Abstract
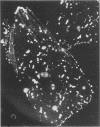
Palatine tonsils of 143 slaughtered pigs aged 4 to 6 months were investigated for the presence of Streptococcus suis type 2. Slices (50 micron) of frozen tonsils were cultured on a selective agar medium containing antibodies against S. suis type 2 in which colonies of this bacterium showed a halo of immunoprecipitation. When tonsils were sectioned in one plane S. suis type 2 was found in 45 of 143 pigs (32%). This percentage increased to 50% when tonsils were sectioned in more then one plane, which was done on 55 tonsils. The first 45 strains showing a ring of immunoprecipitation were studied and found to be biochemically identical to our reference strain 735 (de Moor) and to 23 isolates from human patients with meningitis. In slices incubated for 24 h at 37 degrees C on selective agar plates and stained with hematoxylin and eosin after fixation, it could be demonstrated that S. suis type 2 was confined to the crypt lumen. The same was true in sections fixed directly (without incubation) that were stained by an indirect immunoperoxidase method with a rabbit anti-S. suis type 2 serum.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chattopadhyay B. Group R streptococcal infection amongst pig meat handlers. A review. Public Health. 1979 May;93(3):140–142. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3506(79)80117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifton-Hadley F. A., Alexander T. J. The carrier site and carrier rate of Streptococcus suis type II in pigs. Vet Rec. 1980 Jul 12;107(2):40–41. doi: 10.1136/vr.107.2.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel H. W., Narucka U., Westendorp J. F. Streptococcen bij slachtvarkens. Tijdschr Diergeneeskd. 1974 Nov 15;99(22):1162–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyderman E. Immunoperoxidase technique in histopathology: applications, methods, and controls. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Oct;32(10):971–978. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.10.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. E. The serological classification of streptococci isolated from diseased pigs. Br Vet J. 1976 Mar-Apr;132(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)34738-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunter E. Bericht des Streptokokken-Referenzzentrums über die 1968-1980 von Schweinen isolierten Streptokokken. 1. Mitteilung: Serologische Gruppenzugehörigkeit und pathogene Bedeutung. Arch Exp Veterinarmed. 1982;36(2):279–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont M. H., Edwards P. T., Windsor R. S. Streptococcal meningitis in pigs: results of a five-year survey. Vet Rec. 1980 Nov 15;107(20):467–469. doi: 10.1136/vr.107.20.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels R. H., Stonebraker F. E., Robbins J. B. Use of antiserum agar for detection of Haemophilus influenzae type b in the pharynx. Pediatr Res. 1975 May;9(5):513–516. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197505000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perch B., Kristjansen P., Skadhauge K. Group R streptococci pathogenic for man. Two cases of meningitis and one fatal case of sepsis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;74(1):69–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perch B., Pedersen K. B., Henrichsen J. Serology of capsulated streptococci pathogenic for pigs: six new serotypes of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):993–996. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.993-996.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porcine streptococci causing meningitis and septicaemia in man. Lancet. 1975 Jun 7;1(7919):1286–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Lawson G. H., Rowland A. C. Streptococcal infection in piglets: the palatine tonsils as portals of entry for Streptococcus suis. Res Vet Sci. 1973 Nov;15(3):352–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windsor R. S., Elliott S. D. Streptococcal infection in young pigs. IV. An outbreak of streptococcal meningitis in weaned pigs. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Aug;75(1):69–78. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400047070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanen-Lim O. G., Zanen H. C. Postmortem bacteriology of the lung by printculture of frozen tissue. A technique for in situ culture of microorganisms in whole frozen organs. J Clin Pathol. 1980 May;33(5):474–480. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.5.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]