Abstract
Tributyltin chloride (TBT-Cl) is an endocrine disruptor found in many animal species, and it is also known to be an inhibitor for the V-ATPases that are emerging as potential targets in the treatment of diseases such as osteoporosis and cancer. We demonstrated by using biochemical and single-molecular imaging techniques that TBT-Cl arrests an elementary step for rotary catalysis of the V1 motor domain. In the presence of TBT-Cl, the consecutive rotation of V1 paused for a long duration (∼0.5 s), even at saturated ATP concentrations, and the pausing positions were localized at 120° intervals. Analysis of both the pausing time and moving time revealed that TBT-Cl has little effect on the binding affinity for ATP, but, rather, it arrests the catalytic event(s). This is the first report to demonstrate that an inhibitor arrests an elementary step for rotary catalysis of a V-type ATP-driven rotary motor.
Introduction
Tributyltin chloride (TBT-Cl) has been used widely as an antiseptic, especially as a disinfecting agent on ships. This practice has caused severe contamination of the aquatic ecosystem (1). TBT-Cl is also known to be an endocrine disruptor in many animal species, and it produces a wide range of irritant and toxic effects on mammals (2). However, the precise mechanism of toxicity of TBT-Cl is not well understood.
Vacuolar type ATPases (V-ATPases), which function in a variety of physiologic processes (3), have been reported as targets of TBT-Cl (4–6). In eukaryotic cells, V-ATPases reside within the membranes of intracellular compartments that include endosomes, lysosomes, and secretory vesicles, and within plasma membranes of certain cells, such as osteoclasts. The eukaryotic V-ATPases couple ATP hydrolysis to transmembrane proton translocation. The related enzymes of eukaryotic V-ATPases were found in some bacteria. These prokaryotic V-ATPases function as either ATP synthases or as sodium pumps (7,8).
The V-ATPases are related to the F-type ATP synthase (F-ATPase) in that they are comprised of membrane-embedded subunits, wherein Vo is equivalent to Fo, complexed with peripheral subunits, wherein V1 is equivalent to F1 (3). Similarly to the F-ATPase holoenzyme, the V-ATPase holoenzyme couples ATP hydrolysis by V1 to ion translocation through Vo, using a rotary mechanism (9,10).
The prokaryotic V-type ATPase/synthases from a thermophilic eubacterium, Thermus thermophilus (T. thermophilus), have a simpler subunit composition than that of eukaryotic V-ATPases (11,12). The hydrophilic V1 domain of T. thermophilus is an ATPase made up of four kinds of subunits with A3B3D1F1 stoichiometry. The catalytic A and B subunits in V1 show an apparent sequence similarity to the β and α subunits of F1, respectively (13). In contrast, the D and F subunits, which constitute a rotor shaft in V1 (9), show no sequence homology to either the γ or ɛ subunit of F1. Unlike the isolated Vo domain of eukaryotic V-ATPases, the Vo domain isolated from T. thermophilus has proton permeability (14).
It has been shown that the macrolide antibiotics bafilomycin A1 and concanamycin specifically inhibit proton pump activity of eukaryotic V-ATPases (15). Treatment of cells with these antibiotics has been shown to inhibit physiologic processes such as autophagy and Bax-dependent apoptosis (16), as well as cell proliferation (17). From genetic studies using yeasts, Wang et al. found that subunit a, which is a part of the proton channel in Vo, participates in bafilomycin binding (18). Loss of V-ATPase activity in cells affects several physiologic processes, and therefore, V-ATPases can be very useful in drug development. Thus, it is important to investigate inhibitory mechanisms of V-ATPase inhibitors in detail.
Ballmoos et al. (19) reported that subunit a in Fo of bacterial ATP synthase is specifically labeled upon photo-inactivation with an aryldiazirine derivative of TBT-Cl. In contrast, ATPase activity of isolated F1 is not inhibited by TBT-Cl (20). In the case of V-ATPases, subunits in V1 and Vo have been reported to be targets of different organotin inhibitors. Irradiation of the V-ATPase in bovine adrenal chromaffin granules with a radioactive organotin photo-affinity analog led to labeling of catalytic subunit A in the V-ATPase (5). In contrast, organotin flavone complexes were found to interact with the 16 k-Da proteolipid subunit in Vo of the Nephrops noevegicus V-ATPase (4).
In this study, we report the detailed inhibitory effects of TBT-Cl on the T. thermophilus V-ATPase using both bulk-phase and single-molecule analysis. From this analysis, we propose a mechanism for inhibition of rotational catalysis in V1 by utilization of TBT-Cl.
Materials and Methods
Protein preparation
A mutant A(His-8/C28S/S232A/T235S/C508S)3B(C264S)3D(E48C/Q55C)F (V1) and the subcomplex A(His-8/C28S/S232A/T235S/C508S)3B(C264S)3D(E48C/Q55C) (V1ΔF) derived from T. thermophilus were expressed and purified as described previously (21). For single-molecule experiments, the V1 and V1ΔF were biotinylated at two cysteines located in subunit D by incubation with three-fold molar excess of N-6-(Biotinylamino)hexanoyl-N′-[2-(N-maleimido)ethyl]piperazine, hydrochloride (Dojindo) for 1 h at room temperature. Unreacted reagents were removed with NAP5-column (GE Healthcare, Buckinghamshire, UK), and the biotinylated proteins were immediately frozen with liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C. V-ATPase (VoV1 holenzyme) and Vo of T. thermophilus were purified as described previously (14). Protein concentrations were determined with the BCA protein assay (Pierce) for VoV1 and Vo, and absorbance at 280 nm was calibrated by quantitative amino acid analysis for V1 (22). The subcomplex of F1 (α3β3γ), termed F1 unless otherwise noted, was purified as described (23).
