Abstract
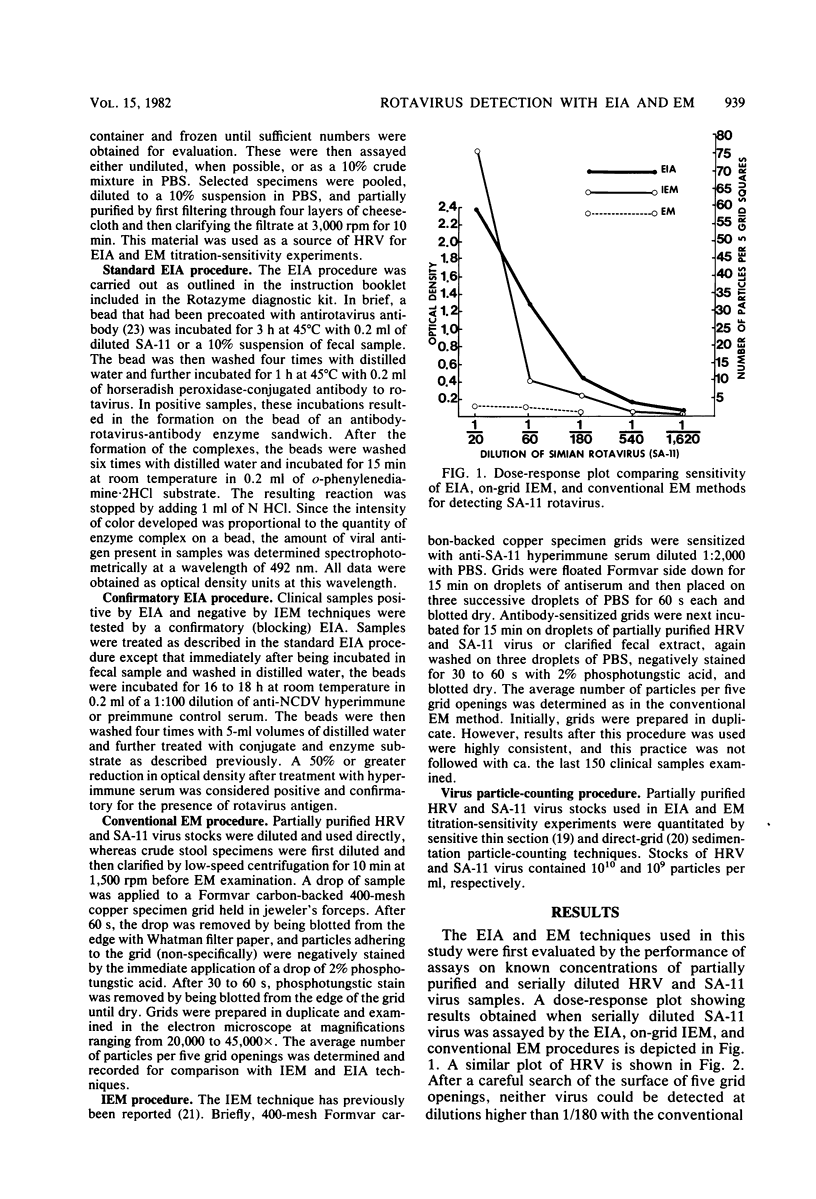
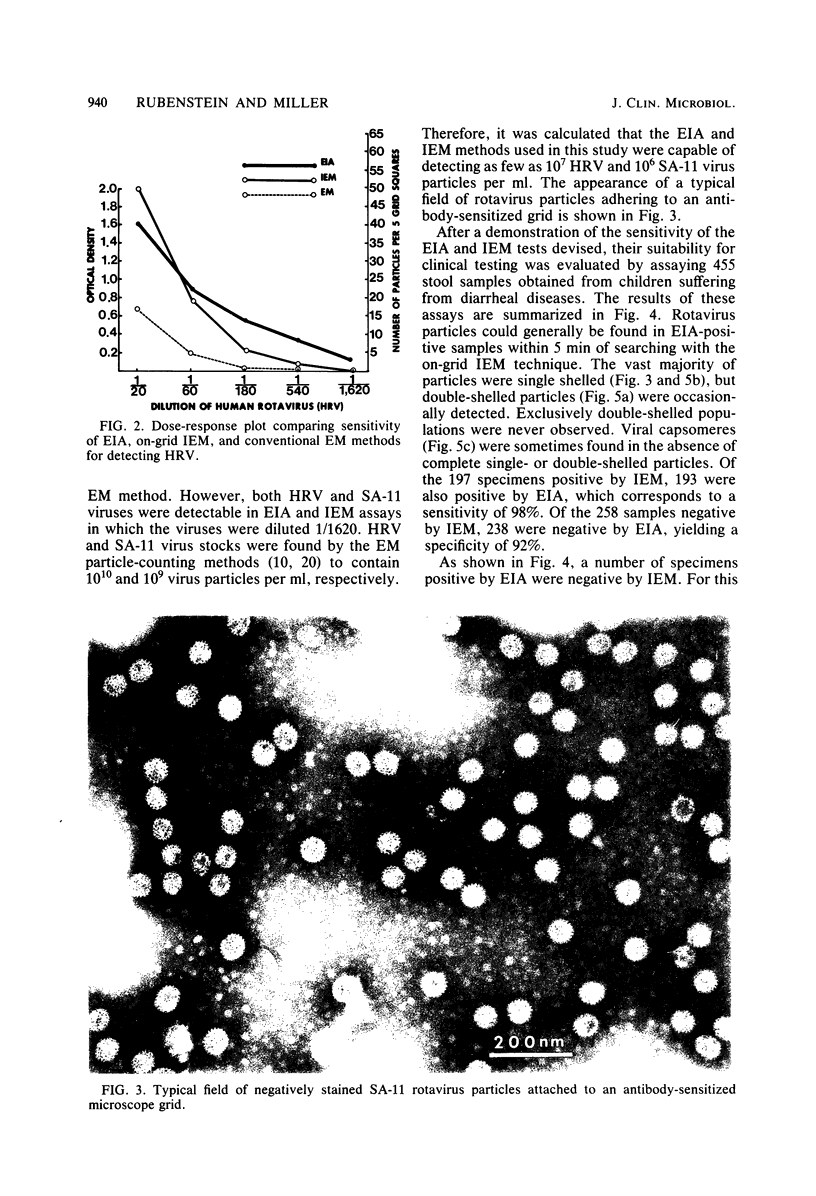
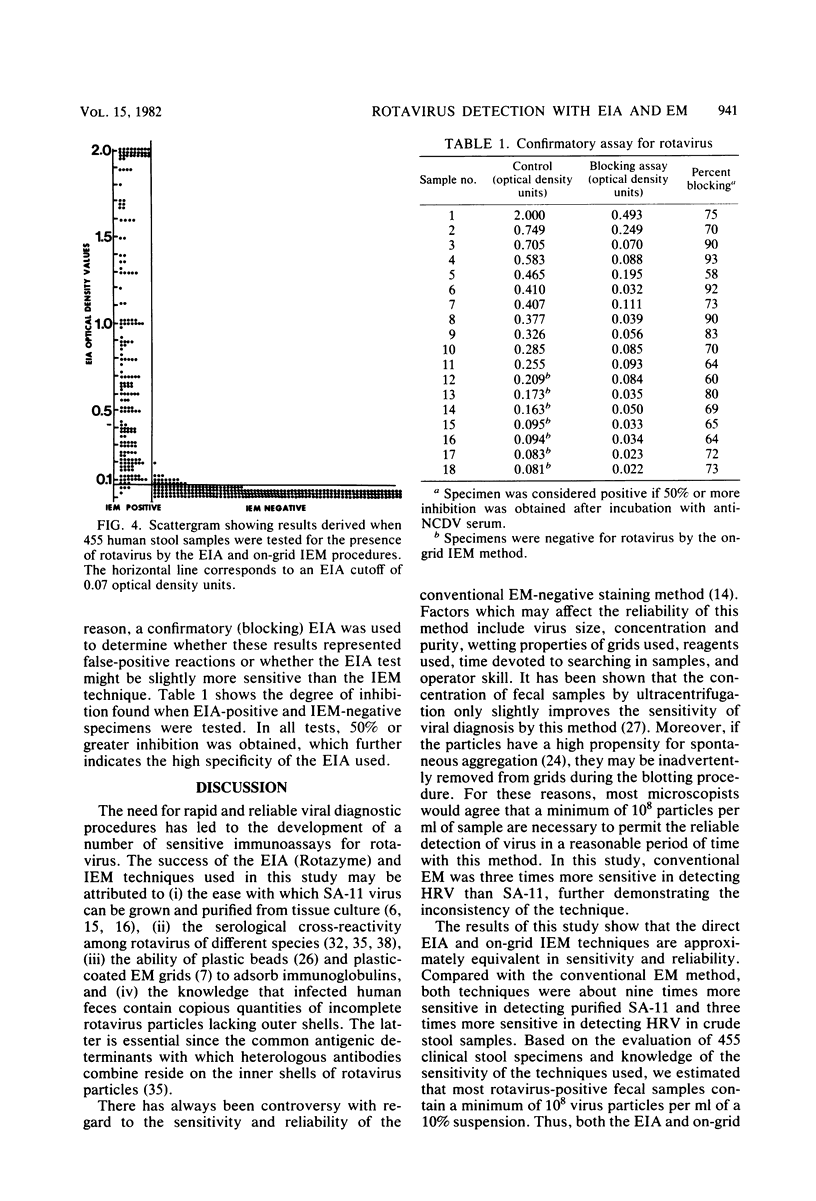
The sensitivity and specificity of an enzyme immunoassay (Rotazyme), an ongrid immunoelectron microscopy procedure, and conventional negative stain electron microscopic techniques were compared. By using partially purified human rotavirus and simian rotavirus (SA-11) of known particle concentration, the enzyme immunoassay was essentially equivalent to the immunoelectron microscopic procedure and significantly more sensitive than conventional electron microscopic techniques. The level of sensitivity was approximately 10(6) particles per ml for simian rotavirus SA-11 and 10(7) particles per ml for human rotavirus. In an evaluation of 455 clinical samples by these techniques, a sensitivity of 98% and specificity of 92% were demonstrated. Samples negative by the immunoelectron microscopic procedure and positive by enzyme immunoassay could be confirmed by a blocking assay.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop R. F., Davidson G. P., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Detection of a new virus by electron microscopy of faecal extracts from children with acute gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1974 Feb 2;1(7849):149–151. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Davidson G. P., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Virus particles in epithelial cells of duodenal mucosa from children with acute non-bacterial gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1973 Dec 8;2(7841):1281–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92867-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt C. D., Kim H. W., Rodriguez W. J., Thomas L., Yolken R. H., Arrobio J. O., Kapikian A. Z., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Comparison of direct electron microscopy, immune electron microscopy, and rotavirus enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of gastroenteritis viruses in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):976–981. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.976-981.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryden A. S., Davies H. A., Thouless M. E., Flewitt T. H. Diagnosis of rotavirus infection by cell culture. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Feb;10(1):121–125. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clementi M., Pauri P., Bagnarelli P., Carloni G., Calegari L. Diagnosis of human rotavirus infections: comparison of an electrophoretic method, a modified complement fixation test and electron microscopy for rotavirus detection. Arch Virol. 1981;67(4):341–344. doi: 10.1007/BF01314837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Berry M. K., Blacklow N. R. Simplified radioimmunoassay for detection of human rotavirus in stools. J Infect Dis. 1978 Dec;138(6):906–910. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.6.906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derrick K. S. Quantitative assay for plant viruses using serologically specific electron microscopy. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):652–653. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellens D. J., de Leeuw P. W. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of rotavirus infections in calves. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):530–532. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.530-532.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Bryden A. S., Davies H., Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Derrick J. M. Relation between viruses from acute gastroenteritis of children and newborn calves. Lancet. 1974 Jul 13;2(7872):61–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91631-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grauballe P. C., Vestergaard B. F., Meyling A., Genner J. Optimized enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of human and bovine rotavirus in stools: Comparison with electron-microscopy, immunoelectro-osmophoresis, and fluorescent antibody techniques. J Med Virol. 1981;7(1):29–40. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890070104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPPS H. E., BERNHEIM B. C., NISALAK A., TJIO J. H., SMADEL J. E. BIOLOGIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A CONTINUOUS KIDNEY CELL LINE DERIVED FROM THE AFRICAN GREEN MONKEY. J Immunol. 1963 Sep;91:416–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Rodriguez W. J., Ross S., Cline W. L., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Reoviruslike agent in stools: association with infantile diarrhea and development of serologic tests. Science. 