Abstract
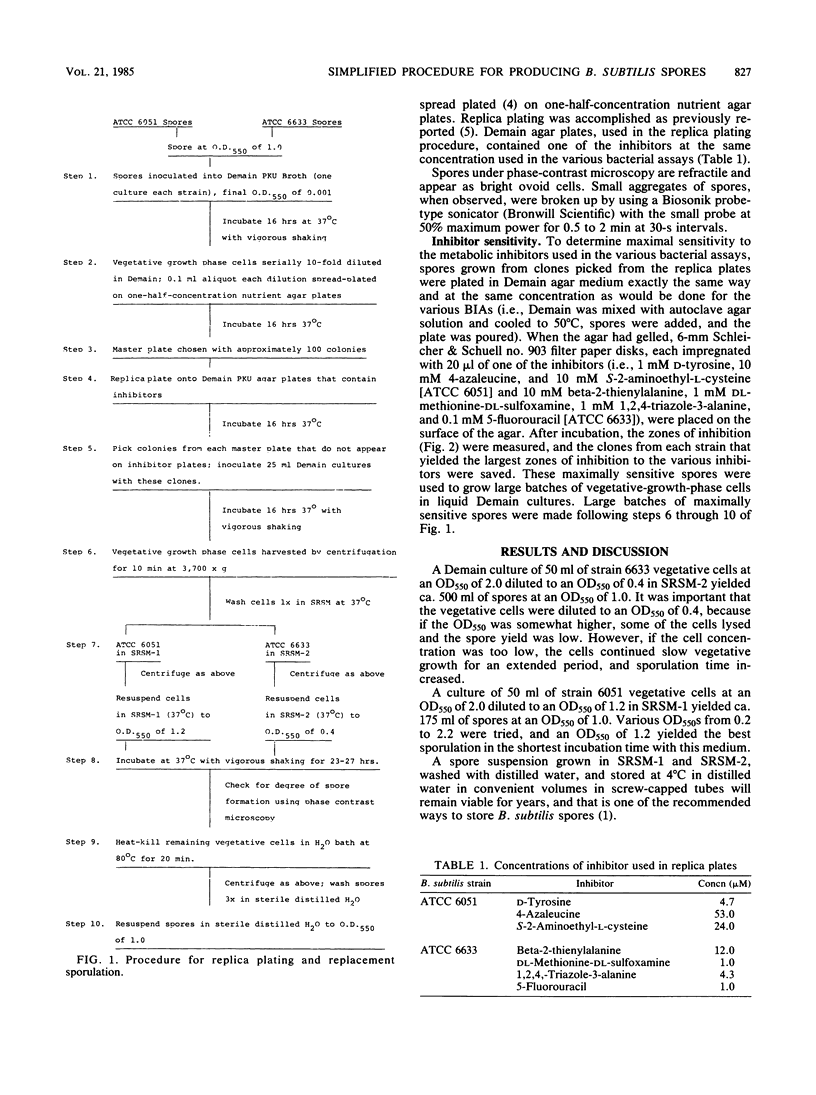
Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6051 and ATCC 6633 spores used in bacterial inhibition screening assays for genetic metabolism defects in newborn infants were produced by using liquid synthetic replacement sporulation media. These media allowed a high degree of sporulation, as judged by direct cell counts. Sporulation took place within 23 to 27 h with these media. Also, a more rational procedure for selecting the most sensitive clones of these organisms to the various inhibitors used in the microbiological screening assays is presented.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Franklin M. L., Clark W. A. Simple, inexpensive, and rapid way to produce Bacillus subtilis spores for the Guthrie bioassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):113–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.113-115.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTHRIE R., SUSI A. A SIMPLE PHENYLALANINE METHOD FOR DETECTING PHENYLKETONURIA IN LARGE POPULATIONS OF NEWBORN INFANTS. Pediatrics. 1963 Sep;32:338–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J., LEDERBERG E. M. Replica plating and indirect selection of bacterial mutants. J Bacteriol. 1952 Mar;63(3):399–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.3.399-406.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaley R. F., Burden L. Replacement sporulation of Bacillus subtilis 168 in a chemically defined medium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.1-8.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinor M. Propagating Bacillus subtilis spores in a liquid medium for the Guthrie bioassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):740–742. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.740-742.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugae K., Freese E. Requirement for Acetate and Glycine (or Serine) for Sporulation Without Growth of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1074–1085. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1074-1085.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]