Bulk-phase measurements of ATPase activity
The ATPase activity of V1, V1ΔF, V-ATPase holoenzyme, and F1 were determined with an ATP-regenerating system (0.2 mM reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, 0.1 mg/ml pyruvate kinase, 0.1 mg/ml lactate dehydrogenase, and 2 mM phosphoenolpyruvate) in solution R (50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 100 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2 (≤2 mM ATP), and equimolar MgCl2 with >2 mM ATP were contained for V1) at 25°C. 0.05% n-Dodecyl-β-D-maltoside was added to measure the ATPase activity of the V-ATPase holoenzyme.
Measurements of proton permeability of Vo-liposomes
Membrane vesicles (44 mg/ml) pretreated with phospholipid (soybean L-α-phosphatidylcholine, type II-S, Sigma Chemical, St. Louis, MO) were suspended in solution A (10 mM HEPES/KOH, pH 7.5, 5 mM MgSO4, 10% glycerol) and sonicated for 5 min at 4°C, and 20 μl of Vo solution (5 mg/ml) was added to 180 μl of the suspension. The mixture was gently stirred, then frozen with liquid nitrogen and thawed at room temperature. For loading with potassium ion, the Vo-liposome was pelleted by centrifugation (200,000 × g, 20 min, 4°C) and incubated with 200 μl of 0.25 M potassium gluconate at 50°C for 30 min. For measurement purposes, the potassium-loaded Vo-liposome was pelleted by centrifugation (200,000 × g, 20 min, 4°C) and resuspended in solution B (10 mM HEPES/NaOH, pH 7.5, 5 mM MgSO4, 0.25 M sucrose). Proton permeability was measured as described previously (11). The various concentrations of TBT-Cl were preincubated with Vo-liposome suspension for 1 h at 4°C. The initial assay mixture contained 50 μg/ml proteoliposome and 0.2 μM 9-amino-6-chloro-2-methoxyacridine in solution B, and the reactions were initiated by injecting 20 μM valinomycin. The assays were carried out at 40°C. 0.1 μM carbonylcyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone was added at the end of assays to check the extent of 9-amino-6-chloro-2-methoxyacridine quenching.
Single-molecule analysis
We measured the ATPase activity of V1 by observing rotating beads attached to the D subunit surrounded by the A3B3 ring, which was fixed on a Ni2+-NTA-modified cover glass by His-tags. A flow chamber was assembled from the cover glass (objective side) and a slide glass with two spacers of 50-μm thickness. The inner glass surface was coated with bovine serum albumin (Sigma) by infusion of solution R containing 2 mg/ml bovine serum albumin to avoid nonspecific interaction. 20 μl of biotinylated enzyme (50 nM in solution R) was infused to the chamber. After 5 min of incubation, 0.03% streptavidin-coated beads (ϕ = 209 nm, Polyscience, Warrington, PA) in solution R were infused and incubated for 8 min to attach the bead to enzyme. Observation of rotation was initiated by infusing the solution R that contained the indicated concentrations of ATP and TBT-Cl and the solution R was supplemented with the ATP-regenerating system. All procedures were done after washing the chamber with solution R. Rotating duplex beads were observed with a dark-field microscope (IX-70; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) with a dark-field condenser (numerical apertures 1.2–1.4, Olympus) and a ×100 objective (numerical apertures 0.5–1.35, Olympus). The images of rotating beads were recorded with a 1- or 2-ms time resolution as an 8-bit Audio Video Interleave file with a complementary metal oxide semiconductor high-speed camera (Hi-DcamII, NAC Image Technology, Tokyo, Japan). Custom software (created by Ryohei Yasuda and Kengo Adachi, affiliated with Japan Science and Technology Agency) was used for analyses of the bead movements and dwelling times of steps. Time-averaged rotation speed was calculated from >10 consecutive revolutions. All experiments were done at 25°C.
Results
Effects of TBT-Cl inhibition on V1 and Vo domains
We investigated the effects of TBT-Cl on the ATPase activity of both the V-ATPase holoenzyme and resolved V1 of T. thermophilus by bulk-phase analysis. In this study, the mutant enzymes, which were found to be resistant to ADP-Mg inhibition, were used for the ATPase assay. The properties for ATPase activity of the mutated enzymes were basically similar to those of the wild-type enzymes (21,22). The F1 from thermophilic Bacillus PS3 was also analyzed as a control. As shown in Fig. 1 A, TBT-Cl did not inhibit the ATPase activity of F1 at μM concentrations, consistent with the previous report (20). In contrast, the ATPase activity of V1 was efficiently inhibited as the TBT-Cl concentration increased. The estimated Ki value for TBT-Cl inhibition was 11.6 ± 0.7 μM (mean ± SE) (Fig. 1 A, red curve). These results indicate that, unlike F1, TBT-Cl inhibits the ATPase activity of V1. TBT-Cl also inhibited the ATPase activity of the V-ATPase holoenzyme; however, the Ki value was apparently lower than that for V1. To examine the effects of TBT-Cl on the Vo domain alone, the Vo domain was reconstituted into potassium-loaded liposomes, and proton permeability was measured. To prepare potassium-loaded Vo-liposomes, potassium gluconate, rather than potassium chloride, was used, because TBT-Cl alone is known to promote Cl-/H+ symport activity in liposomes (24). The Vo-liposomes preincubated with the various concentrations of TBT-Cl were subjected to the proton permeability experiments. As shown in Fig. 1 B, the untreated Vo-liposomes showed apparent proton permeability. However, after incubation with TBT-Cl, the Vo-liposomes exhibited weaker proton permeability in a dose-dependent manner. The proton permeability of the Vo-liposome was completely abolished by the preincubation with 50 μM TBT-Cl. These results indicate that TBT-Cl interacts with the Vo domain and blocks proton translocation through the Vo domain, suggesting that TBT-Cl affects both the V1 and the Vo domains.
