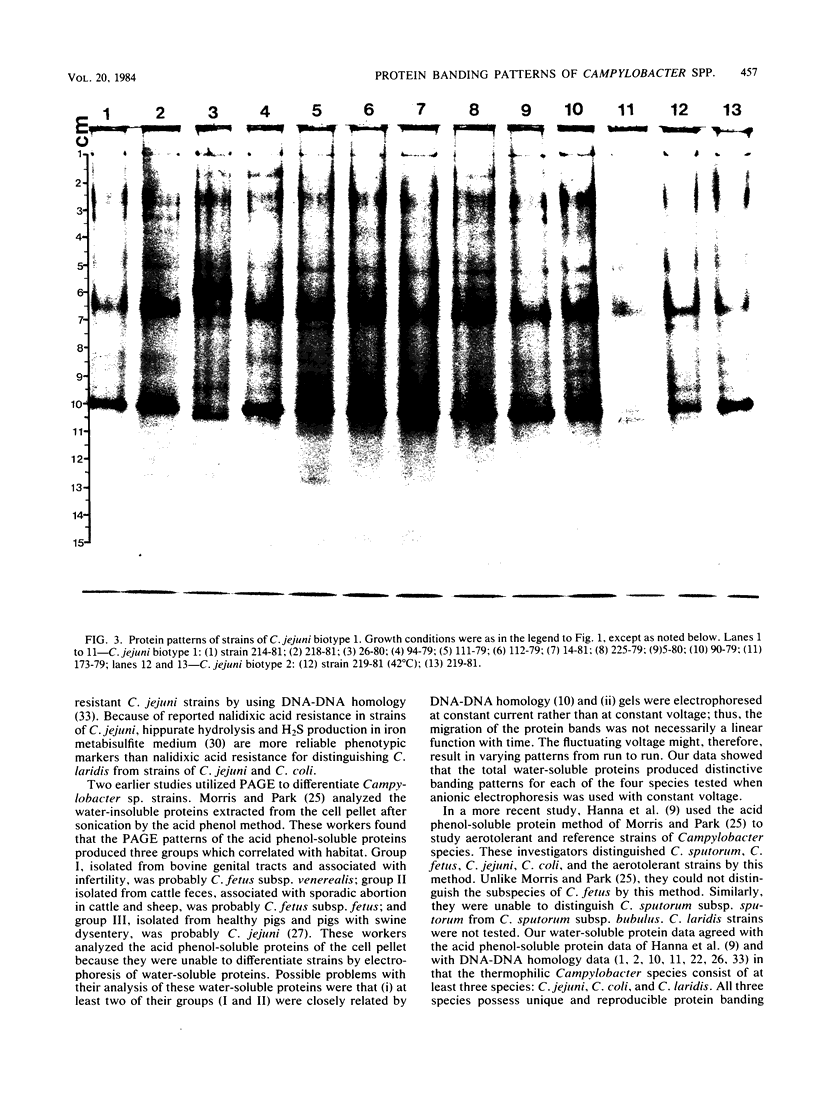
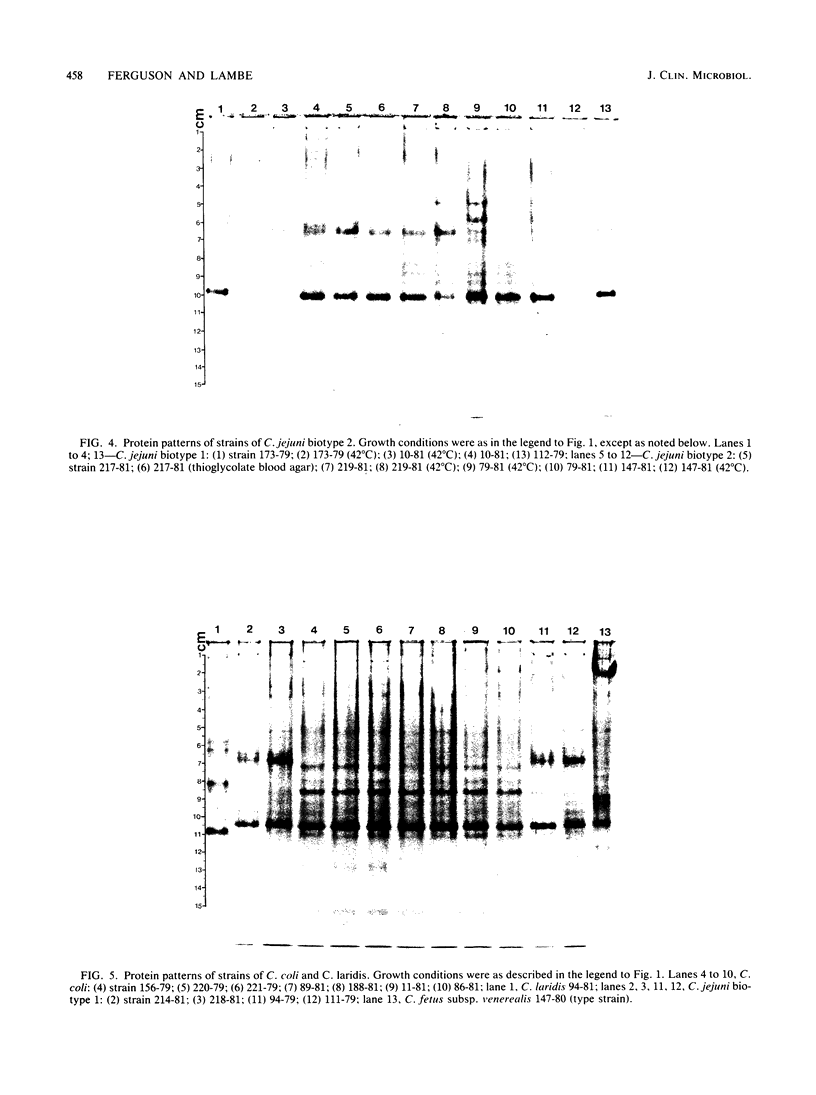
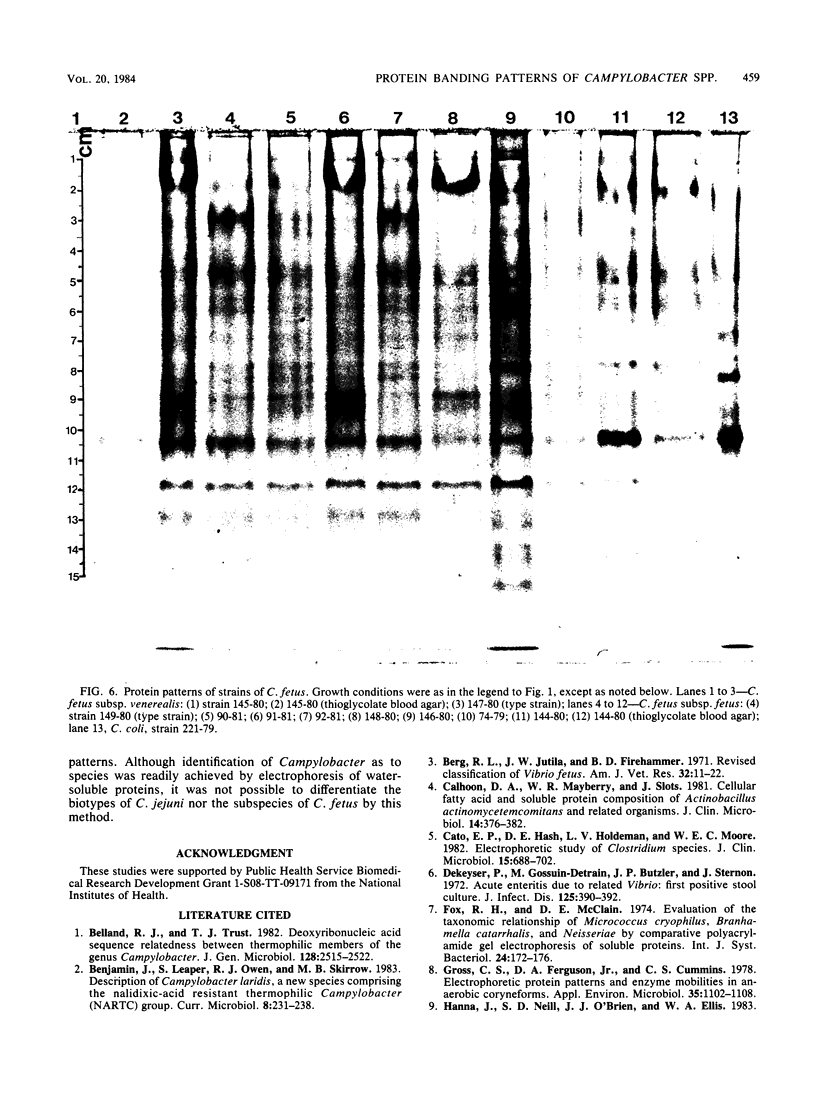
Soluble protein extracts of 37 catalase-positive strains of Campylobacter species were examined by polyacrylamide slab gel electrophoresis (PAGE). Electrophoretic banding patterns showed good correlation with biochemical tests and with available DNA homology data in distinguishing species of Campylobacter but did not differentiate subspecies or biotypes. PAGE patterns indicated that Campylobacter coli is a distinct species. Furthermore, the PAGE patterns indicated that C. jejuni and nalidixic acid-resistant thermophilic Campylobacter species (C. laridis) are each distinct species. The protein banding patterns of C. fetus subsp. venerealis and C. fetus subsp. fetus strains were distinctly different from those of the three thermophilic species.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belland R. J., Trust T. J. Deoxyribonucleic acid sequence relatedness between thermophilic members of the genus Campylobacter. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Nov;128(11):2515–2522. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-11-2515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. L., Jutila J. W., Firehammer B. D. A revised classification of Vibrio fetus. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Jan;32(1):11–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoon D. A., Mayberry W. R., Slots J. Cellular fatty acid and soluble protein composition of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and related organisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Oct;14(4):376–382. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.4.376-382.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato E. P., Hash D. E., Holdeman L. V., Moore W. E. Electrophoretic study of Clostridium species. