Abstract
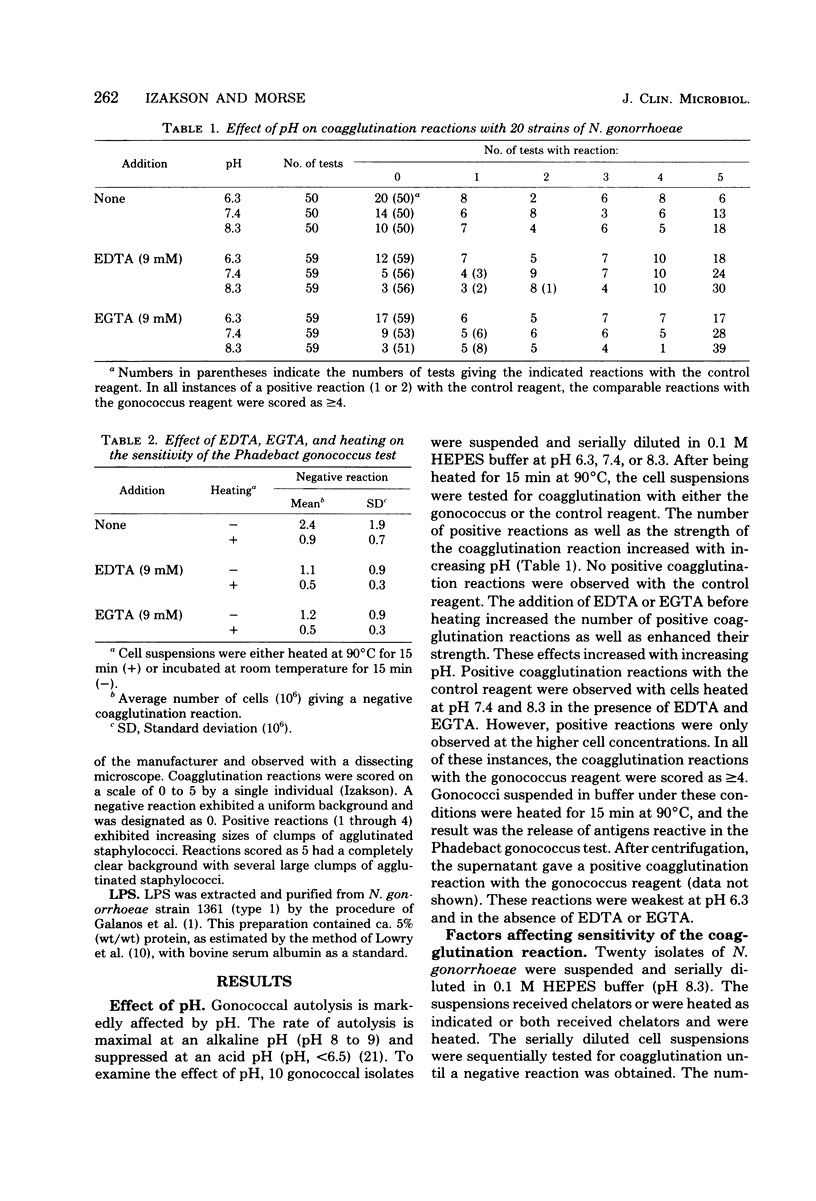
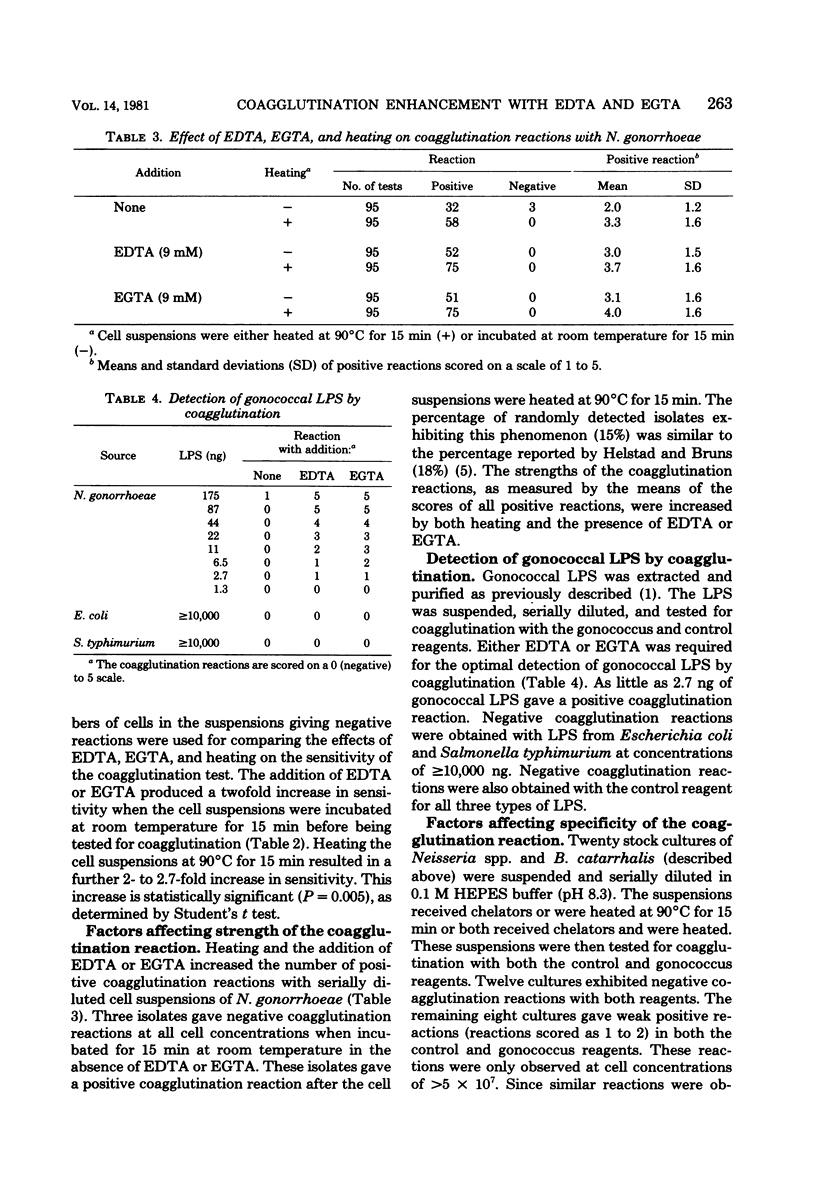
Incubation of gonococci under conditions optimal for autolysis resulted in increased sensitivity and enhancement of the coagglutination reaction of the Phadebact gonococcus test. These conditions included an alkaline pH (pH 8.3) and the presence of divalent cation chelators such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid or ethylene glycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N-tetraacetic acid. Heating cell suspensions at 90 degrees C for 15 min before assay by coagglutination produced a further increase in sensitivity and enhancement of the reaction. Gonococcal lipopolysaccharide was found to be an important antigen in these coagglutination reactions. The detection of lipopolysaccharide was markedly enhanced by the addition of chelating agents.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Stinnett J. D., Eagon R. G. Ultrastructural and chemical alteration of the cell envelope of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, associated with resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate resulting from growth in a Mg2+-deficient medium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):302–311. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.302-311.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn G., Nyberg I. Identification of streptococcal groups A,B,C, and G by slide co-agglutination of antibody-sensitized protein A-containing staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):99–101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.99-101.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton K. D., Stallings R. A., Wasilauskas B. L. Comparison of a slide coagglutination technique with the Minitek system for confirmation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):290–292. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.290-292.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helstad A. G., Bruns M. K. Rapid laboratory identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by coagglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):753–754. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.753-754.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. Release of lipopolysaccharide by EDTA treatment of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leland D. S., Lachapelle R. C., Wlodarski F. M. Method for rapid detection of group B streptococci by coagglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):323–326. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.323-326.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. S., Martin J. E., Jr Evaluation of the phadebact gonococcus test, a coagglutination procedure for confirmation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):153–156. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.153-156.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim D. V., Wall T. Confirmatory identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by slide coagglutination. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Feb;26(2):218–222. doi: 10.1139/m80-033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menck H. Identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in cultures from tonsillo-pharyngeal specimens by means of a slide co-agglutination test (Phadebact Gonococcus Test). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Jun;84(3):139–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Bartenstein L. Factors affecting autolysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Apr;145(4):1418–1421. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-38025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Warner R. C. Physicochemical studies on a lipopolysaccharide from the cell wall of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):4994–5001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. B., Daoust V. The lipopolysaccharides of Neisseria gonorrhoeae colony types 1 and 4. Can J Biochem. 1975 May;53(5):623–629. doi: 10.1139/o75-084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. D., McCracken G. H., Jr Detection of group B streptococcal antigens in body fluids of neonates. J Pediatr. 1978 Sep;93(3):491–492. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead A., Main J. S., Ward M. E., Watt P. J. Studies on lipopolysaccharides isolated from strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):123–131. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner R. A. Bacitracin and coagglutination for grouping of beta-hemolytic streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 May;7(5):463–466. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.5.463-466.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb B. J., Edwards M. S., Baker C. J. Comparison of slide coagglutination test and countercurrent immunoelectrophoresis for detection of group B streptococcal antigen in cerebrospinal fluid from infants with meningitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Mar;11(3):263–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.3.263-265.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. S., Hebeler B. H., Morse S. A. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: relationship between autolysis in buffer and the hydrolysis of peptidoglycan. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):210–219. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.210-219.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