Figure 1.
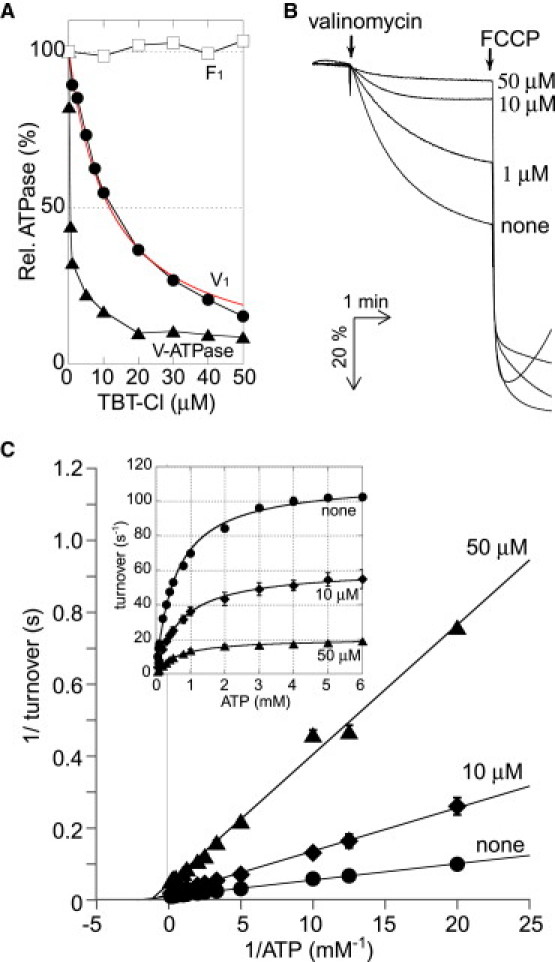
Bulk- phase analysis for effects of TBT-Cl on V-ATPase. (A) The ATPase activities of V1 (●), V-ATPase holoenzyme (▴), and F1 (□) at 4 mM (V1 and V-ATPase holoenzyme) or 2 mM (F1) ATP in the presence of indicated concentrations of TBT-Cl. The Ki value TBT-Cl for inhibition of V1 ATPase activity by TBT-Cl was estimated to be 11.6 ± 0.7 μM by fitting data to the equation v = Vmax[S]/(Km + [S])(1 + [I]/Ki) (red line). The ATPase activities were calculated using averaged values from two or three measurements. (B) Proton permeability of Vo-liposomes in the presence of indicated concentrations of TBT-Cl. The reaction was started by addition of valinomycin, and terminated by injection of FCCP. (C) Lineweaver-Burk plots representing reciprocal of the V1 ATPase activity versus reciprocal of ATP concentrations in the presence of 50 μM (▴), 10 μM (♦), and no TBT-Cl (●). The plots are fitted by linear regression on full data sets. (Inset) [S]-v plots derived from the Lineweaver-Burk plots. The lines show fitting functions with Vmax = 21.1 ± 0.5 s−1 and Km = 628 ± 12 μM (50 μM), Vmax = 60.9 ± 5.0 s−1 and Km = 704 ± 46 μM (10 μM), and Vmax = 112.0 ± 0.3 s−1 and Km = 560 ± 15 μM (no TBT-Cl), respectively. Each point represents mean ± SE of three measurements.
Bulk phase kinetics for TBT-Cl inhibition of V1
To analyze the ways in which TBT-Cl inhibited V1, we measured steady-state ATPase activity of V1 at different concentrations of TBT-Cl. Fig. 1 C shows Lineweaver-Burk plots in the presence of the indicated concentrations of TBT-Cl. The plots portray the graphic consequences of noncompetitive inhibition, and the ATPase activity obeyed simple Michaelis-Menten kinetics (Fig. 1 C, inset). Apparent Km and Vmax values were deduced by analysis of the plots. The Vmax was decreased from 112.0 ± 0.3 s−1 (no TBT-Cl) to 60.9 ± 5.0 s−1 (10 μM TBT-Cl) and 21.1 ± 0.5 s−1 (50 μM TBT-Cl) (mean ± SE) without any appreciable change of Km, suggesting that TBT-Cl acts in a noncompetitive fashion. In addition, the ATPase activity of V1 was mostly restored after the TBT-Cl-inhibited enzyme was applied to a gel filtration column (data not shown). These results indicate that TBT-Cl interacts with V1 noncovalently.
Rotation of V1 in the presence of TBT-Cl under Vmax conditions
We analyzed the inhibition mechanism of V1 by TBT-Cl using the single-molecule technique. The rotation of 209 nm duplex bead attached to the D subunit surrounded by the A3B3 ring was recorded with a high-speed camera, which enabled us to observe the rotation of V1 at high time resolution. At 4 mM ATP in the absence of TBT-Cl, the bead rotated continuously (Fig. 2 A, black line), and the maximum rotation speed was calculated to be 19.7 ± 2.9 Hz (mean ± SE, 5 molecules). The rate was about one half of the rate calculated from the bulk-phase activity (37.3 Hz = 112.0 s−1 /3), most likely due to the impelled frictional load on the beads attached to the rotor shaft (25). Although the rotation at 4 mM ATP seemed smooth, it was frequently interrupted with undefined short pauses (Fig. S1 A in the Supporting Material), which is not obvious at video time resolution (33 ms). The distribution of this pausing time showed a single exponential decay, and the fit with a single exponential gave a time constant of 0.02 ± 0.00 s (mean ± SE) (Fig. S1 B). The average occurrence of the pauses was 0.9 per revolution, and >96.4% of these duration times were ≤0.2 s. The cause of these short pauses has not been determined. Hirono-Hara et al. reported similar undetermined short pauses observed in F1 (26).
