Abstract
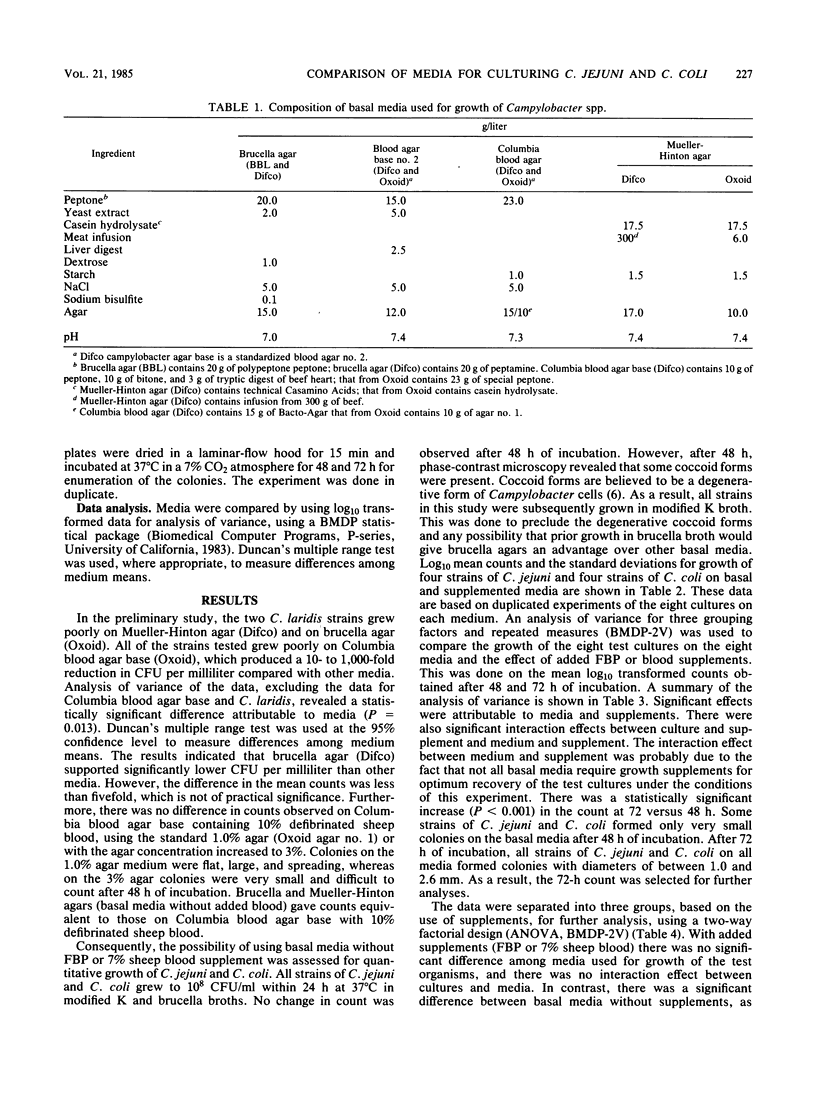
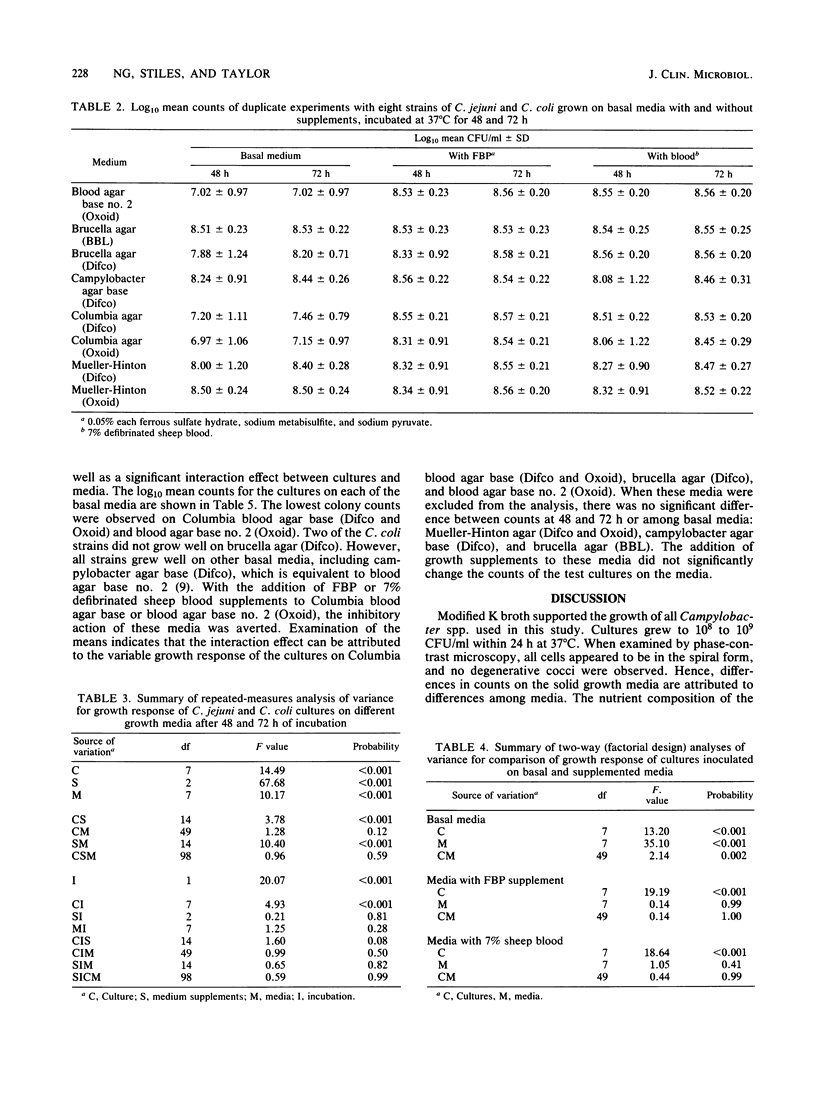
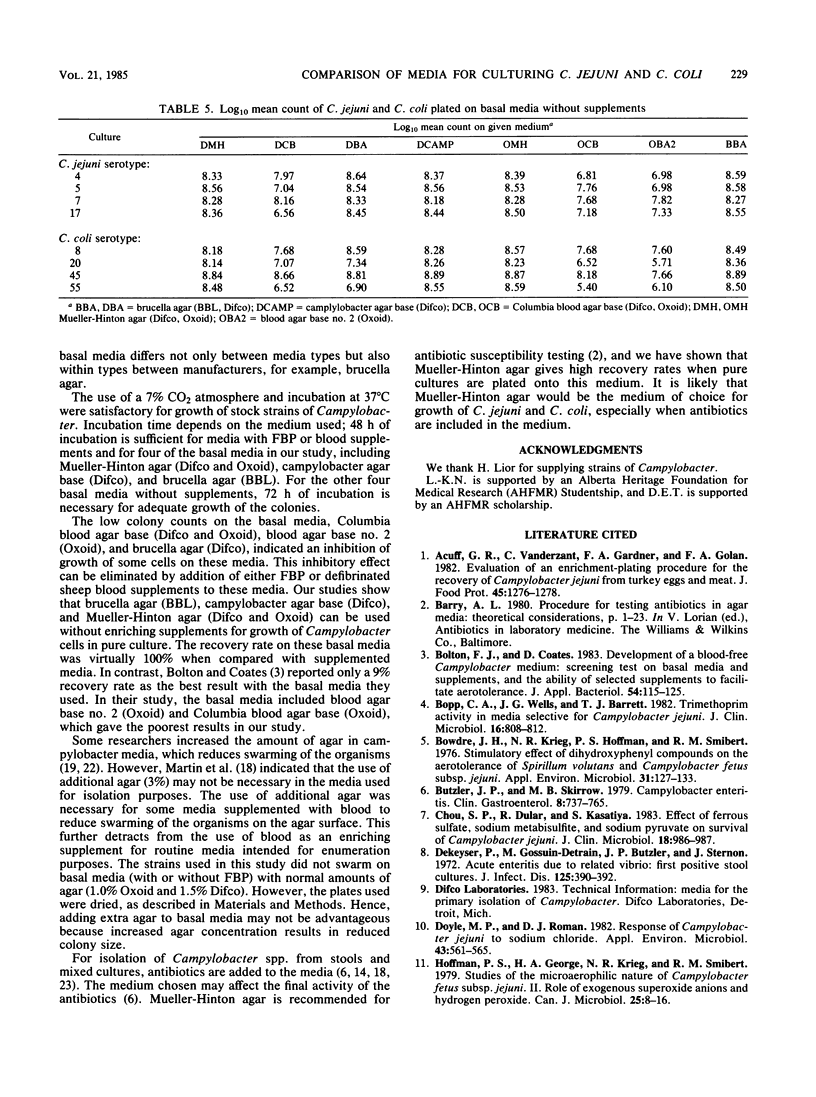
Four strains of Campylobacter jejuni and four strains of Campylobacter coli were used to compare the quantitative growth of Campylobacter cells on blood agar base no. 2 (Oxoid), brucella agar (BBL Microbiology Systems and Difco Laboratories), campylobacter agar base (Difco), Columbia blood agar base (Difco and Oxoid), and Mueller-Hinton agar (Difco and Oxoid). Columbia blood agar base and blood agar base no. 2 were inhibitory to most of the strains tested, as evidenced by reduced (10- to 1,000-fold) colony counts compared with other basal media. One of the brucella agars was inhibitory to two of the C. coli strains. The inhibitory effect of these media could be eliminated by addition of FBP (0.05% each ferrous sulfate hydrate, sodium metabisulfite, and sodium pyruvate) or 7% defibrinated sheep blood. However, addition of FBP or blood to brucella agar, campylobacter agar base, or Mueller-Hinton agar did not significantly affect the count, indicating that supplements are not required in these media for growth of Campylobacter in pure culture.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton F. J., Coates D. Development of a blood-free Campylobacter medium: screening tests on basal media and supplements, and the ability of selected supplements to facilitate aerotolerance. J Appl Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;54(1):115–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1983.tb01308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bopp C. A., Wells J. G., Barrett T. J. Trimethoprim activity in media selective for Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):808–812. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.808-812.