Abstract
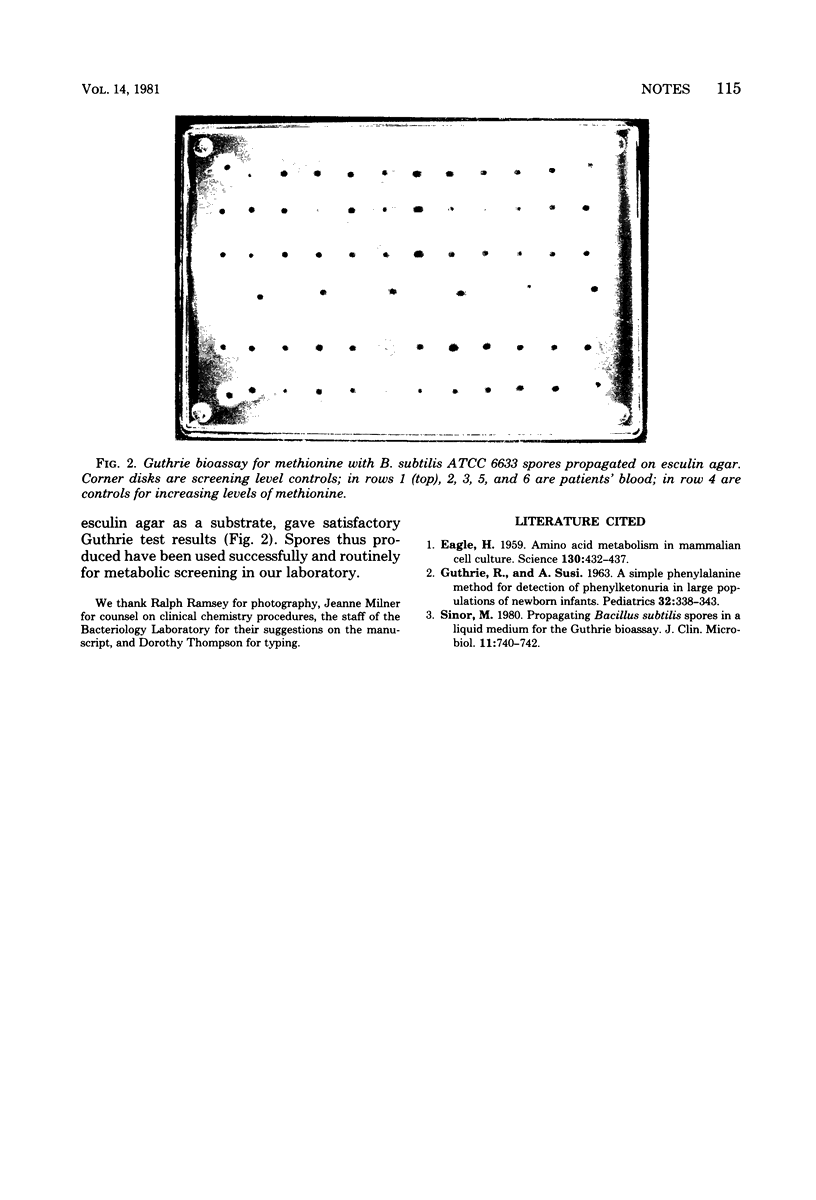
Esculin agar has been found to be a simple, inexpensive, rapid, and reliable means to promote production of spores of inhibitor-sensitive clones of Bacillus subtilis strains ATCC 6051 and 6633 for use in the Guthrie bioassay screening tests for genetic metabolic disorders.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTHRIE R., SUSI A. A SIMPLE PHENYLALANINE METHOD FOR DETECTING PHENYLKETONURIA IN LARGE POPULATIONS OF NEWBORN INFANTS. Pediatrics. 1963 Sep;32:338–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinor M. Propagating Bacillus subtilis spores in a liquid medium for the Guthrie bioassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):740–742. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.740-742.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]