Figure 2.
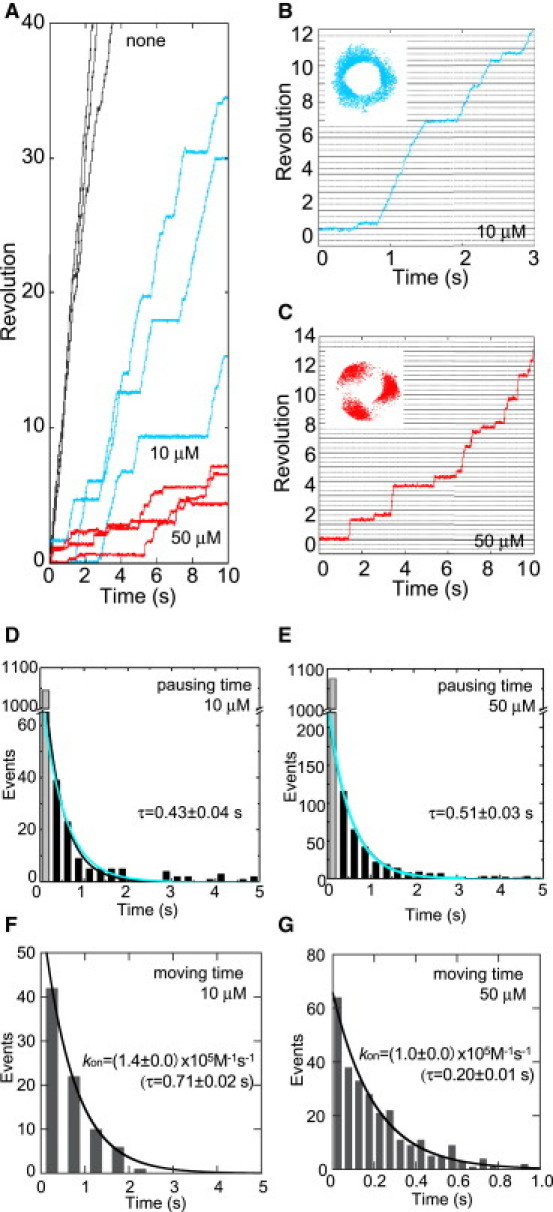
Effect of TBT-Cl on the rotation of V1 at saturating ATP concentration. (A) Time course of the rotation within V1 at 4 mM ATP in the presence of 50 μM (red line) and 10 μM (blue line) TBT-Cl, and in the absence of TBT-Cl (black line). (B and C) Expanded time courses of rotation in the presence of 10 μM (B) and 50 μM (C). (Insets) Traces of the centroid of the bead image. (D and E) Histograms of the pausing times during rotation of V1 in the presence of 10 μM (D) and 50 μM TBT-Cl (E). Black curve lines are fitted with a single exponential function, y = C × exp(−t/τ). Estimated time constant, τ, was shown on the figure and Table 1. The first bin is shown as gray bar. Blue lines show the result of a global fit for these two histograms with a time constant τoff = 0.52 ± 0.02. Total counts of events were 1151 (5 molecules) (D) and 1400 (7 molecules) (E). (F and G) Histograms of the moving times during rotation in the presence of 10 μM (F) and 50 μM (G) TBT-Cl. A moving time was defined as a consecutive rotation time between neighboring pauses (>0.2 s). The lines are single exponential fits with y = C × exp(−t/τ). Total counts of events were 81 (5 molecules) (F) and 279 (7 molecules) (G). C and τ are a proportional constant and a time constant, respectively.
In the presence of TBT-Cl, in addition to the undefined short pauses, long pauses were frequently observed (Fig. 2, A–C) and the rotation rate was dramatically decreased. The histogram of all pauses that were observed in the presence of 10 μM TBT-Cl could not be fitted with a simple single exponential, but it was fitted well with a sum of two exponentials using an adequate time bin-width. This suggests that the two pauses represent at least two different molecular events. The histogram of the short pause was well fitted with a single exponential, but it was not fitted with a sum of two exponentials by small time bin-width (0.02 s). At the long time region of the histogram by the bin size, the frequency was very low, and therefore these events were not included in the fitting. A time constant obtained from this fitting was 0.04 ± 0.00 s (mean ± SE) (Fig. S1 C). This value was affected by long duration pauses, and therefore it might be calculated to be longer. The average occurrence of the short pause for ≤0.2 s events was 1.3 per revolution. This is comparable with the undefined pauses observed at 4 mM ATP in the absence of TBT-Cl. Therefore, the short pauses observed here were inherent, and those caused by TBT-Cl were determined to be those lasting >0.2 s. A curve calculated from the long pauses indicates that its time constant was 0.43 ± 0.04 s (mean ± SE) (Fig. 2 D). The first bin of the histogram (Fig. 2 D, gray bar), in which there are mixed events of pausing times, most of short pauses and short time portions of long pauses, was excluded from fitting for having little effect on a fit for long pauses. When the TBT-Cl concentration was increased to 50 μM TBT-Cl, V1 apparently rotated stepwise, pausing at almost every 120° position (Fig. 2 C). Under this condition, two types of pauses were also observed and short and long time constants were obtained from the distribution of pauses. The average occurrence of short pause was 1.0 per revolution and the time constant was 0.05 ± 0.00 s (mean ± SE); this value was close to the undefined pauses (Fig. S1 D). The long time constant of 0.51 ± 0.03 s (mean ± SE) is close to the long time constant of 0.43 s at 10 μM TBT-Cl (Fig. 2 E). These results suggest that a long time constant is due to release of TBT-Cl from the enzyme. Furthermore, a global fit analysis was performed on these two histograms with a time constant, τoff (Fig. 2, D and E, blue lines), which indicates that these two histograms are statistically the same.
