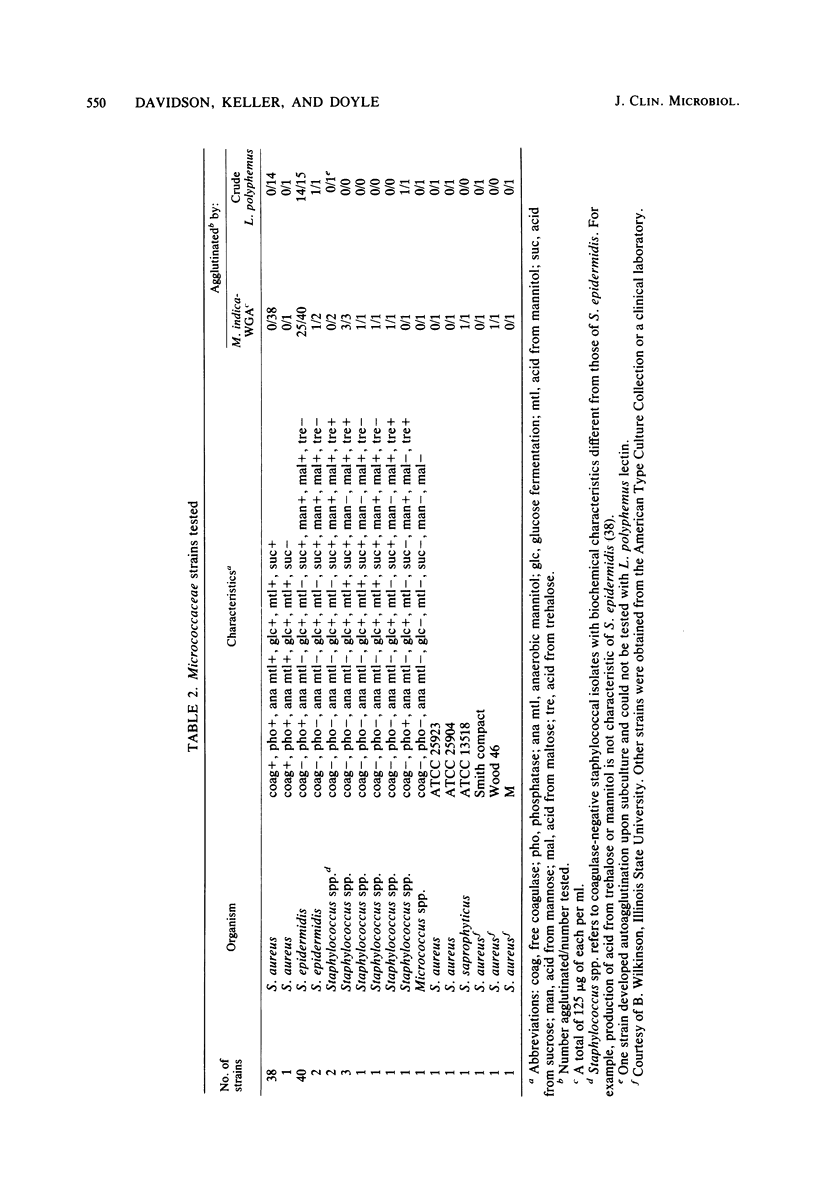
Abstract
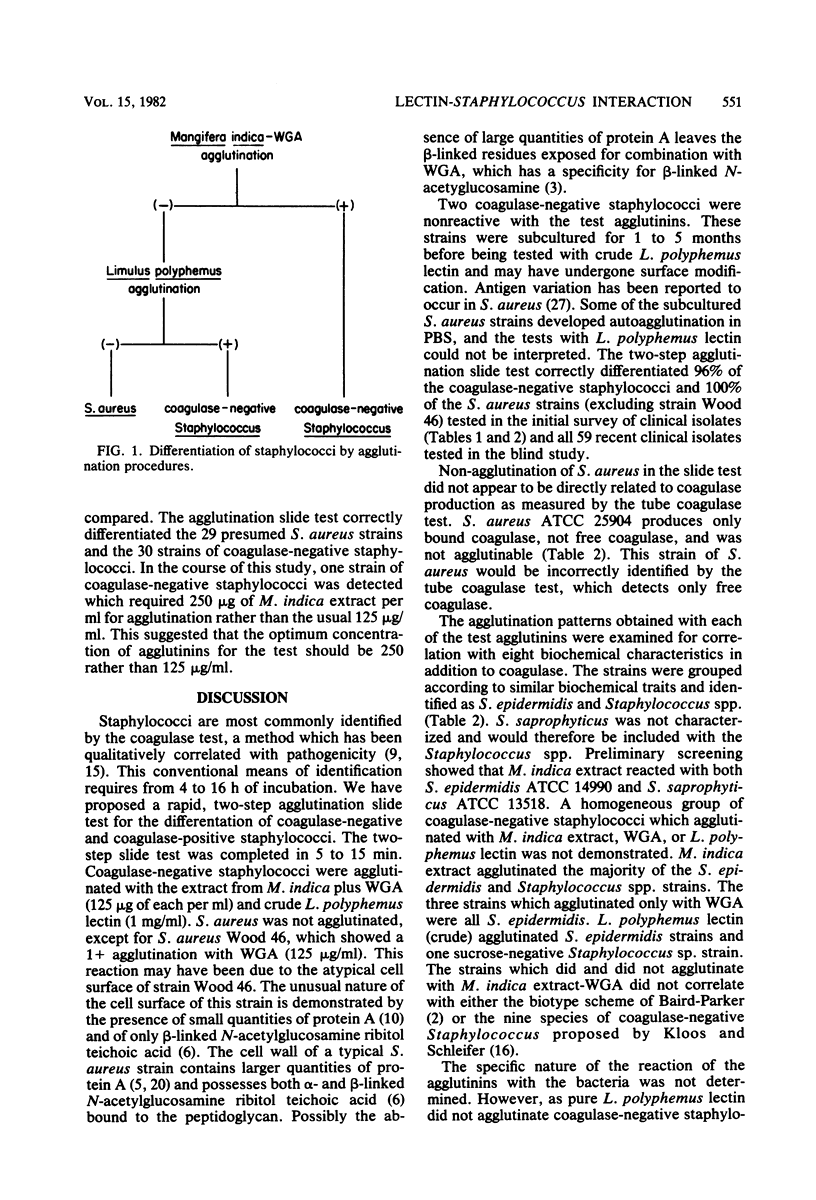
The screening of staphylococci with a panel of 14 lectins and extracts demonstrating lectin-like activity led to the development of a rapid agglutination slide test for the differentiation of certain coagulase-negative staphylococci and human strains of Staphylococcus aureus. The coagulase-negative staphylococci were agglutinated by agglutinins from Mangifera indica, Triticum vulgaris, and crude Limulus polyphemus. The test is rapid, requiring only 5 to 15 min to identify an unknown strain of staphylococci, as opposed to the 4 to 16 h required to perform the conventional tube coagulase test.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P. Z., Connelly M. C., Apicella M. A. Interaction of lectins with Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Apr;26(4):468–474. doi: 10.1139/m80-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M., Goldberg A. R. Identification of a tumor-specific determinant on neoplastic cell surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):359–366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E., Baldo B. A., Uhlenbruck G. Anti-galactan precipitins in the hemolymph of Tridacna maxima and Limulus polyphemus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1975;64:13–18. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3261-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON A. L., BADDILEY J., HOFSTAD T., LOSNEGARD N., OEDING P. SEROLOGICAL INVESTIGATIONS ON TEICHOIC ACIDS FROM THE WALLS OF STAPHYLOCOCCI. Nature. 1964 May 30;202:872–874. doi: 10.1038/202872a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Birdsell D. C. Interaction of concanavalin A with the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):652–658. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.652-658.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. B., Kloos W. E. Use of shake cultures in a semisolid thioglycolate medium for differentiating staphylococci from micrococci. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):326–331. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.326-331.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A. Significance of protein a production by staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):672–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.672-673.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E. Role of lipopolysaccharide in wheat germ agglutinin-mediated agglutination of Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Oct;12(4):498–501. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.4.498-501.