Abstract
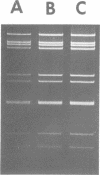
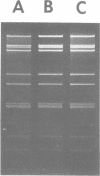
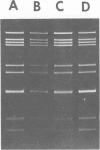
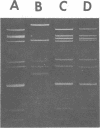
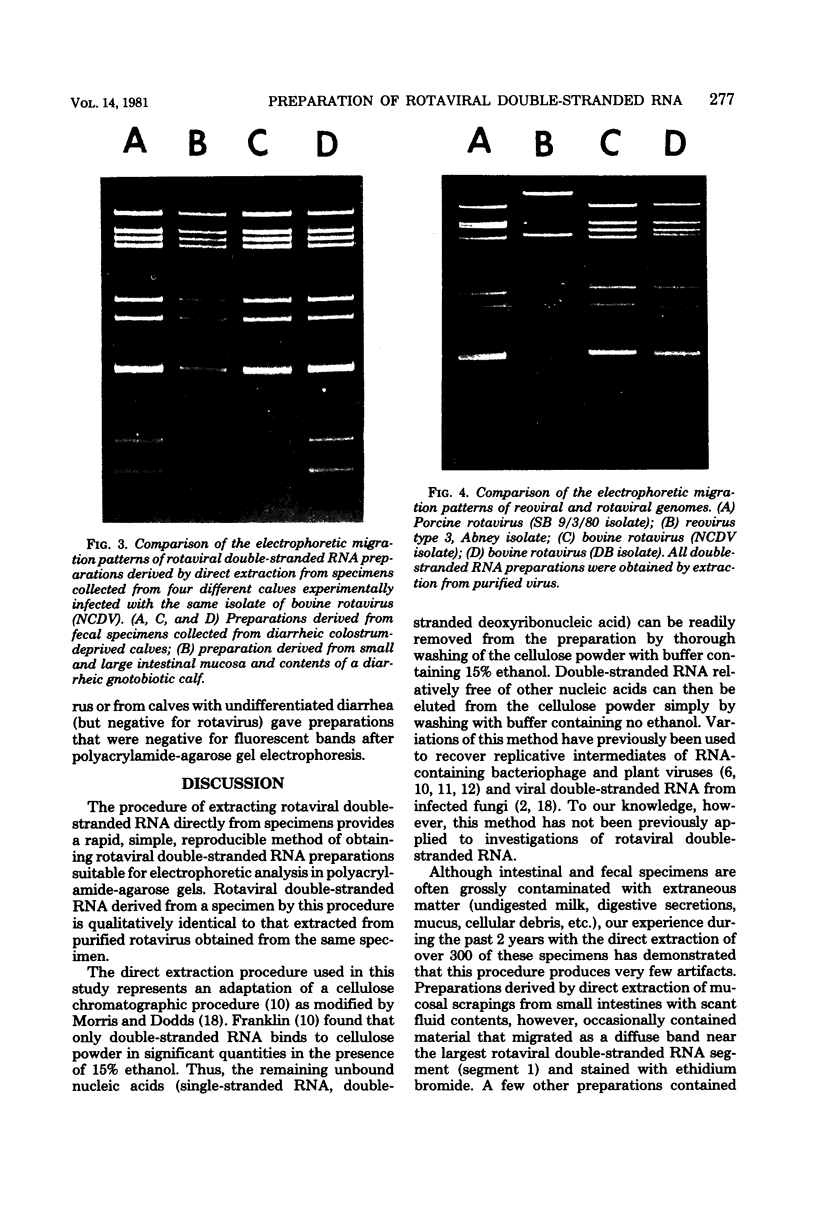
A procedure for extracting rotaviral double-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) directly from fecal and intestinal specimens collected from calves and pigs is described. This procedure provides a rapid, simple, reproducible method of obtaining rotaviral double-stranded RNA preparations suitable for electrophoretic analysis in polyacrylamide-agarose composite gels. The rotaviral genome electrophoretic migration pattern produced by double-stranded RNA extracted directly from a specimen by this procedure was qualitatively identical to the electrophoretic migration pattern obtained with double-stranded RNA extracted from purified rotavirus derived from the same specimen. Direct extraction of specimens containing porcine rotavirus-like virus by this procedure gave preparations that had electrophoretic migration patterns similar, but not identical, to the characteristic electrophoretic migration pattern of the rotaviral genome. Sufficient rotaviral double-stranded RNA could be extracted from 6 ml of fecal or intestinal specimen by this procedure to permit 15 or more electrophoretic assays.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohl E. H., Kohler E. M., Saif L. J., Cross R. F., Agnes A. G., Theil K. W. Rotavirus as a cause of diarrhea in pigs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Feb 15;172(4):458–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. F., Moorhead P. D. An azure and eosin rapid staining technique. Can J Comp Med. 1969 Oct;33(4):317–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener T. O., Schneider I. R. Virus degradation and nucleic acid release in single-phase phenol systems. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Mar 20;124(1):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds J. A., Tremaine J. H., Ronald W. P. Some properties of carnation ringspot virus single- and double-stranded ribonucleic acid. Virology. 1977 Dec;83(2):322–328. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y. Identification of rotaviruses of different origins by the plaque-reduction test. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Jan;41(1):151–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Bryden A. S., Davies H. Diagnostic electron microscopy of faeces. I. The viral flora of the faeces as seen by electron microscopy. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Aug;27(8):603–608. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.8.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M. Purification and properties of the replicative intermediate of the RNA bacteriophage R17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1504–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German T. L., de Zoeten G. A. Purification and properties of the replicative forms and replicative intermediates of pea enation mosaic virus. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):172–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90188-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. O., Mitchell D. M., Siegel A. Replication of tobacco mosaic virus. I. Isolation and characterization of double-stranded forms of ribonucleic acid. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):182–191. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90125-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Garon C. F., Wyatt R. G., Mebus C. A., van Kirk D. H., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Differentiation of human and calf reoviruslike agents associated with diarrhea using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of RNA. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):86–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Sereno M. M., Wyatt R. G., Mebus C. A., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Comparison of human and animal rotavirus strains by gel electrophoresis of viral RNA. Virology. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Allan G. M., Todd D., McFerran J. B. Isolation and cell culture propagation of rotaviruses from turkeys and chickens. Arch Virol. 1979;61(1-2):13–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01320587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Resolution of multiple ribonucleic acid species by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1818–1827. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., La Torre J., Kelley D. E., Greenberg J. R. On the lability of poly(A) sequences during extraction of messenger RNA from polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAYMOND S. A convenient apparatus for vertical gel electrophoresis. Clin Chem. 1962 Sep-Oct;8:455–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Holmes I. H. Comparison of the genomes of simian, bovine, and human rotaviruses by gel electrophoresis and detection of genomic variation among bovine isolates. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):839–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.839-846.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Biochemical and biophysical characteristics of diarrhea viruses of human and calf origin. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1229–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1229-1235.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Cross R. F., House J. A. Rotavirus-like, calicivirus-like, and 23-nm virus-like particles associated with diarrhea in young pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.105-111.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands J. A., Cupp J., Keith A., Snipes W. Temperature sensitivity of the assembly process of the enveloped bacteriophage phi6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 10;373(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90151-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Characteristics of the genome of human infantile enteritis virus (Rotavirus). J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):267–270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.267-270.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Bohl E. H., Cross R. F., Kohler E. M., Agnes A. G. Pathogenesis of porcine rotaviral infection in experimentally inoculated gnotobiotic pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Feb;39(2):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Bryden A. S., Flewett T. H., Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Snodgrass D. R., Herring J. A. Serological relationships between rotaviruses from different species as studied by complement fixation and neutralization. Arch Virol. 1977;53(4):287–294. doi: 10.1007/BF01315627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verly E., Cohen J. Demonstration of size variation of RNA segments between different isolates of calf rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jun;35(3):583–586. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-3-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood H. A. Viruses with double-stranded RNA genomes. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jun;20(Suppl):61–85. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-20-Supplement-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Jones J. M., Flewett T. H., Davies H. A., Davis H. A., White G. B. Morphological and antigenic relationships between viruses (rotaviruses) from acute gastroenteritis of children, calves, piglets, mice, and foals. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.804-810.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Barbour B., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for identification of rotaviruses from different animal species. Science. 1978 Jul 21;201(4352):259–262. doi: 10.1126/science.208150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]