Continuous time of the rotation between consecutive pauses due to the binding of TBT-Cl was analyzed to estimate kon for TBT-Cl. To avoid the effect of undefined pauses, the short pauses (≤0.2 s) were excluded from this analysis. The histograms of rotating time at 10 and 50 μM TBT-Cl were fitted well with a single exponential (Fig. 2, F and G), suggesting that the binding of one TBT-Cl molecule is sufficient to make V1 stop rotation and fall into pause. The estimated kon was (1.4 ± 0.0) × 105 M−1s−1 (10 μM) and (1.0 ± 0.0) × 105 M−1s−1 (50 μM) (mean ± SE), and the dissociation constants, Kd, were deduced to be 16.6 μM and 19.6 μM, respectively (Table 1). These values are in the same range as is the Ki of 11.6 ± 0.7 μM estimated from the bulk-phase experiment illustrated in Fig. 1 A.
Table 1.
Kinetic parameters of the effect of TBT-Cl on V1
| ATP (μM) | TBT-Cl (μM) | τoff (s) | τon (s) | kon (105 M−1s−1) | Kd (μM) | τATP (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4000 | 0 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 10 | 0.43 ± 0.04 | 0.71 ± 0.02 | 1.4 ± 0.0 | 16.6 | — | |
| 50 | 0.51 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 19.6 | — | |
| 10 | 0 | — | — | — | — | 0.23 ± 0.01 |
| 10 | 0.94 ± 0.8 | — | — | — | (0.11 ± 0.01) |
Each value was obtained from single-molecule measurements of V1 under several conditions (mean ± SE). τon and τoff are the time constants of TBT-Cl-bind and-release to/from V1. The values were calculated from the histogram of moving times (τon) and pausing times (τoff) (Figs. 2 and 3). Kd values were calculated from koff /kon. Dash means undetermined parameters.
TBT-Cl inhibition at low ATP concentration
At 10 μM ATP, V1 rotates stepwise, pausing at every 120° (Fig. 3 A, red line and dots). Under this condition, the dwell time for ATP binding to enzyme is the rate-limiting step. The histogram was fitted well to a single exponential equation, giving a time constant τATP of 0.23 ± 0.01 s (mean ± SE) (Fig. 3 B, inset), which is consistent with the previous report (27). In the presence of 10 μM TBT-Cl, the V1-ATPase also rotated stepwise, pausing at every 120° interval (Fig. 3 A, blue line and dots). However, the rotation speed was much slower than that observed in the absence of TBT-Cl, as a consequence of the longer pauses. The frequency of events at a long time range increased in the presence of 10 μM TBT-Cl (Fig. 3 C). The histogram of this pausing time could be fitted well to the sum of two single exponentials, giving a short-τ value (τ1) and a long-τ value (τ2) (Fig. 3 B). The long-τ value of 0.94 ± 0.08 s (mean ± SE) was not observed in the absence TBT-Cl at 10 μM ATP. This value is close to the time constants observed in the presence of TBT-Cl at 4 mM ATP (Table 1), suggesting that release of TBT-Cl from the enzyme is responsible for the deduced long-τ value. On the other hand, the short-τ value of 0.11 ± 0.01, less than time bin-width size, was close to the τATP value of 0.23 s determined in the absence of TBT-Cl. A global fit analysis represents long- and short-τ values as comparable with τoff and τATP (Fig. 3 B). These results indicate that the pauses observed in the presence of TBT-Cl at low ATP concentration are due to two independent events: 1) the ATP binding, and 2) the TBT-Cl release. This suggests that TBT-Cl has little effect on binding affinity for ATP.
Figure 3.
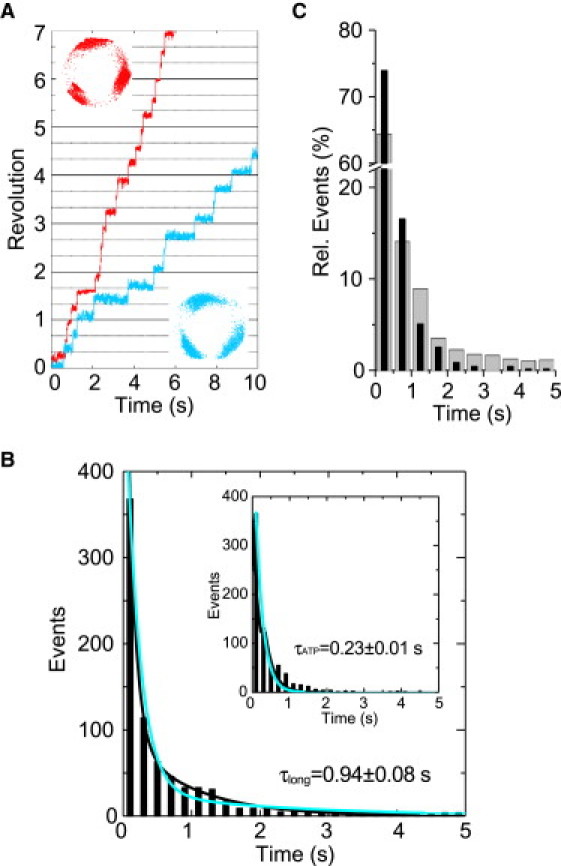
Effect of TBT-Cl on the rotation of V1 at a low ATP concentration. (A) Time courses of rotation in the absence (red line and dots) and presence (blue line and dots) of 10 μM TBT-Cl. (Inset) Traces of the centroid of the bead images. (B) Histogram of pausing time at 10 μM ATP in the presence of 10 μM TBT-Cl. It was fitted with sum of two exponential, y = C1 × exp(−t/τ1) + C2 × exp(−t/τ2) (τ1 < τ2). Estimated time constants, shown on the figure and in Table 1. (τ1 value was calculated to be 0.11 ± 0.01, which was below the bin width.) Total counts of events were 713 (8 molecules). (Inset) Histogram of pausing time at 10 μM ATP with no TBT-Cl. The line is fit with y = C × exp(−t/τATP). Total counts of events were 795 (9 molecules). Blue lines show the result of a global fit for these two histograms with time constants τATP = 0.20 ± 0.01 and τoff = 2.16 ± 1.03. (C) Frequency of pausing time at 10 μM ATP with no TBT-Cl (black bar) and 10 μM TBT-Cl (gray bar).