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbride K. J., Pistole T. G. Isolation and characterization of a bacterial agglutinin in the serum of Limulus polyphemus. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1979;29:525–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., Hayes C. E. The lectins: carbohydrate-binding proteins of plants and animals. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1978;35:127–340. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. F., Jr, Gramling P. K., O'Dell N. M. Species identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci from urinary tract isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Oct;8(4):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.4.435-437.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E. Natural populations of the genus Staphylococcus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:559–592. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocka F. E., Magoc T., Searcy R. L. Evaluation of rapid tests for staphylococci characterization. Am J Med Technol. 1973 Jul;39(7):269–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler W., Prokop O. Agglutination von Streptokokken der Gruppe C durch ein Agglutinin aus Helix pomatia. Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1967 Jun;133(1):50–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler W., Prokop O. Agglutinationversuche an Streptokokken mit dem Phytagglutinin aus Dolichos biflorus. Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1967 Jul;133(2):171–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIENER I. E., PALLANSCH M. J. Purification of a toxic substance from defatted soy bean flour. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;197(1):29–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Genigeorgis C. A., Hoeprich P. D. Occurrence of protein A in Staphylococcus aureus and closely related Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):752–753. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.752-753.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor L., Tournier P., Chalon A. M. Agglutinabilité par la concanavaline A de divers bacilles a Gram ngatif. Etude chez les Salmonella de la corrélation avec la structure antigénique O. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1973 Jun;124A(4):467–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Sharon N., Mirelman D. Interaction of wheat-germ agglutinin with bacterial cells and cell-wall polymers. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):257–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade N. A., Staat R. H., Langley S. D., Doyle R. J. Lectin-like activity from Persea americana. Carbohydr Res. 1980 Jan 15;78(2):349–363. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(80)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottensooser F., Nakamizo Y., Sato M., Miyamoto Y., Takizawa K. Lectins detecting group C streptococci. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):971–973. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.971-973.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira A. T. Further studies on antigen variation in Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):245–247. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.245-247.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pistole T. G. Broad-spectrum bacterial agglutinating activity in the serum of the Horsehoe crab, Limulus polyphemus. Dev Comp Immunol. 1978 Feb;2(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(78)80026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayman M. K., Park C. E., Philpott J., Todd E. C. Reassessment of the coagulase and thermostable nuclease tests as means of identifying Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Apr;29(4):451–454. doi: 10.1128/am.29.4.451-454.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder W. J., Ekstedt R. D. Study of the interaction of concanavalin A with staphylocccal teichoic acids. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):334–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey F. A., Liu T. Y. Limulin: a C-reactive protein from Limulus polyphemus. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):969–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer R. L., Keller K. F., Doyle R. J. Lectins in diagnostic microbiology: use of wheat germ agglutinin for laboratory identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):669–672. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.669-672.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N. Lectins. Sci Am. 1977 Jun;236(6):108-16, 118-9. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0677-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperber W. H., Tatini S. R. Interpretation of the tube coagulase test for identification of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Apr;29(4):502–505. doi: 10.1128/am.29.4.502-505.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. Interaction of wheat-germ agglutinin with streptococci and streptococcal cell wall polymers. Immunobiology. 1979 Aug;156(1-2):57–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegrzynowicz Z., Heczko P. B., Jeljaszewicz J., Neugebauer M., Pulverer G. Pseudocoagulase activity of staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):15–19. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.15-19.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


