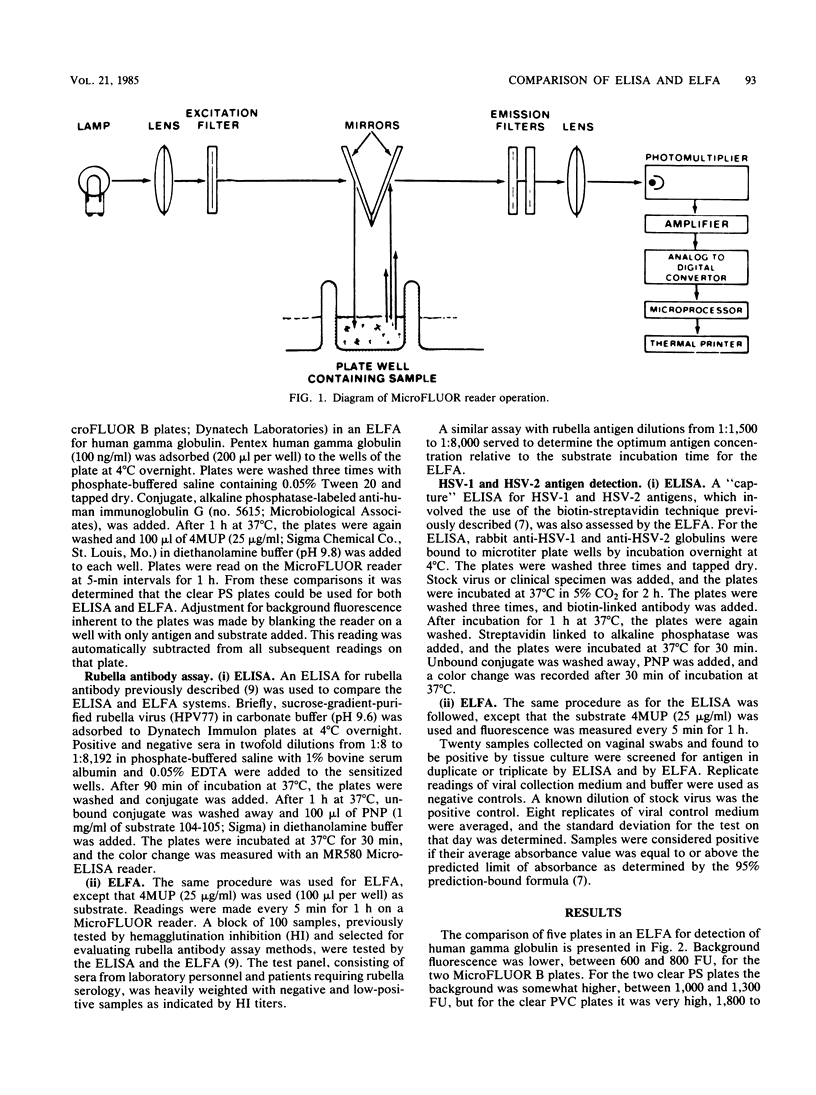
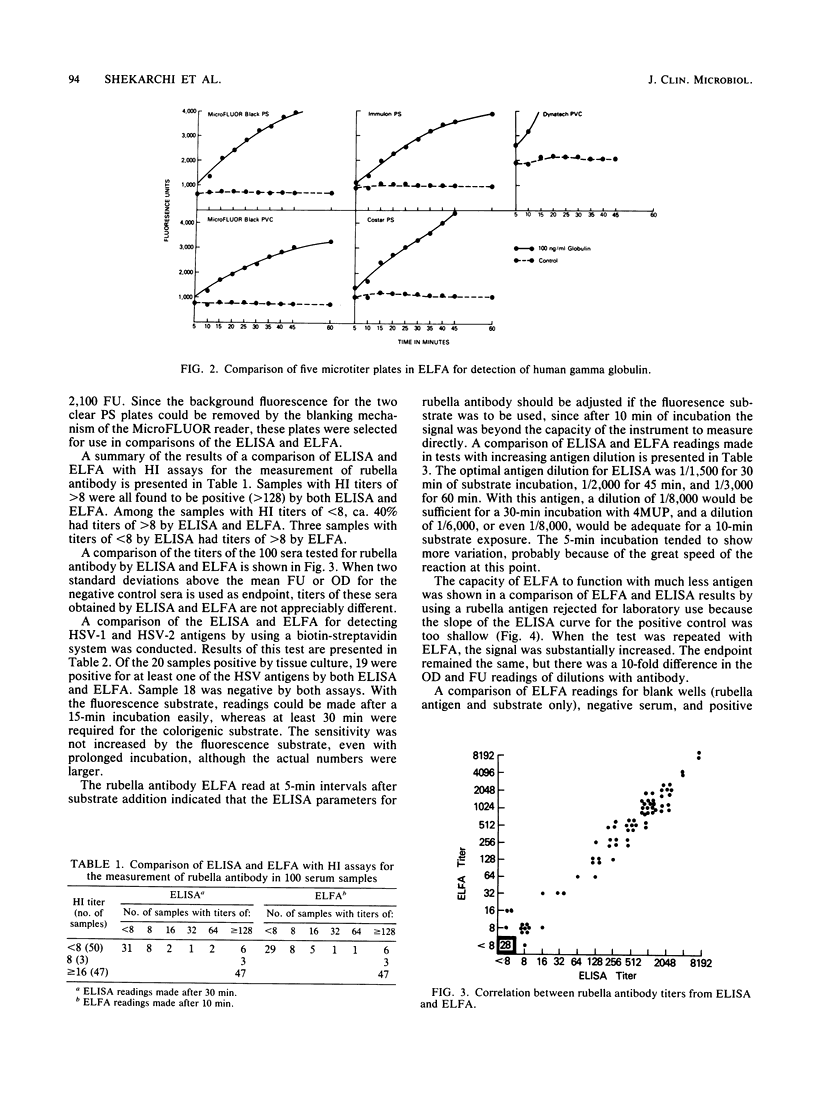
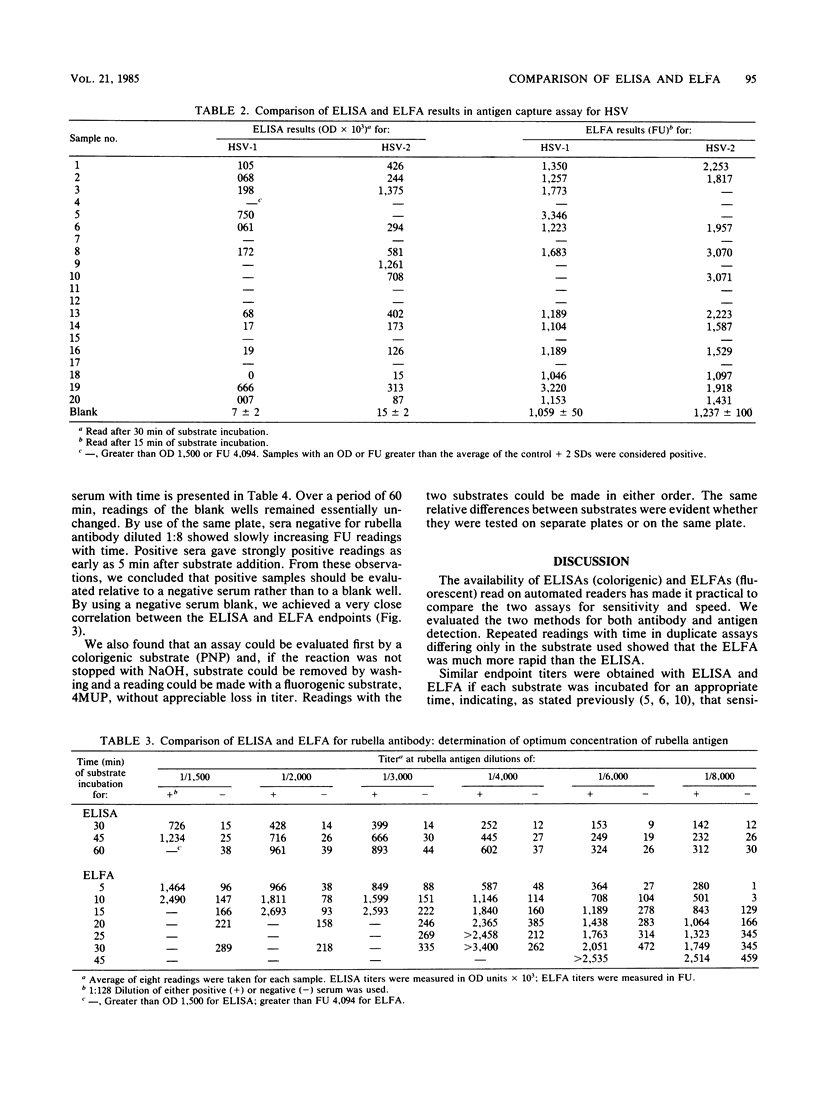
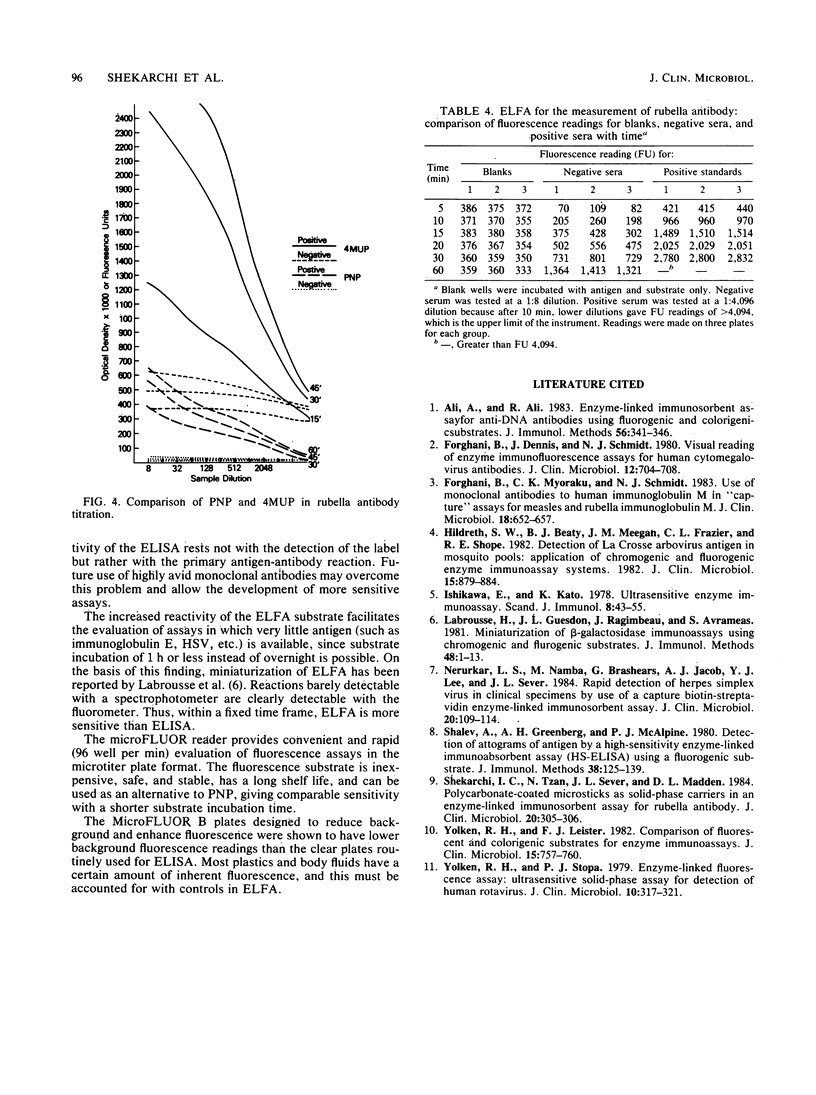
Abstract
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was compared with the enzyme-linked fluorescence assay (ELFA) for the detection of rubella antibody and herpes simplex virus antigen. Test parameters, specimens, antigen or antibody, and conjugates for the two types of assays were identical except that p-nitrophenyl phosphate was used as the substrate for the ELISA and 4-methylumbelliferyl phosphate was used as the substrate for ELFA. Automated readers were used for both assays. Antibody titers and sensitivity of antigen detection were quite similar for ELISA and ELFA. ELFA for rubella antibody, however, could be conducted with less antigen or shorter substrate incubation time (5 min for ELFA versus 30 min for ELISA). For herpes simplex virus antigen detection, ELFA could also be read after a shorter substrate incubation time (15 min for ELFA versus 30 min for ELISA). Clear polystyrene microtiter plates routinely used for ELISA could be used for ELFA, but clear polyvinyl chloride plates had high background fluorescence. Black polystyrene and polyvinyl chloride plates gave lower background fluorescence than did clear plates. ELFA is of particular value as a substitute for ELISAs in which long substrate incubations are required or antigens of only low titer are available.