Effect of TBT-Cl on step motions
To address the effect of TBT-Cl on the stepping motion of V1, we measured the angular velocity for each step due to the TBT-Cl binding or the ATP binding (Fig. 4 A). At 10 μM ATP, the angular velocity of steps between consecutive durations due to the ATP binding dwell was calculated to be 69.4 ± 6.3 π rad s−1 (mean ± SE) (Fig. 4 B). In the presence of 50 μM TBT-Cl and 4 mM ATP, the observed pauses (>0.2 s) are primarily because of release of TBT-Cl from the enzyme (Fig. 2 C). The velocity for the 120° steps between the neighboring pauses (>0.2 s) was deduced to be 70.5 ± 8.3 π rad s−1 (mean ± SE). This is comparable to the velocity due to the ATP binding dwell. These results indicate that the binding of TBT-Cl to V1 does not affect the rotational velocity between pauses.
Figure 4.
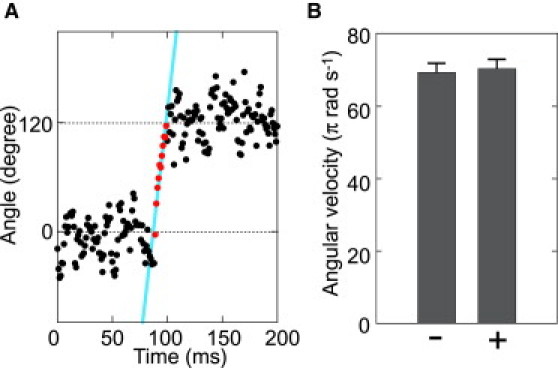
Angular velocity of step motion in the presence of TBT-Cl. (A) Magnification of step at 4 mM ATP in the presence of 50 μM TBT-Cl. Steps distinguished from pauses are fitted with linear segments to estimate the average angular velocity. (B) The angular velocity of the single 120° step motion at 10 μM ATP in the absence of TBT-Cl (−) and at 4 mM ATP in the presence of 50 μM TBT-Cl (+). Each velocity was calculated from 25 steps for 5 molecules.
TBT-Cl inhibition of V1ΔF (A3B3D)
The rotor shaft in V1 is comprised of the subunits D and F, which have no sequence homology to the γ and ɛ subunits of the rotor shaft in F1. The subunit F has a structural similarity to the regulatory subunit CheY of the flagella motor, which regulates rotational direction in response to phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of its active site (28). This motif is well conserved in subunit F, suggesting that the subunit F might be the target of TBT-Cl. To test this possibility, we investigated the effect of TBT-Cl on A3B3D (referred to as V1ΔF), the minimum rotary unit in the V-ATPase (21). The ATPase activity of V1ΔF obeyed simple Michaelis-Menten kinetics, and the Lineweaver-Burk plots shown in Fig. 5 A are consistent with noncompetitive inhibition as observed with V1 (Fig. 1 C).
Figure 5.
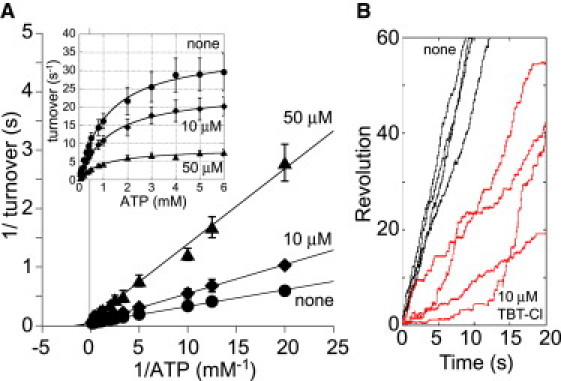
Effect of TBT-Cl on ATPase activity and rotation of V1ΔF. (A) Lineweaver-Burkplots representing reciprocal of the V1ΔF ATPase activity versus reciprocal of ATP concentrations in the presence of 50 μM (▴) and 10 μM (♦), and in the absence of TBT-Cl (●). The graphics in the plots portray the consequences of noncompetitive inhibition. The plots are fitted by linear regression on full data sets. (Inset) [S]-v plots derived from the Lineweaver-Burk plots. The lines show fitting functions with Vmax = 8.6 ± 1.7 s−1 and Km = 1.0 ± 0.1 mM (50 μM TBT-Cl), Vmax = 24.4 ± 6.4 s−1 and Km = 1.2 ± 0.2 mM (10 μM TBT-Cl), and Vmax = 35.7 ± 11.1 s−1 and Km = 1.2 ± 1.2 mM (no TBT-Cl), respectivly. Each point represents mean ± SE of three measurements. (B) Time course of the rotation of V1ΔF in the presence of 10 μM (red line) and in the absence of TBT-Cl (black line).