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowdre J. H., Krieg N. R., Hoffman P. S., Smibert R. M. Stimulatory effect of dihydroxyphenyl compounds on the aerotolerance of Spirillum volutans and Campylobacter fetus subspecies jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jan;31(1):127–133. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.1.127-133.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. P., Dular R., Kasatiya S. Effect of ferrous sulfate, sodium metabisulfite, and sodium pyruvate on survival of Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):986–987. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.986-987.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekeyser P., Gossuin-Detrain M., Butzler J. P., Sternon J. Acute enteritis due to related vibrio: first positive stool cultures. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):390–392. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Roman D. J. Response of Campylobacter jejuni to sodium chloride. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):561–565. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.561-565.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., George H. A., Krieg N. R., Smibert R. M. Studies of the microaerophilic nature of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. II. Role of exogenous superoxide anions and hydrogen peroxide. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jan;25(1):8–16. doi: 10.1139/m79-002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Krieg N. R., Smibert R. M. Studies of the microaerophilic nature of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. I. Physiological aspects of enhanced aerotolerance. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jan;25(1):1–7. doi: 10.1139/m79-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Fleming P. C. Campylobacter enteritis in children. J Pediatr. 1979 Apr;94(4):527–533. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauwers S., De Boeck M., Butzler J. P. Campylobacter enteritis in Brussels. Lancet. 1978 Mar 18;1(8064):604–605. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Woodward D. L., Edgar J. A., Laroche L. J., Gill P. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.761-768.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Molecular identification of surface protein antigens of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):675–682. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.675-682.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. T., Patton C. M., Morris G. K., Potter M. E., Puhr N. D. Selective enrichment broth medium for isolation of Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):853–855. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.853-855.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton C. M., Mitchell S. W., Potter M. E., Kaufmann A. F. Comparison of selective media for primary isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):326–330. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.326-330.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins D. M., Coolbaugh J. C., Walker R. I., Weiss E. Biphasic culture system for rapid Campylobacter cultivation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):284–289. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.284-289.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., De Grandis S. A., Karmali M. A., Fleming P. C. Transmissible plasmids from Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):831–835. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesley R. D., Swaminathan B., Stadelman W. J. Isolation and enumeration of Campylobacter jejuni from poultry products by a selective enrichment method. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1097–1102. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1097-1102.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