1974 Sep 20;185(4156):1049–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4156.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madeley C. R. Viruses in the stools. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Jan;32(1):1–10. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malherbe H. H., Strickland-Cholmley M. Simian virus SA11 and the related O agent. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;22(1):235–245. doi: 10.1007/BF01240518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Inouye S., Kono R. Plaque assay of neonatal calf diarrhea virus and the neutralizing antibody in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.1-4.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. F., Allen P. T., Dmochowski L. Quantitative studies of oncornaviruses in thin sections. J Gen Virol. 1973 Oct;21:57–68. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-21-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushahwar I. K., Overby L. R. An enzyme immunoassay for hepatitis B e-antigen and antibody. J Virol Methods. 1981 Sep;3(2):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(81)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narang H. K., Codd A. A. Frequency of preclumped virus in routine fecal specimens from patients with acute nonbacterial gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):982–988. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.982-988.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaieff A., Obert G., van Regenmortel M. H. Detection of rotavirus by serological trapping on antibody-coated electron microscope grids. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):101–104. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.101-104.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORESKES I., SINGER J. M. INFLUENCE OF PH, IONIC STRENGTH AND HUMAN GAMMA GLOBULIN CONCENTRATION ON STABILITY OF POLYSTYRENE LATEX PARTICLE SUSPENSIONS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Mar;115:753–755. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. J., Phillips A. D. Rapid preparation of faecal specimens for detection of viral particles by electron microscopy. Med Lab Sci. 1980 Oct;37(4):371–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. S., Gravell M., Darlington R. Protein kinase in enveloped herpes simplex virions. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90374-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanekata T., Yoshida Y., Okada H. Detection of rotavirus in faeces by latex agglutination. J Immunol Methods. 1981;41(3):377–385. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkkinen H. K., Tuokko H., Halonen P. E. Comparison of enzyme-immunoassay and radioimmunoassay for detection of human rotaviruses and adenoviruses from stool specimens. J Virol Methods. 1980;1(6):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(80)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Bryden A. S., Flewett T. H., Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Snodgrass D. R., Herring J. A. Serological relationships between rotaviruses from different species as studied by complement fixation and neutralization. Arch Virol. 1977;53(4):287–294. doi: 10.1007/BF01315627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandervelde E. M., Cohen B. J., Cossart Y. E. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent-assay test for hepatitis B surface antigen. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Aug;30(8):714–716. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.8.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James W. D., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Human rotavirus type 2: cultivation in vitro. Science. 1980 Jan 11;207(4427):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.6243190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Thornhill T. S., Sereno M. M., Kim H. W., Chanock R. M. In vitro cultivation in human fetal intestinal organ culture of a reovirus-like agent associated with nonbacterial gastroenteritis in infants and children. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130(5):523–528. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Barbour B., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for identification of rotaviruses from different animal species. Science. 1978 Jul 21;201(4352):259–262. doi: 10.1126/science.208150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Kim H. W., Clem T., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1977 Aug 6;2(8032):263–267. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90951-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]