The apparent Vmax values deduced from the plots were also decreased without any appreciable change in the Km values. In the presence of 10 μM TBT-Cl, V1ΔF rotates with frequent pauses such that the averaged rotation speed is much lower than that in the absence of TBT-Cl (Fig. 5 B). These results clearly indicate that ATPase activity of V1ΔF was also noncompetitively inhibited by TBT-Cl, as with V1, and the subunit F is not the target of TBT-Cl.
Discussion
As observed with the F-ATPase, TBT-Cl inhibits the ATPase activity of the V-ATPase. Ueno et al. found that TBT-Cl decreased the rotation rate of the γ subunit within TFoF1, the ATP synthase from thermophilic Bacillus PS3, but it had no effect on rotation of the γ subunit in isolated F1 (20). We demonstrated in this study that preincubation of the Vo-liposome with TBT-Cl completely abolishes proton permeability (Fig. 1 B). In T.thermophilus V-ATPases, subunit Vo-a complexed with the proteolipid ring comprises the proton channel and shows proton permeability (12). Although T.thermophilus Vo-a showed no sequence homology to the subunit a in Fo, several lines of evidence suggest that the proton channel in the T.thermophilus Vo has a structure similar to that of the Fo proton channel (29). It seems likely that TBT-Cl interacts with the T.thermophilus Vo channel and Fo channel in a similar manner. It is noted that the eukaryotic Vo domain appeared considerably different from that of prokaryotic counterparts; it contains hydrophilic stator subunits and a hetero-oligomeric rotor ring, and it shows no proton permeability when V1 domain dissociates from Vo domain (4). Further study is necessary to clarify inhibitory effects of TBT on the function of eukaryotic Vo domain. Binding of TBT-Cl to the Vo channel led to nearly complete inhibition of the ATPase activity of the holoenzyme. Also, unlike F1, the ATPase activity of V1 was dramatically inhibited with TBT-Cl in the micromolar range. Bulk-phase experiments indicated that TBT-Cl binds to V1 noncovalently and inhibits its ATPase activity noncompetitively (Fig. 1). Because the ATPase activity of V1ΔF was also inhibited, subunit F is not the target of TBT-Cl (Fig. 5). The catalytic A subunit is homologous to the F1-β subunit (13); however, subunit A contains nonhomologous regions, which could be the target of TBT-Cl. Further studies are necessary to identify the binding site for TBT-Cl on V1. Our results clearly indicate that TBT-Cl binds to the V1 domain in addition to the Vo domain, and it inhibits the activity of holoenzyme V-ATPase. This is the first report to demonstrate that TBT-Cl can inhibit V1 holoenzyme in a noncompetitive manner.
We also examined the inhibition mechanism of V1 by TBT-Cl using single-molecule imaging techniques. TBT-Cl apparently decreased the averaged rotational rate of V1 and imposed stepwise rotation on V1, even at saturating ATP concentration. Analysis of the pausing time in the presence of TBT-Cl indicated that each pause was caused by the binding of one TBT-Cl molecule to the enzyme (Fig. 2). Pauses caused by TBT-Cl were also observed at low ATP concentrations, in which V1 rotates stepwise due to the ATP binding dwell. Under this condition, V1 paused at each 120° dwell position (Fig. 3). Two time-rate constants were deduced from the dwell-time analysis. As summarized in Table 1, the short-τ value in the presence of TBT-Cl is comparable to the τ value due to ATP binding events. On the other hand, the long-τ value at low ATP concentration is close to the τ value due to the events of TBT-Cl binding at saturating ATP concentration. These results indicate that the ATP binding and TBT-Cl binding events occur mostly at the same dwell position but are independent of each other, which is consistent with the bulk-phase analysis. We recently demonstrated that the dwell for the ATP binding is the same as or very close to the catalytic dwell where ATP hydrolysis or product release takes place (22). In contrast, single-molecule analysis of F1 revealed that 120° step consists of 80° substep driven by ATP binding and 40° substep by product release (30,31). From the single-molecule analyses of V1, it is concluded that TBT-Cl inhibits the catalytic event(s) but does not alter the binding affinity for ATP in the mechanochemical cycle of V1.
Our results demonstrate that TBT-Cl inhibits a specific event in the mechanochemical cycle catalyzed by the V1 motor. This new finding provides a basis for designing new experiments to unravel details of the rotary catalysis by V1. For example, a crystal structure of V1 containing both bound ATP and TBT-Cl would provide a snapshot of the rotary motor in which the 120° rotational step had just completed.
Acknowledgments
We thank our colleagues, especially Drs. H. Imamura, E. Muneyuki, H. Ueno, T. Masaike, T. Nishizaka, Y. Hirono-Hara, F. Motojima, and T. Yano, for critical discussions. We also thank E. Saita, M. Nakano, M. Belz, T. Murakami-Fuse, and S. Funamoto for their technical advice. We are grateful to R. Yasuda and K. Adachi for programming the custom software.
This work was partly supported by Grants-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan (Nos. 1837005, 18657041, and 19042008) and a target proteins research program (B-37, to KY).
