Abstract
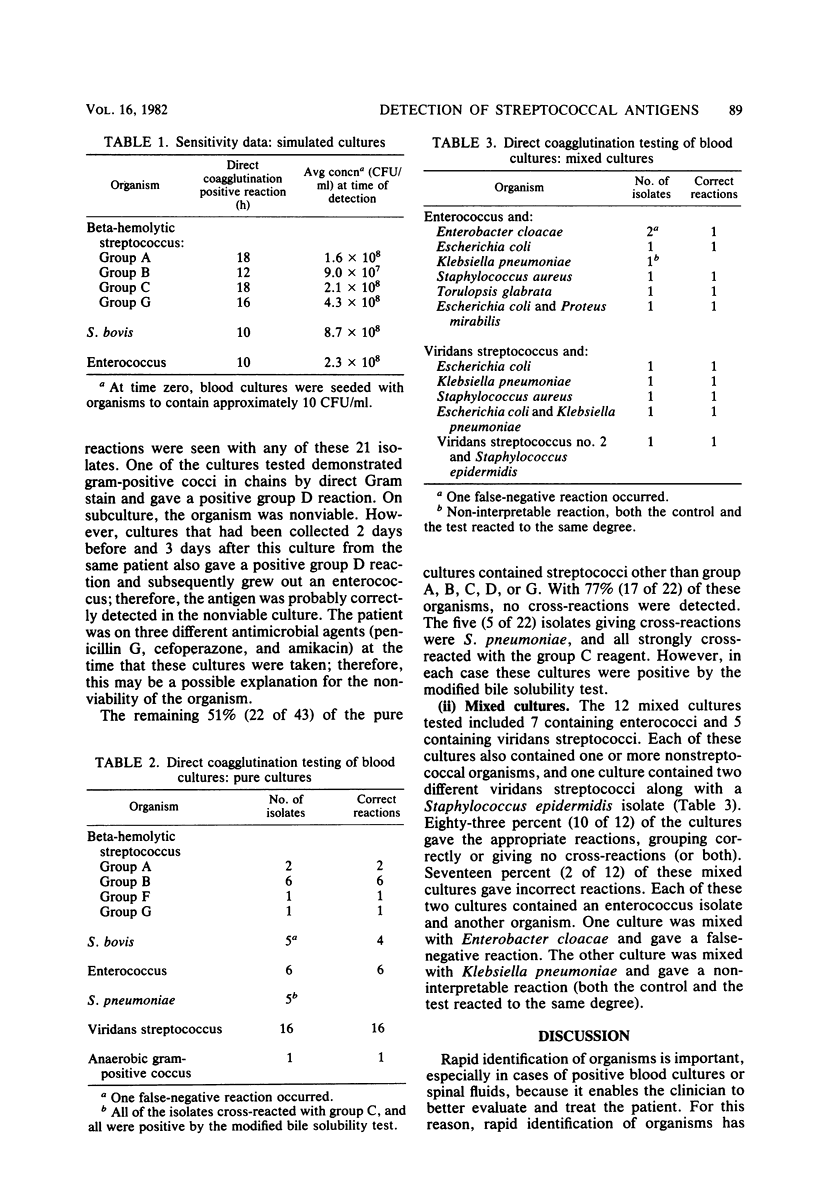
A direct, rapid, and simple method for the detection of streptococcal antigens of Lancefield groups A, B, C, D, and G from blood cultures was developed by using a coagglutination test. Fifty-five clinical specimens and 117 simulated blood cultures containing gram-positive cocci were tested. Out of 6,261 clinical blood cultures screened, 55 cultures from 53 patients were positive, with organisms resembling streptococci, by Gram stain. Of these cultures, 78% (43 of 55) were pure cultures of streptococci, and 22% (12 of 55) were mixed with at least one other organism. Of the 43 pure cultures only, correct reactions were obtained (grouping correctly or giving no cross-reactions, or both) with 86% (37 of 43) of the isolates, 12% (5 of 43) exhibited cross-reactions, and 2% (1 of 43) gave false-negative reactions. All of the cross-reacting isolates were Streptococcus pneumoniae, which reacted with the group C reagent, and the false-negative reaction occurred with a Streptococcus bovis isolate. However, by using a direct modified bile solubility test, the correct identification of the S. pneumoniae isolates was obtained. Therefore, by using the modified bile solubility test in conjunction with the direct grouping method, 98% (42 of 43) of the isolates in pure culture could be identified accurately and rapidly after the detection of a positive Gram stain. Correct grouping reactions were obtained with 83% (10 of 12) of the mixed blood cultures, and false-negative results occurred with 17% (2 of 12) of them. Both cultures contained an enterococcus and a gram-negative rod. Of the 117 simulated blood cultures, there was only one incorrect grouping reaction; this occurred with an S. bovis isolate that cross-reacted with the group C reagent. The direct grouping reaction was positive when blood cultures contained a minimum of 1 × 108 to 8 × 108 colony-forming units per ml. In general, this procedure provided information on the identification of the organism 24 h earlier than by conventional identification methods.
