Abstract
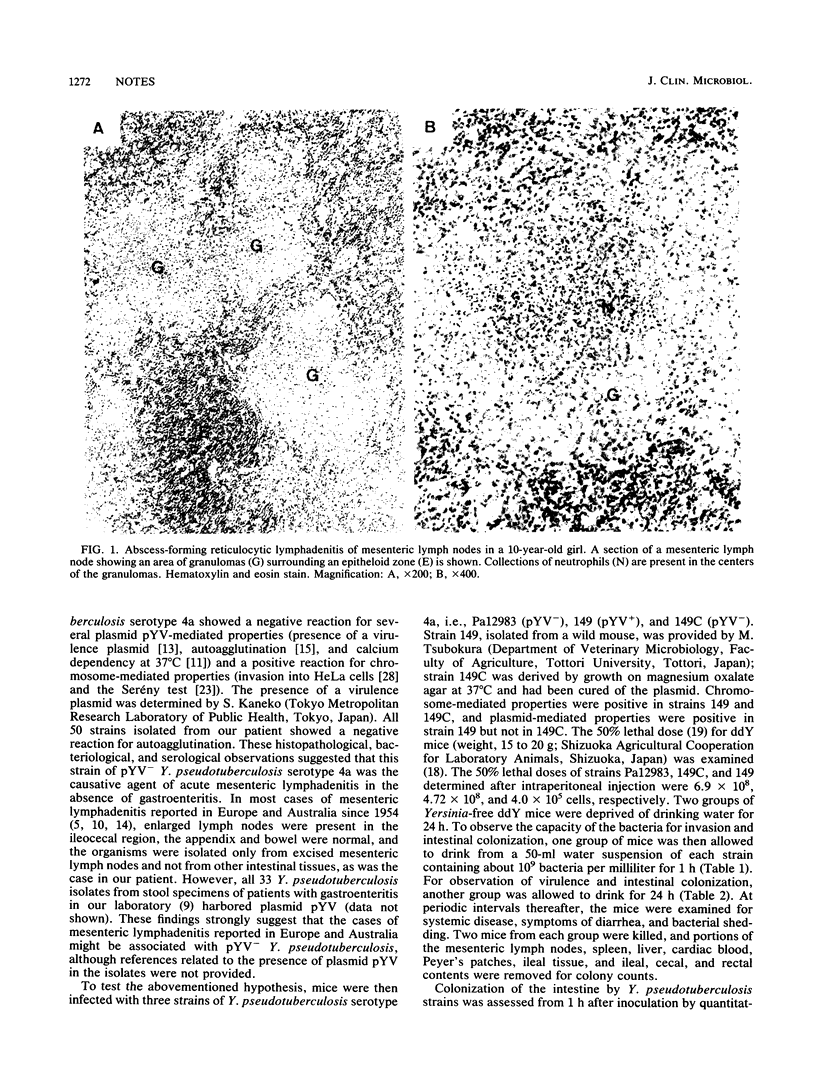
A serotype 4a strain of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis lacking the virulence plasmid pYV (pYV- strain) was isolated from the mesenteric lymph nodes but not from the stool or the appendix of a 10-year-old girl with a diagnosis of acute mesenteric lymphadenitis. Microscopically, reticulocytic abscess and lymphadenitis were persent in the enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes. Antibody against the isolate was detected in the serum. The isolate was negative for the presence of plasmid pYV and plasmid pYV-mediated properties, including autoagglutination and calcium dependency, but was positive for chromosome-mediated properties, including invasion into HeLa cells and tissues of mice and the Serény test. Mice were orally infected with this pYV- strain, and rapid elimination from the intestine occurred 14 days later. Hence, the potential to inhibit the phagocytosis encoded by plasmid pYV was lacking. As the pYV- strain was recovered from the mesenteric lymph nodes and the spleen, the invasiveness was encoded by chromosomal genes. The count of the pYV- strain in the mesenteric lymph nodes increased to 10(4.6) cells per g within 4 days. These findings suggest that pYV- Y. pseudotuberculosis was the causative agent of acute mesenteric lymphadenitis in the absence of gastroenteritis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakour R., Balligand G., Laroche Y., Cornelis G., Wauters G. A simple adult-mouse test for tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica strains of low experimental virulence. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Apr;19(2):237–246. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-2-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. The Vwa+ virulence factor of yersiniae: the molecular basis of the attendant nutritional requirement for Ca++. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S748–S758. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G. R., Biot T., Lambert de Rouvroit C., Michiels T., Mulder B., Sluiters C., Sory M. P., Van Bouchaute M., Vanooteghem J. C. The Yersinia yop regulon. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1455–1459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Laroche Y., Balligand G., Sory M. P., Wauters G. Yersinia enterocolitica, a primary model for bacterial invasiveness. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):64–87. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIELS J. J. Enteric infections with Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis. An acute abdominal syndrome. J Int Coll Surg. 1962 Nov;38:397–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., Gomyoda M., Ishikura S., Nishio T., Moriki S., Endo J., Kaneko S., Tsubokura M. Cat-contaminated environmental substances lead to Yersinia pseudotuberculosis infection in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2706–2709. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2706-2709.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., Gomyoda M., Kaneko S. Mice and moles inhabiting mountainous areas of Shimane Peninsula as sources of infection with Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2448–2455. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2448-2455.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., Gomyoda M., Shiozawa K., Kaneko S., Tsubokura M. Yersinia pseudotuberculosis infection contracted through water contaminated by a wild animal. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):584–585. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.584-585.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., Hoshina K., Nakamura R., Ito Y., Gomyoda M. Epidemiological study of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis in Shimane Prefecture, Japan. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1987;9:103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., KUPFERBERG L. L., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. III. Effects of calcium ions on the growth of virulent and avirulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1959 Mar;77(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.3.317-321.