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali A., Ali R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for anti-DNA antibodies using fluorogenic and colorigenic substrates. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 11;56(3):341–346. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(83)80023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Dennis J., Schmidt N. J. Visual reading of enzyme immunofluorescence assays for human cytomegalovirus antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):704–708. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.704-708.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Myoraku C. K., Schmidt N. J. Use of monoclonal antibodies to human immunoglobulin M in "capture" assays for measles and rubella immunoglobulin M. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):652–657. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.652-657.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildreth S. W., Beaty B. J., Meegan J. M., Frazier C. L., Shope R. E. Detection of La Crosse arbovirus antigen in mosquito pools: application of chromogenic and fluorogenic enzyme immunoassay systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):879–884. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.879-884.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerurkar L. S., Namba M., Brashears G., Jacob A. J., Lee Y. J., Sever J. L. Rapid detection of herpes simplex virus in clinical specimens by use of a capture biotin-streptavidin enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):109–114. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.109-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalev A., Greenberg A. H., McAlpine P. J. Detection of attograms of antigen by a high-sensitivity enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay (HS-ELISA) using a fluorogenic substrate. J Immunol Methods. 1980;38(1-2):125–139. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90337-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shekarchi I. C., Tzan N., Sever J. L., Madden D. L. Polycarbonate-coated microsticks as solid-phase carriers in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for rubella antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):305–306. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.305-306.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Leister F. J. Comparison of fluorescent and colorigenic substrates for enzyme immunoassays. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):757–760. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.757-760.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Stopa P. J. Enzyme-linked fluorescence assay: Ultrasensitive solid-phase assay for detection of human rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.317-321.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