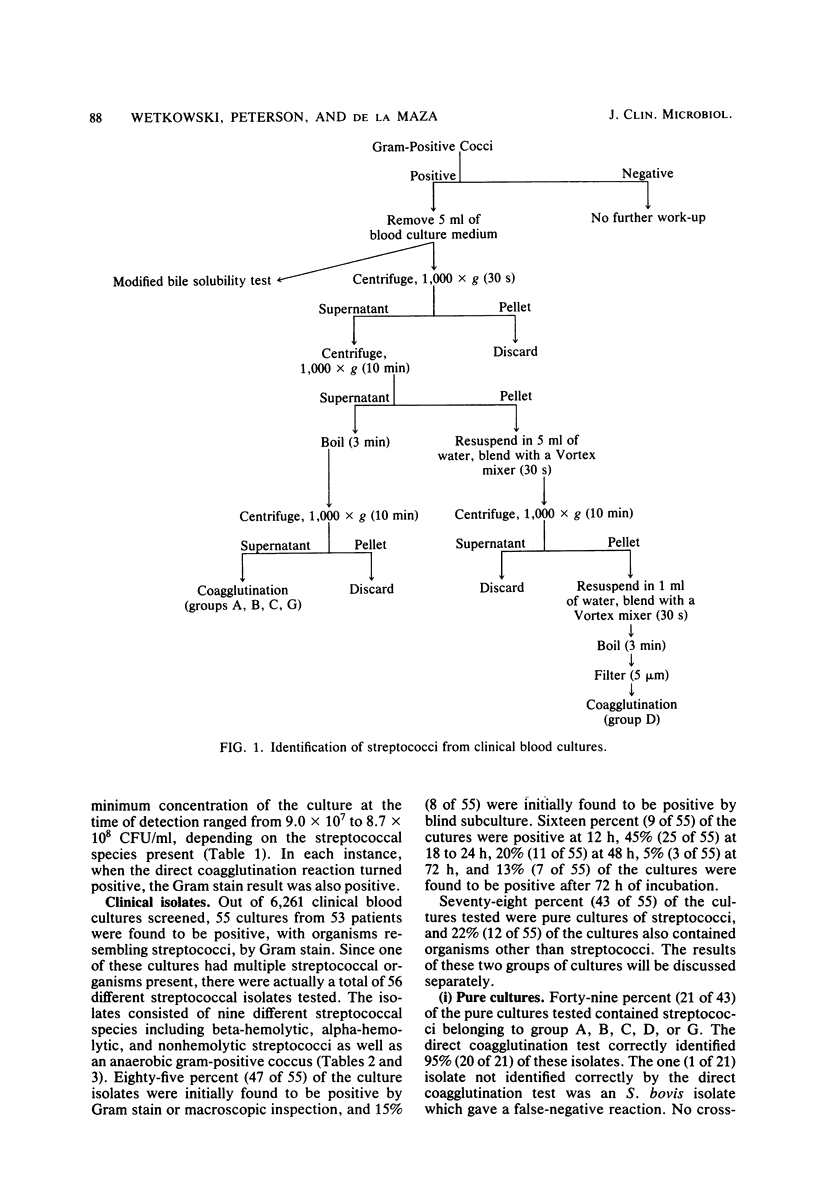
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artman M., Weiner M., Frankl G. Counterimmunoelectrophoresis for early detection and rapid identification of Haemophilus influenzae type b and Streptococcus pneumoniae in blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Oct;12(4):614–616. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.4.614-616.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Kahlmeter G., Jonsson S., Kronvall G. New method for the serological grouping of Streptococci with specific antibodies adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):881–885. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.881-885.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doskeland S. O., Berdal B. P. Bacterial antigen detection in body fluids: methods for rapid antigen concentration and reduction of nonspecific reactions. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):380–384. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.380-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn G., Nyberg I. Identification of streptococcal groups A,B,C, and G by slide co-agglutination of antibody-sensitized protein A-containing staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):99–101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.99-101.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. L., Harada W. A. Rapid method for identification of group B streptococci in neonatal blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):279–282. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.279-282.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leland D. S., Lachapelle R. C., Wlodarski F. M. Method for rapid detection of group B streptococci by coagglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):323–326. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.323-326.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R. Modification of the bile solubility test for rapid identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):290–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.290-291.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb B. J., Baker C. J. Commercial latex agglutination test for rapid diagnosis of group B streptococcal infection in infants. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):442–444. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.442-444.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb B. J., Edwards M. S., Baker C. J. Comparison of slide coagglutination test and countercurrent immunoelectrophoresis for detection of group B streptococcal antigen in cerebrospinal fluid from infants with meningitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Mar;11(3):263–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.3.263-265.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


