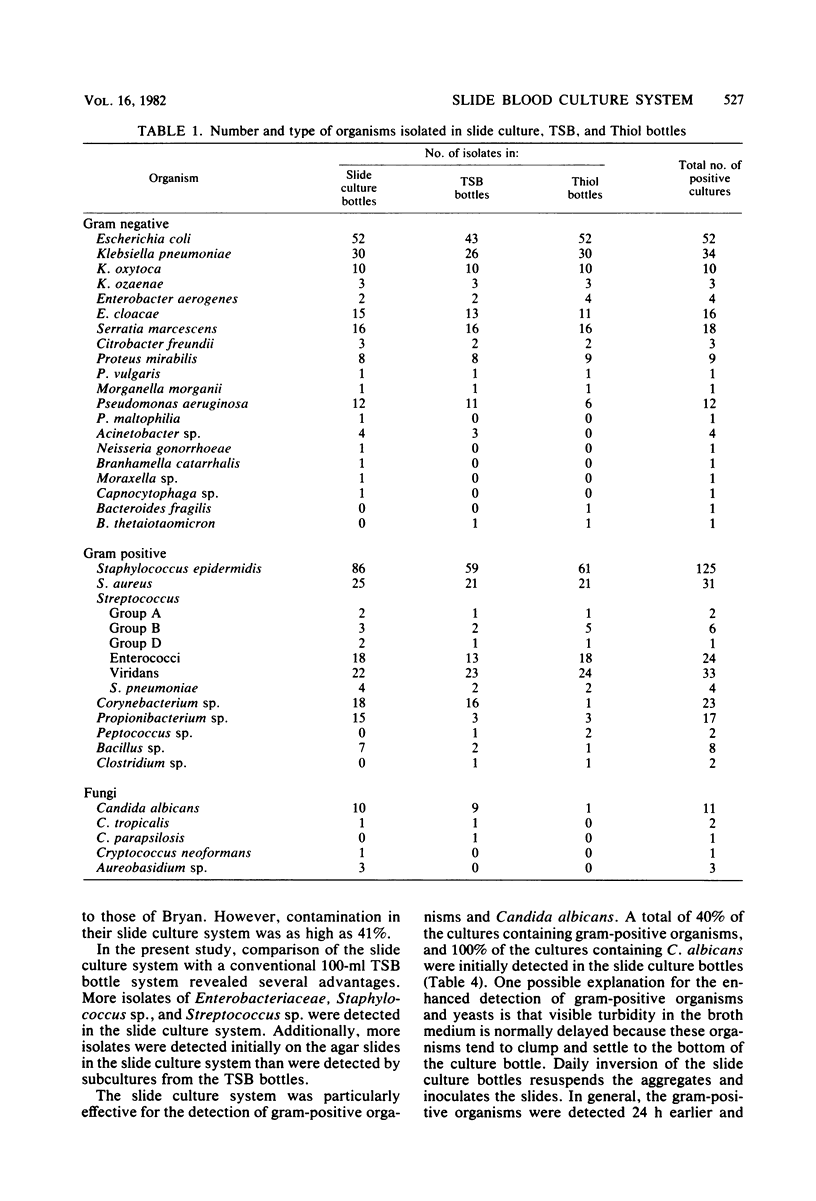
Abstract
The recovery of bacteria and fungi from blood cultures was compared in conventional tryptic soy broth (TSB) bottles and in TSB bottles with an agarcoated slide attachment. A total of 2,662 sets of blood cultures, including 413 that were positive (15.5%), were evaluated. Significantly more gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria were recovered in the slide culture bottles than in conventional bottles (299 versus 253 isolates). Growth of gram-positive organisms and fungi was detected in the slide culture bottles 24 to 48 h earlier than in the TSB bottles. In addition, 76% of the isolates in the slide culture system were detected on the agar slide. In comparison, only 40% of the isolates in the TSB bottles were detected initially by blind subculturing. The incidences of contamination were 2.7% (71 cultures) for the slide culture system and 1.5% (39 cultures) for the TSB bottles.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryan L. E. Comparison of a slide blood culture system with a supplemented peptone broth culture method. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Oct;14(4):389–392. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.4.389-392.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan L. M., Merz W. G. Evaluation of two commercially prepared biphasic media for recovery of fungi from blood. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Oct;8(4):469–470. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.4.469-470.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. M., Mueske C. A., Ilstrup D. M., Washington J. A., 2nd Evaluation of a biphasic medium for blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):673–676. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.673-676.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehn T. E., Capitolo C., Mayo J. B., Armstrong D. Comparative recovery of fungi from biphasic and conventional blood culture media. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):681–683. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.681-683.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Sondag J. E. Evaluation of routine subcultures of macroscopically negative blood cultures for detection of anaerobes. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Oct;8(4):427–430. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.4.427-430.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paisley J. W., Rosenblatt J. E., Hall M., Washington J. A., 2nd Evaluation of a routine anaerobic subculture of blood cultures for detection of anaerobic bacteremia. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):764–766. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.764-766.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. D., Washington J. A., 2nd Detection of fungi in blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):309–310. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.309-310.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT E. G. A practical blood culture procedure. Am J Clin Pathol. 1951 Mar;21(3):290–294. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/21.3_ts.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steurenthaler W. Erfahrungen mit einem neuartigen Blutkultursystem (BCB-System "Roche") in der Kinderklinik. Med Welt. 1979 Feb 2;30(5):173–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd Blood cultures: principles and techniques. Mayo Clin Proc. 1975 Feb;50(2):91–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