Supporting Material
References
- 1.Fent K., Meier W. Tributyltin-induced effects on early life stages of minnows Phoxinus phoxinus. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1992;22:428–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00212563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Shimasaki Y., Kitano T., Oshima Y., Inoue S., Imada N. Tributyltin causes masculinization in fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003;22:141–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nishi T., Forgac M. The vacuolar H+-ATPases—nature's most versatile proton pumps. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002;3:94–103. doi: 10.1038/nrm729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hughes G., Harrison M.A., Kim Y.I., Griffiths D.E., Finbow M.E. Interaction of dibutyltin-3-hydroxyflavone bromide with the 16 kDa proteolipid indicates the disposition of proton translocation sites of the vacuolar ATPase. Biochem. J. 1996;317:425–431. doi: 10.1042/bj3170425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Apps D.K., Webster L.C. Interaction of organotins with a vacuolar-type H+-ATPase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996;227:839–845. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.1594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Shimizu S., Imanaka T., Takano T., Ohkuma S. Major ATPases on clofibrate-induced rat liver peroxisomes are not associated with 70 kDa peroxisomal membrane protein (PMP70) J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 1992;112:376–384. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kakinuma Y., Igarashi K. Purification and characterization of the catalytic moiety of vacuolar-type Na+-ATPase from Enterococcus hirae. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 1994;116:1302–1308. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yokoyama K., Muneyuki E., Amano T., Mizutani S., Yoshida M. V-ATPase of Thermus thermophilus is inactivated during ATP hydrolysis but can synthesize ATP∗. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:20504–20510. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.32.20504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Imamura H., Nakano M., Noji H., Muneyuki E., Ohkuma S. Evidence for rotation of V1-ATPase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100:2312–2315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0436796100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yokoyama K., Nakano M., Imamura H., Yoshida M., Tamakoshi M. Rotation of the proteolipid ring in the V-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:24255–24258. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303104200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yokoyama K., Akabane Y., Ishii N., Yoshida M. Isolation of prokaryotic VoV1-ATPase from a thermophilic eubacterium Thermus thermophilus. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:12248–12253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yokoyama K., Ohkuma S., Taguchi H., Yasunaga T., Wakabayashi T. V-Type H+-ATPase/synthase from a thermophilic eubacterium, Thermus thermophilus. Subunit structure and operon. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:13955–13961. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.18.13955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tsutsumi S., Denda K., Yokoyama K., Oshima T., Date T. Molecular cloning of genes encoding major two subunits of a eubacterial V-type ATPase from Thermus thermophilus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1991;1098:13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yokoyama K., Nagata K., Imamura H., Ohkuma S., Yoshida M. Subunit arrangement in V-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:42686–42691. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305853200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bowman E.J., Graham L.A., Stevens T.H., Bowman B.J. The bafilomycin/concanamycin binding site in subunit c of the V-ATPases from Neurospora crassa and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:33131–33138. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404638200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Boya P., Gonzalez-Polo R.A., Casares N., Perfettini J.L., Dessen P. Inhibition of macroautophagy triggers apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005;25:1025–1040. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.3.1025-1040.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tanigaki K., Sasaki S., Ohkuma S. In bafilomycin A1-resistant cells, bafilomycin A1 raised lysosomal pH and both prodigiosins and concanamycin A inhibited growth through apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 2003;537:79–84. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wang Y., Inoue T., Forgac M. Subunit a of the yeast V-ATPase participates in binding of bafilomycin. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:40481–40488. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509106200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.von Ballmoos C., Brunner J., Dimroth P. The ion channel of F-ATP synthase is the target of toxic organotin compounds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:11239–11244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402869101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ueno H., Suzuki T., Kinosita K., Jr., Yoshida M. ATP-driven stepwise rotation of FoF1-ATP synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:1333–1338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407857102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Imamura H., Ikeda C., Yoshida M., Yokoyama K. The F subunit of Thermus thermophilus V1-ATPase promotes ATPase activity but is not necessary for rotation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:18085–18090. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M314204200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Imamura H., Takeda M., Funamoto S., Shimabukuro K., Yoshida M. Rotation scheme of V1-motor is different from that of F1-motor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:17929–17933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507764102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Noji H., Yasuda R., Yoshida M., Kinosita K., Jr. Direct observation of the rotation of F1-ATPase. Nature. 1997;386:299–302. doi: 10.1038/386299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Matsuya H., Okamoto M., Ochi T., Nishikawa A., Shimizu S. Reversible and potent uncoupling of hog gastric H+ + K+-ATPase by prodigiosins. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000;60:1855–1863. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00509-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yasuda R., Noji H., Kinosita K., Jr., Yoshida M. F1-ATPase is a highly efficient molecular motor that rotates with discrete 120 degree steps. Cell. 1998;93:1117–1124. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81456-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hirono-Hara Y., Noji H., Nishiura M., Muneyuki E., Hara K.Y. Pause and rotation of F1-ATPase during catalysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2001;98:13649–13654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.241365698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yasuda R., Noji H., Yoshida M., Kinosita K., Jr., Itoh H. Resolution of distinct rotational substeps by submillisecond kinetic analysis of F1-ATPase. Nature. 2001;410:898–904. doi: 10.1038/35073513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Makyio H., Iino R., Ikeda C., Imamura H., Tamakoshi M. Structure of a central stalk subunit F of prokaryotic V-type ATPase/synthase from Thermus thermophilus. EMBO J. 2005;24:3974–3983. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kawasaki-Nishi S., Nishi T., Forgac M. Arg-735 of the 100-kDa subunit a of the yeast V-ATPase is essential for proton translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2001;98:12397–12402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.221291798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Shimabukuro K., Yasuda R., Muneyuki E., Hara K.Y., Kinosita K., Jr. Catalysis and rotation of F1 motor: cleavage of ATP at the catalytic site occurs in 1 ms before 40 degree substep rotation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100:14731–14736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2434983100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Adachi K., Oiwa K., Nishizaka T., Furuike S., Noji H. Coupling of rotation and catalysis in F1-ATPase revealed by single-molecule imaging and manipulation. Cell. 2007;130:309–321. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