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):688–702. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.688-702.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekeyser P., Gossuin-Detrain M., Butzler J. P., Sternon J. Acute enteritis due to related vibrio: first positive stool cultures. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):390–392. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross C. S., Ferguson D. A., Jr, Cummins C. S. Electrophoretic protein patterns and enzyme mobilities in anaerobic coryneforms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1102–1108. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1102-1108.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Steigerwalt A. G., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J. Serogroups of Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and Campylobacter fetus defined by direct immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Mar;17(3):529–538. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.3.529-538.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis A. W., Wolff J. M. Grouping of lactic streptococci by gel electrophoresis of soluble cell extracts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):391–398. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.391-398.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O. Human infections with Vibrio fetus and a closely related vibrio. J Infect Dis. 1957 Sep-Oct;101(2):119–128. doi: 10.1093/infdis/101.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersters K., De Ley J. Identification and grouping of bacteria by numerical analysis of their electrophoretic protein patterns. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):333–342. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosunen T. U., Danielsson D., Kjellander J. Serology of Campylobacter fetus ss. jejuni )"related" campylobacters). Demonstration of strain-specific and interstrain-related antigens by immunoelectrophoresis and co-agglutination. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Aug;88(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambe D. W., Jr, Ferguson D. A., Jr, Wiener S. L., Butzler J. P. Campylobacter fetus ssp jejuni: isolation from patients with gastroenteritis. South Med J. 1981 Feb;74(2):157–161. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198102000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Hash D. E., Holdeman L. V., Cato E. P. Polyacrylamide slab gel electrophoresis of soluble proteins for studies of bacterial floras. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):900–907. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.900-907.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. A., Park R. W. A comparison using gel electrophoresis of cell proteins of campylobacters (vibrios) associated with infertility, abortion and swine dysentery. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Sep;78(1):165–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-1-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig P. J. Campylobacter infections in human beings. J Pediatr. 1979 Jun;94(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Benjamin J. Differentiation of enteropathogenic Campylobacter. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Nov;33(11):1122–1122. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.11.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom A., Dyer J. K., Marsh C., Tribble J. L. Identification and characterization of species of the family Bacteriodaceae by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Dent Res. 1976 Mar-Apr;55(2):252–256. doi: 10.1177/00220345760550021501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]