Abstract
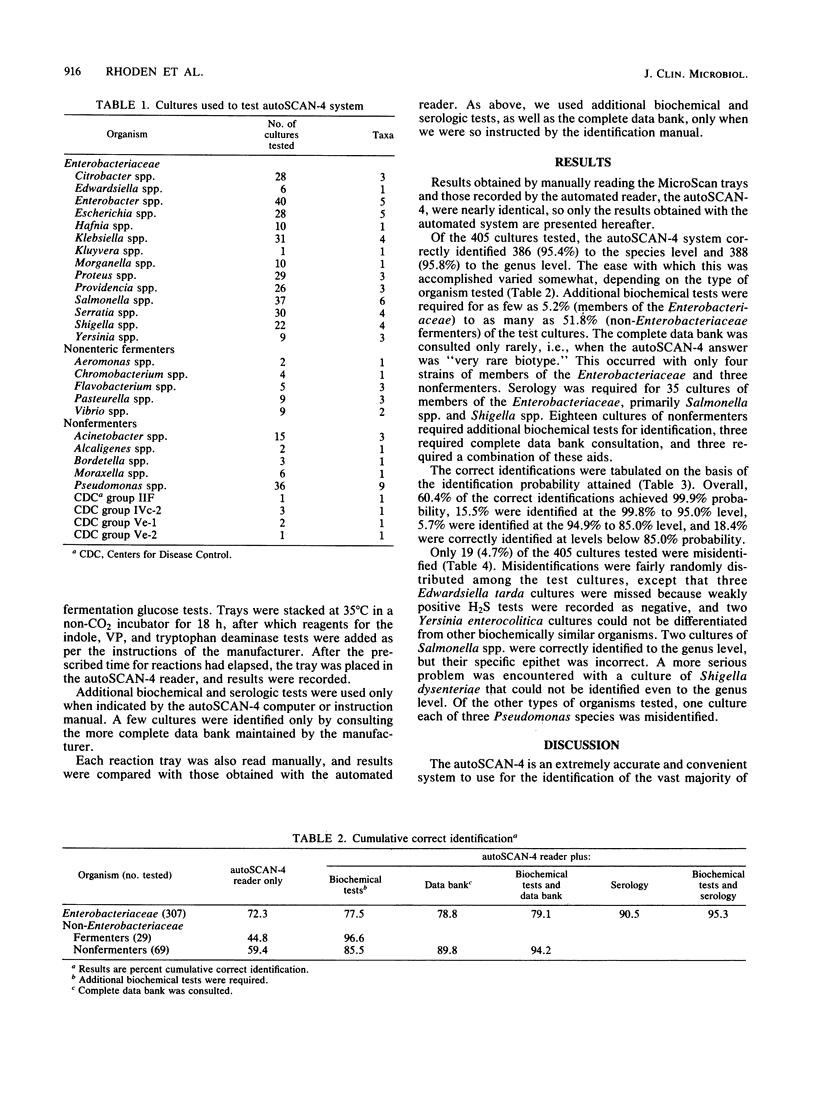
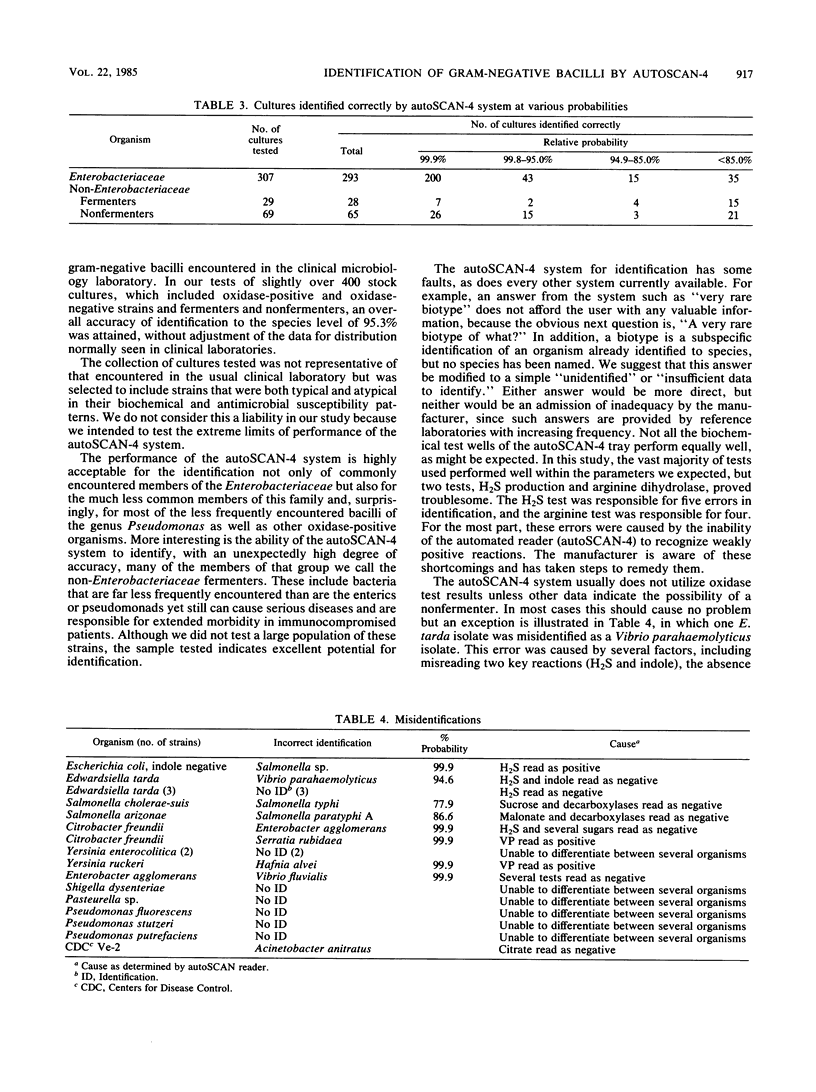
A production model of the autoSCAN-4 system (American MicroScan, Inc., Mahwah, N.J.) was tested with not more than 11 strains each of 73 groups or species of gram-negative bacilli from various Centers for Disease Control culture collections. The strains included typical and atypical strains of enteric fermenters, nonenteric fermenters, and nonfermenters. The autoSCAN-4 system identified 95.3% of all 405 cultures accurately: 95.4% of 307 members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, 96.6% of 29 nonenteric fermenters, and 94.2% of 69 nonfermenters. Manual readings of the same trays provided essentially the same results, with a maximum change of only +1.6% identification accuracy of members of the Enterobacteriaceae. These data were obtained by all required additional tests, including serology and computer consultation when indicated. Only 19 of the cultures tested were misidentified. These were distributed randomly throughout the various groups and species except that Edwardsiella tarda was usually missed because of poor H2S reactions in the test medium. Of six Yersinia enterocolitica isolates, two were not identified. Only one nonenteric fermenter, a Pasteurella sp., and four nonfermenters (three Pseudomonas sp. and one Centers for Disease Control group Ve-2) were misidentified.
Full text
PDF