Abstract
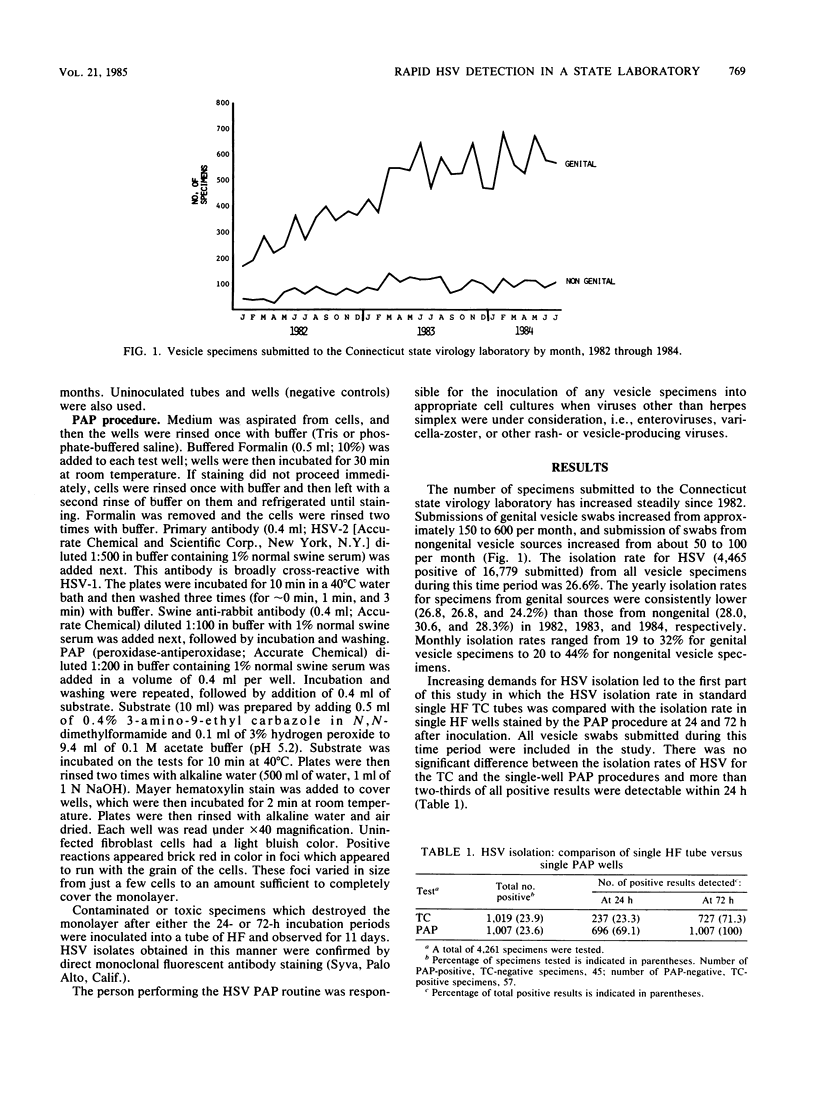
Of 16,779 specimens received for herpes simplex virus (HSV) isolation since 1982, 4,465 (26.6%) were positive for HSV by either standard tissue culture or an antigen detection system (peroxidase-antiperoxidase; PAP). The overall isolation rate for genital vesicle specimens was lower (26.1%) than that for nongenital specimens (29.3%). Monthly isolation rates ranged from 19 to 32% for genital specimens and from 20 to 44% for nongenital specimens. Increasing demands for HSV isolation led to comparison of tissue culture with PAP. In the first comparison, HSV was isolated in single human fibroblast cell cultures from 1,019 of 4,261 specimens (23.9%), whereas single human fibroblast wells stained at 24 and 72 h postinoculation were PAP positive for 1,007 of 4,261 specimens (23.6%). In the second comparison, HSV was isolated from 225 of 1,026 (21.9%) specimens and duplicate human foreskin fibroblast cell wells stained at 24 and 72 h were PAP positive in 241 of 1,026 (23.5%). With the dual-well PAP system, all results were reported within 72 h, approximately 70% of positives were reported within 24 h, and considerable savings in time and materials resulted.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Callihan D. R., Menegus M. A. Rapid detection of herpes simplex virus in clinical specimens with human embryonic lung fibroblast and primary rabbit kidney cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):563–565. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.563-565.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayram S. L., Aarnaes S., de la Maza L. M. Comparison of cultureset to a conventional tissue culture-fluorescent-antibody technique for isolation and identification of herpes simplex virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):215–216. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.215-216.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden F. G., Sorensen A. S., Bateman J. A. Comparison of the Immulok cultureset kit and virus isolation for detection of herpes simplex virus in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):222–224. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.222-224.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. B., Leavitt R. W., Richards D. F. Evaluation of the virocult transport tube for isolation of herpes simplex virus from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):120–122. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.120-122.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land S. A., Skurrie I. J., Gilbert G. L. Rapid diagnosis of herpes simplex virus infections by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):865–869. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.865-869.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry M. L., Mayo D. R., Hsiung G. D. Comparison of guinea pig embryo cells, rabbit kidney cells, and human embryonic lung fibroblast cell strains for isolation of herpes simplex virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):842–847. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.842-847.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Howell C. L. Rapid detection and identification of herpes simplex virus in cell culture by a direct immunoperoxidase staining procedure. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):550–553. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.550-553.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. F. Comparison of human fibroblast cells and primary rabbit kidney cells for isolation of herpes simplex virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):548–549. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.548-549.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. A., Smith T. F. Evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of herpes simplex virus antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):730–732. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.730-732.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerurkar L. S., Jacob A. J., Madden D. L., Sever J. L. Detection of genital herpes simplex infections by a tissue culture-fluorescent-antibody technique with biotin-avidin. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):149–154. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.149-154.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerurkar L. S., Namba M., Brashears G., Jacob A. J., Lee Y. J., Sever J. L. Rapid detection of herpes simplex virus in clinical specimens by use of a capture biotin-streptavidin enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):109–114. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.109-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez T. R., Mosman P. L., Juchau S. V. Experience with Virocult as a viral collection and transportation system. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984 Jan;2(1):7–9. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(84)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin S. J., Rogers S. Comparison of Cultureset and primary rabbit kidney cell culture for the detection of herpes simplex virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):920–922. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.920-922.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warford A. L., Levy R. A., Rekrut K. A. Evaluation of a commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of herpes simplex virus antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):490–493. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.490-493.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