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewstone A. E., Campbell P. E. Mesenteric lymphadenitis due to Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis. Aust Paediatr J. 1970 Mar;6(1):129–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNAPP W., MASSHOFF W. Zur Atiologie der abszedierenden retikulozytären Lymphadenitis, einer praktisch wichtigen, vielfach unter dem Bilde einer akuten Appendizitis verlaufenden Erkrankung. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1954 Aug 27;79(35):1266–1271. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1119840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Maruyama T. Pathogenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O3 biotype 3 strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):454–455. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.454-455.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W. J., Cavanaugh D. C. Correlation of autoagglutination and virulence of yersiniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):430–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.430-432.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian C. J., Hwang W. S., Kelly J. K., Pai C. H. Invasiveness of Yersinia enterocolitica lacking the virulence plasmid: an in-vivo study. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Nov;24(3):219–226. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-3-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Factors essential for the penetration of mammalian cells by Yersinia. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:15–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki M., Vesikari T., Rantala I., Sundqvist C., Grönroos P. Pathogenicity of 42-44 Mdal plasmid positive and negative Yersinia pseudotuberculosis I and Yersinia enterocolitica 0:8 and 0:9 studied in the guinea pig eye model (Serény test). Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Aug;91(4):241–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Tzipori S., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., Prpic J. K. The pathogenesis of Yersinia enterocolitica infection in gnotobiotic piglets. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Jun;19(3):297–308. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Bölin I., Wolf-Watz H. Inhibition of phagocytosis in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis: a virulence plasmid-encoded ability involving the Yop2b protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2139–2143. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2139-2143.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental shigella keratoconjunctivitis; a preliminary report. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonet M., Mazigh D., Berche P. Growth of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis in mouse spleen despite loss of a virulence plasmid of mol. wt 47 X 10(6). J Med Microbiol. 1984 Dec;18(3):371–375. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-3-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonet M., Richard S., Berche P. Electron microscopic evidence for in vivo extracellular localization of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis harboring the pYV plasmid. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):841–845. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.841-845.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Cibull M. L. Differential clearance and host-pathogen interactions of YopE- and YopK- YopL- Yersinia pestis in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1200–1210. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1200-1210.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Brubaker R. R. In vivo comparison of avirulent Vwa- and Pgm- or Pstr phenotypes of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):895–900. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.895-900.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Sundqvist C., Mäki M. Adherence and toxicity of Yersinia enterocolitica 0:3 and 0:9 containing virulence-associated plasmids for various cultured cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Apr;91(2):121–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]